Attachment style refers to the consistent patterns of emotional bonding and behavior formed in early relationships, shaping how individuals connect with pets over time. Attachment strategy involves the specific actions and coping mechanisms employed to maintain closeness or manage distance within the pet-owner relationship. Understanding the difference helps improve communication and emotional support between pets and their owners.
Table of Comparison
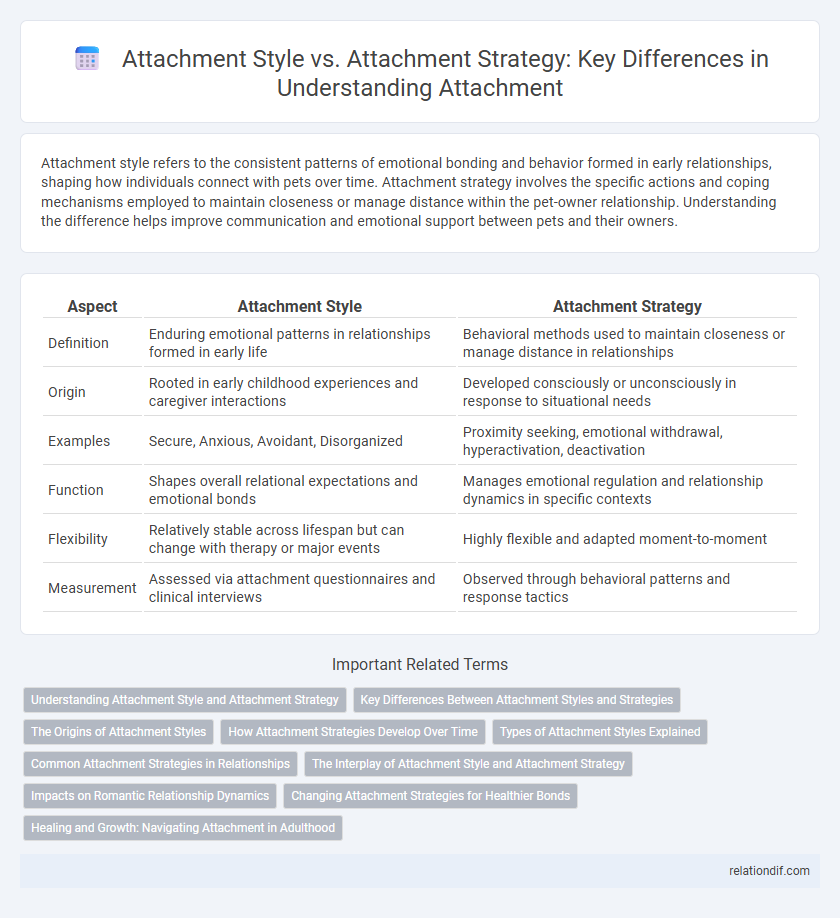
| Aspect | Attachment Style | Attachment Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Enduring emotional patterns in relationships formed in early life | Behavioral methods used to maintain closeness or manage distance in relationships |
| Origin | Rooted in early childhood experiences and caregiver interactions | Developed consciously or unconsciously in response to situational needs |
| Examples | Secure, Anxious, Avoidant, Disorganized | Proximity seeking, emotional withdrawal, hyperactivation, deactivation |
| Function | Shapes overall relational expectations and emotional bonds | Manages emotional regulation and relationship dynamics in specific contexts |
| Flexibility | Relatively stable across lifespan but can change with therapy or major events | Highly flexible and adapted moment-to-moment |
| Measurement | Assessed via attachment questionnaires and clinical interviews | Observed through behavioral patterns and response tactics |
Understanding Attachment Style and Attachment Strategy
Attachment style refers to the consistent patterns of emotional bonding people develop in early relationships, influencing behavior in close connections throughout life. Attachment strategy involves the conscious or unconscious tactics individuals use to manage their attachment needs, often shaped by their underlying attachment style. Understanding both concepts clarifies how early experiences impact adult relationship dynamics and emotional regulation processes.
Key Differences Between Attachment Styles and Strategies
Attachment styles represent the enduring patterns of emotional bonding formed in early relationships, often categorized as secure, anxious, avoidant, or disorganized. Attachment strategies refer to the conscious or unconscious tactics individuals use to manage attachment-related emotions and maintain proximity or distance in relationships. Key differences include that attachment styles are stable personality traits influencing overall relational behavior, while attachment strategies are adaptive responses that can vary depending on context and individual needs.
The Origins of Attachment Styles
Attachment styles originate from early caregiver-child interactions, shaping patterns of emotional bonding and security throughout life. These styles--secure, anxious, avoidant, and disorganized--reflect the consistency and responsiveness of caregiving, which influence an individual's expectations and behaviors in relationships. Attachment strategies, derived from these styles, represent adaptive responses developed to manage emotional needs and relational dynamics based on perceived attachment security.
How Attachment Strategies Develop Over Time
Attachment strategies develop over time through repeated interpersonal experiences, shaping how individuals regulate emotions and seek support in close relationships. These strategies reflect adaptive patterns that emerge from early attachment styles but can evolve due to life events, therapy, or changes in relational contexts. Understanding the dynamic interplay between attachment style and strategy enhances insight into personal growth and relational functioning.
Types of Attachment Styles Explained
Attachment styles refer to consistent patterns of emotional bonding formed in early childhood, influencing behavior in relationships. The primary types include secure, anxious-preoccupied, dismissive-avoidant, and fearful-avoidant attachment styles, each characterized by distinct interaction patterns and emotional responses. Attachment strategies, by contrast, are the adaptive behaviors individuals employ to manage their attachment needs based on their underlying attachment style.
Common Attachment Strategies in Relationships
Common attachment strategies in relationships include secure, anxious-preoccupied, dismissive-avoidant, and fearful-avoidant styles. Secure attachment strategies foster trust and healthy boundaries, promoting emotional intimacy and effective communication. In contrast, anxious-preoccupied strategies often involve heightened sensitivity to rejection, while dismissive-avoidant and fearful-avoidant strategies rely on emotional distancing to cope with vulnerability.
The Interplay of Attachment Style and Attachment Strategy
Attachment style represents the characteristic patterns of emotional bonds formed in early relationships, while attachment strategy refers to the conscious or unconscious behaviors employed to maintain or modify these bonds. The interplay of attachment style and strategy shapes individual responses to intimacy and stress, influencing relationship dynamics and emotional regulation. Research highlights that adaptive attachment strategies can mitigate the effects of insecure attachment styles, promoting healthier interpersonal connections.
Impacts on Romantic Relationship Dynamics
Attachment style, rooted in early caregiver interactions, shapes individuals' emotional expectations and behaviors in romantic relationships, influencing intimacy, trust, and conflict resolution. Attachment strategy, a conscious approach to managing attachment needs, dynamically adjusts based on situational factors and partner responses, impacting communication patterns and relationship satisfaction. Distinguishing between stable attachment styles and flexible attachment strategies elucidates variations in relationship dynamics, emotional regulation, and long-term relational outcomes.
Changing Attachment Strategies for Healthier Bonds
Changing attachment strategies involves consciously modifying behaviors that stem from one's attachment style to foster healthier emotional connections. Unlike attachment styles, which are relatively stable patterns formed early in life, attachment strategies are flexible responses individuals use to navigate relationships. By adopting more secure strategies--such as increased emotional openness and trust--people can improve relationship satisfaction and psychological well-being.
Healing and Growth: Navigating Attachment in Adulthood
Attachment style reflects the patterned ways individuals form emotional bonds based on early relational experiences, while attachment strategy involves the conscious or unconscious methods used to manage these bonds in adulthood. Healing and growth in attachment require identifying maladaptive strategies and fostering secure attachment behaviors through therapeutic interventions like cognitive-behavioral therapy and mindfulness practices. Emphasizing self-awareness and emotional regulation enhances resilience, enabling healthier adult relationships and personal development.
Attachment style vs attachment strategy Infographic
 relationdif.com
relationdif.com