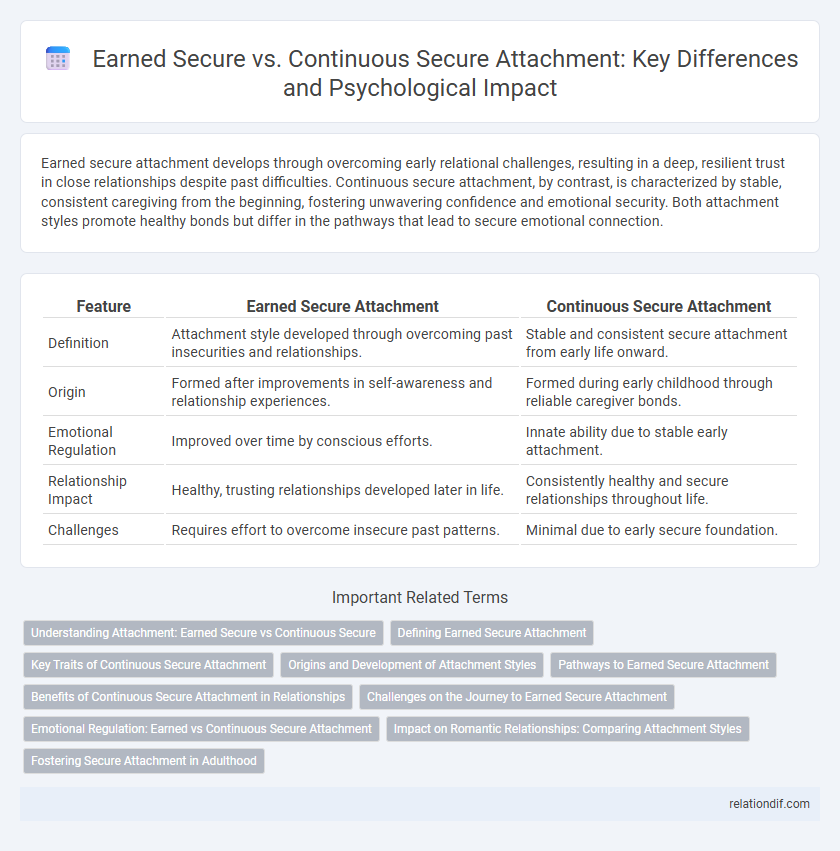
Earned secure attachment develops through overcoming early relational challenges, resulting in a deep, resilient trust in close relationships despite past difficulties. Continuous secure attachment, by contrast, is characterized by stable, consistent caregiving from the beginning, fostering unwavering confidence and emotional security. Both attachment styles promote healthy bonds but differ in the pathways that lead to secure emotional connection.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Earned Secure Attachment | Continuous Secure Attachment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Attachment style developed through overcoming past insecurities and relationships. | Stable and consistent secure attachment from early life onward. |
| Origin | Formed after improvements in self-awareness and relationship experiences. | Formed during early childhood through reliable caregiver bonds. |
| Emotional Regulation | Improved over time by conscious efforts. | Innate ability due to stable early attachment. |
| Relationship Impact | Healthy, trusting relationships developed later in life. | Consistently healthy and secure relationships throughout life. |
| Challenges | Requires effort to overcome insecure past patterns. | Minimal due to early secure foundation. |
Understanding Attachment: Earned Secure vs Continuous Secure
Earned secure attachment develops through overcoming previous insecure attachment patterns by building trust and emotional resilience over time. Continuous secure attachment, however, is characterized by consistently stable and responsive caregiving from early childhood without disruption. Understanding these distinctions highlights how earned secure individuals actively reconstruct secure relational frameworks, whereas continuous secure individuals benefit from uninterrupted nurturing environments.
Defining Earned Secure Attachment
Earned secure attachment refers to individuals who develop a secure attachment style later in life despite early experiences of insecure or disorganized attachment. This transformation typically occurs through reflective self-awareness, therapeutic intervention, or supportive relationships that foster trust and emotional regulation. Unlike continuous secure attachment, which is characterized by stable, consistent caregiving from childhood onward, earned secure attachment highlights resilience and growth beyond initial attachment disruptions.
Key Traits of Continuous Secure Attachment
Continuous secure attachment is characterized by consistent emotional availability, dependable responsiveness, and mutual trust between caregiver and child. This attachment style fosters resilience, stable self-esteem, and effective emotion regulation throughout development. Key traits also include open communication and a strong sense of safety that promotes exploration and social competence.
Origins and Development of Attachment Styles
Earned secure attachment emerges from individuals who initially developed insecure attachment due to adverse early experiences but later cultivate security through positive relationships and self-reflection. Continuous secure attachment originates from consistent responsive caregiving during infancy, fostering stable and confident relational patterns throughout life. Understanding these developmental trajectories highlights the plasticity of attachment styles and the crucial impact of ongoing relational experiences.
Pathways to Earned Secure Attachment
Pathways to earned secure attachment involve reflective functioning, emotional regulation development, and corrective relational experiences that reshape internal working models formed by early attachment disruptions. Therapeutic interventions, such as attachment-based therapy and mentalization-based treatment, facilitate the integration of past attachment traumas, promoting earned security through enhanced self-awareness and relational competence. These processes enable individuals to shift from continuous insecure attachment patterns to earned secure attachment, characterized by trust, emotional resilience, and healthy interpersonal connections.
Benefits of Continuous Secure Attachment in Relationships
Continuous secure attachment fosters consistent emotional availability and trust, promoting resilient and stable relationships. It enhances effective communication and conflict resolution by maintaining a reliable support system between partners. This dynamic reduces anxiety and bolsters intimacy, resulting in long-term relational satisfaction and psychological well-being.
Challenges on the Journey to Earned Secure Attachment
Challenges on the journey to Earned Secure attachment often involve overcoming deep-seated trust issues rooted in early relational trauma and inconsistent caregiving. Individuals must work through emotional regulation difficulties and self-worth deficits while fostering consistent, supportive relationships that contrast past attachment patterns. Therapeutic intervention and sustained self-reflection are critical to reshaping internal working models toward secure attachment security.
Emotional Regulation: Earned vs Continuous Secure Attachment
Continuous secure attachment supports consistent emotional regulation through stable, responsive caregiving from early childhood, fostering a reliable internal working model of self and relationships. Earned secure attachment develops emotional regulation abilities despite earlier adverse experiences by reinterpreting past relationships and forming new, healthier relational patterns in adulthood. Both types promote emotional resilience, but continuous secure attachment typically ensures more automatic regulation, while earned secure attachment often requires conscious effort and therapeutic engagement.
Impact on Romantic Relationships: Comparing Attachment Styles
Earned secure attachment often leads to healthier romantic relationships by fostering trust, emotional intimacy, and effective conflict resolution, contrasting with continuous secure attachment where individuals maintain consistent security from early life. Individuals with earned secure attachment may initially struggle with vulnerability but ultimately develop stable bonds through self-awareness and growth. Continuous secure attachment typically supports seamless emotional connection and resilience during relationship stress, highlighting differences in attachment history's impact on romantic dynamics.
Fostering Secure Attachment in Adulthood
Earned secure attachment develops through reflective self-awareness and consistent supportive relationships that help individuals overcome early attachment insecurities. Continuous secure attachment originates from stable, nurturing caregiving during childhood, providing a reliable foundation for emotional regulation and trust in adulthood. Fostering secure attachment in adulthood involves cultivating empathy, open communication, and responsiveness within relationships to reinforce trust and emotional safety.
Earned secure vs continuous secure Infographic
 relationdif.com
relationdif.com