Dismissive attachment involves avoiding closeness and emotional intimacy with pets, often leading to neglect or minimal interaction despite caring for their physical needs. Fearful attachment combines a desire for connection with fear of rejection or harm, causing inconsistent and anxious behavior toward the pet. Understanding these attachment styles improves communication and strengthens the human-pet bond.
Table of Comparison
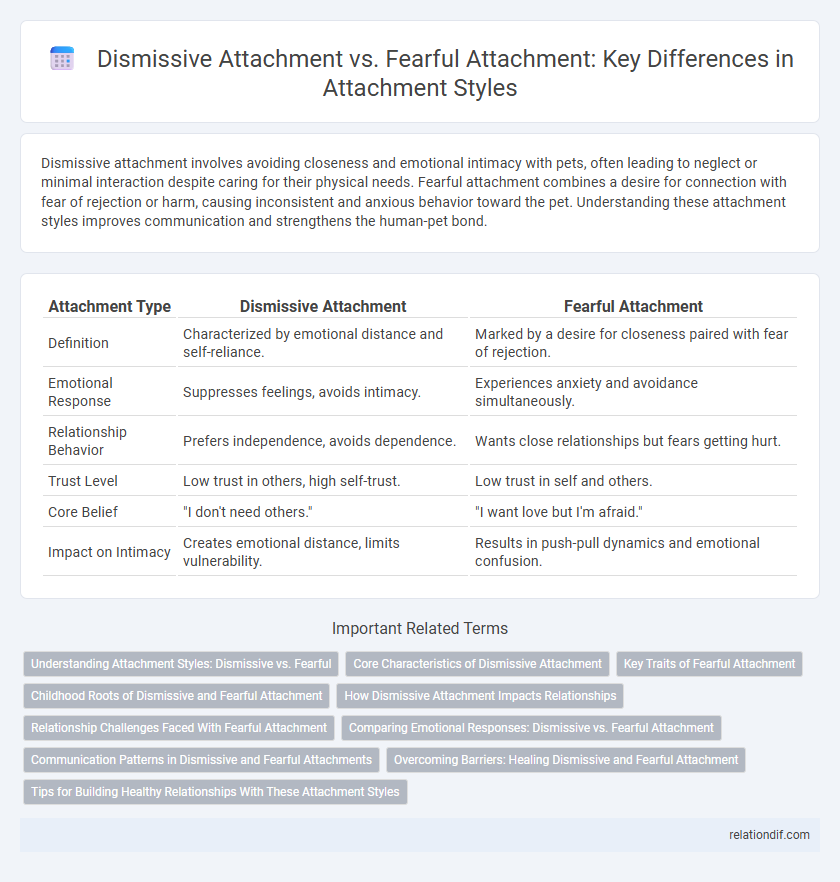
| Attachment Type | Dismissive Attachment | Fearful Attachment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Characterized by emotional distance and self-reliance. | Marked by a desire for closeness paired with fear of rejection. |
| Emotional Response | Suppresses feelings, avoids intimacy. | Experiences anxiety and avoidance simultaneously. |
| Relationship Behavior | Prefers independence, avoids dependence. | Wants close relationships but fears getting hurt. |
| Trust Level | Low trust in others, high self-trust. | Low trust in self and others. |
| Core Belief | "I don't need others." | "I want love but I'm afraid." |
| Impact on Intimacy | Creates emotional distance, limits vulnerability. | Results in push-pull dynamics and emotional confusion. |
Understanding Attachment Styles: Dismissive vs. Fearful
Dismissive attachment is characterized by a strong sense of independence and avoidance of intimacy, often stemming from a positive self-view but negative perceptions of others. Fearful attachment involves a combination of anxiety and avoidance, where individuals desire closeness but fear rejection due to low self-esteem and mistrust of others. Understanding these attachment styles helps in recognizing patterns of emotional regulation and relationship dynamics that influence personal connections and psychological wellbeing.
Core Characteristics of Dismissive Attachment
Dismissive attachment is characterized by emotional detachment, a strong desire for independence, and avoidance of intimacy, often leading individuals to suppress feelings and downplay the importance of relationships. People with dismissive attachment typically exhibit high self-reliance and resist relying on others for support or comfort. This attachment style contrasts with fearful attachment, which involves anxiety about closeness combined with a fear of rejection and mistrust.
Key Traits of Fearful Attachment
Fearful attachment is characterized by a deep fear of rejection coupled with a strong desire for closeness, leading to conflicting behaviors of seeking intimacy and pushing others away. Individuals with fearful attachment often exhibit low self-esteem, high anxiety, and difficulty trusting others, which results in emotional avoidance and challenges in forming secure relationships. This attachment style is strongly linked to past trauma or inconsistent caregiving, contributing to heightened vulnerability and interpersonal struggles.
Childhood Roots of Dismissive and Fearful Attachment
Dismissive attachment often originates from childhood experiences where caregivers were emotionally unavailable or unresponsive, leading children to suppress their feelings and develop self-reliance as a defense mechanism. Fearful attachment typically results from inconsistent or traumatic caregiving, causing children to experience anxiety and mistrust, which manifests as conflicting desires for closeness and fear of rejection. Both attachment styles reflect early relational patterns that shape emotional regulation and interpersonal dynamics in adulthood.
How Dismissive Attachment Impacts Relationships
Dismissive attachment often leads to emotional distancing and difficulty in expressing vulnerability, which can create barriers to deep intimacy in relationships. Individuals with dismissive attachment may prioritize independence and self-reliance, causing partners to feel neglected or unimportant. This pattern frequently results in misunderstandings and unresolved conflicts, weakening the overall stability and satisfaction within romantic connections.
Relationship Challenges Faced With Fearful Attachment
Fearful attachment often causes intense relationship challenges, including fear of intimacy and difficulty trusting others, which leads to avoidance of emotional closeness despite a deep desire for connection. Individuals with fearful attachment typically experience heightened anxiety and self-doubt, contributing to misunderstandings and conflicts in romantic relationships. Their unpredictable approach to closeness and distance creates instability, making it hard for partners to feel secure and supported.
Comparing Emotional Responses: Dismissive vs. Fearful Attachment
Dismissive attachment is characterized by emotional detachment and a tendency to suppress feelings, leading to avoidance of closeness and vulnerability. Fearful attachment combines a desire for intimacy with fear of rejection, resulting in heightened anxiety and conflicting emotional responses. The contrast lies in dismissive individuals minimizing emotional expression, while fearful individuals experience intense emotional turmoil despite their avoidance behaviors.
Communication Patterns in Dismissive and Fearful Attachments
Dismissive attachment is characterized by communication patterns that emphasize emotional distance and self-reliance, often leading to limited self-disclosure and avoidance of vulnerability in conversations. Fearful attachment displays contradictory communication behaviors, combining a desire for closeness with fear of rejection, resulting in mixed signals, hesitancy, and difficulty expressing emotions clearly. Both attachment styles hinder effective emotional communication and create barriers to intimacy within relationships.
Overcoming Barriers: Healing Dismissive and Fearful Attachment
Healing dismissive and fearful attachment requires increasing emotional awareness and building trust through consistent, safe relationships. Therapeutic approaches like cognitive-behavioral therapy and emotion-focused therapy help individuals recognize attachment patterns and develop healthier coping mechanisms. Creating secure connections reduces avoidance and anxiety, promoting emotional resilience and deeper intimacy.
Tips for Building Healthy Relationships With These Attachment Styles
Understanding dismissive attachment involves recognizing a strong desire for independence paired with emotional distance, while fearful attachment is marked by a fear of rejection and mistrust in relationships. Establishing healthy relationships with these styles requires fostering open communication, practicing empathy, and setting clear boundaries to create a safe emotional environment. Consistent reassurance and patience are crucial for building trust and encouraging vulnerability in partners with these attachment patterns.
Dismissive attachment vs fearful attachment Infographic
 relationdif.com
relationdif.com