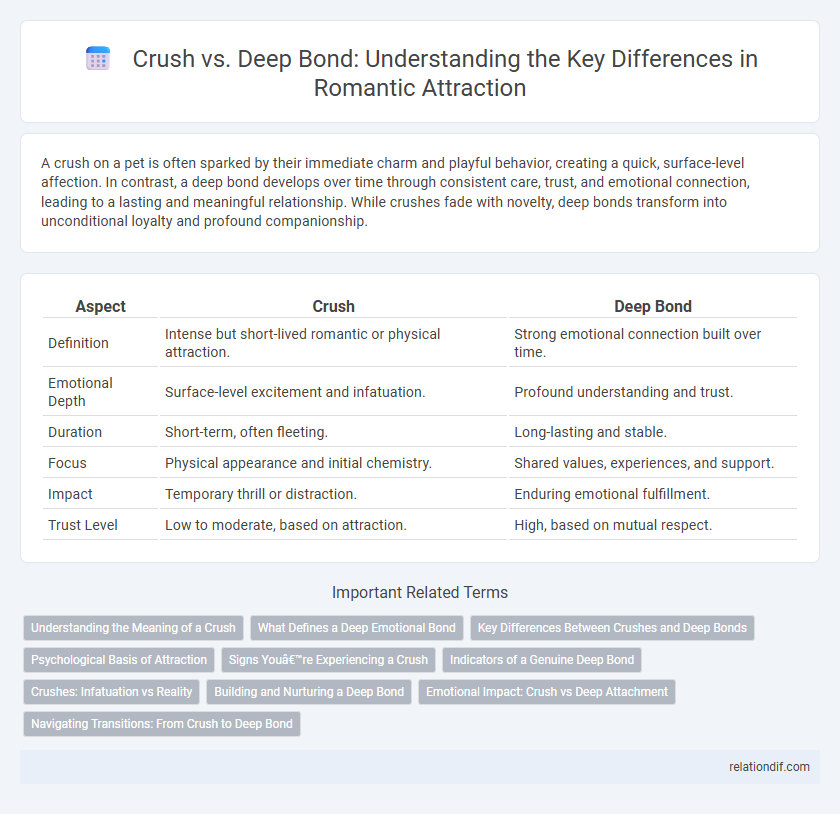
A crush on a pet is often sparked by their immediate charm and playful behavior, creating a quick, surface-level affection. In contrast, a deep bond develops over time through consistent care, trust, and emotional connection, leading to a lasting and meaningful relationship. While crushes fade with novelty, deep bonds transform into unconditional loyalty and profound companionship.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Crush | Deep Bond |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Intense but short-lived romantic or physical attraction. | Strong emotional connection built over time. |
| Emotional Depth | Surface-level excitement and infatuation. | Profound understanding and trust. |
| Duration | Short-term, often fleeting. | Long-lasting and stable. |
| Focus | Physical appearance and initial chemistry. | Shared values, experiences, and support. |
| Impact | Temporary thrill or distraction. | Enduring emotional fulfillment. |
| Trust Level | Low to moderate, based on attraction. | High, based on mutual respect. |
Understanding the Meaning of a Crush
A crush is an intense but often fleeting attraction characterized by idealized perceptions and infatuation, distinct from a deep bond which involves emotional intimacy and lasting connection. Understanding the meaning of a crush involves recognizing its basis in physical attraction and curiosity rather than shared experiences or emotional support. Unlike deep bonds that develop through trust and mutual understanding, crushes primarily activate reward centers in the brain linked to novelty and excitement.
What Defines a Deep Emotional Bond
A deep emotional bond is defined by consistent trust, vulnerability, and profound understanding between individuals, far surpassing the fleeting excitement of a crush. Unlike a crush, which is often based on infatuation and surface-level attraction, a deep bond is built through shared experiences and emotional support over time. This connection fosters mutual respect and genuine care, creating lasting emotional intimacy.
Key Differences Between Crushes and Deep Bonds
Crushes typically involve intense infatuation and idealization based on physical attraction and limited interaction, whereas deep bonds develop through sustained emotional connection, trust, and shared experiences. Crushes are often fleeting and centered on surface-level qualities, while deep bonds endure over time, supporting mutual understanding and vulnerability. Recognizing these key differences helps distinguish temporary passion from lasting emotional intimacy in relationships.
Psychological Basis of Attraction
Crushes often arise from surface-level cues such as physical appearance and novelty, activating the brain's reward system through the release of dopamine, which triggers intense but short-lived feelings of excitement. Deep bonds are formed through sustained emotional intimacy, trust, and shared experiences, engaging oxytocin and vasopressin pathways that promote long-term attachment and stability. Psychological theories indicate that while crushes focus on immediate gratification and idealization, deep bonds rely on mutual understanding and emotional regulation, supporting enduring relational satisfaction.
Signs You’re Experiencing a Crush
Rapid heartbeat, constant thoughts about the person, and a heightened desire for their attention are clear signs you're experiencing a crush. You may feel nervous or excited in their presence, accompanied by butterflies in your stomach and an intense focus on their appearance or actions. This infatuation often centers on idealized traits rather than deep emotional connection, distinguishing it from a deep bond.
Indicators of a Genuine Deep Bond
Indicators of a genuine deep bond include consistent emotional support, mutual trust, and open communication, which create a foundation beyond the initial excitement of a crush. Physical attraction may spark interest, but a deep bond is characterized by shared values, empathy, and a commitment to each other's growth. Long-term compatibility and resilience during conflicts further distinguish a deep bond from transient infatuation.
Crushes: Infatuation vs Reality
Crushes often involve intense infatuation characterized by idealized perceptions and heightened emotional arousal, which can distort reality and obscure genuine compatibility. This fleeting passion contrasts with the stability and mutual understanding found in deep bonds, where attraction is grounded in shared values and consistent emotional support. Recognizing the difference between a crush and a deep bond is essential for developing healthy, lasting relationships beyond mere surface-level allure.
Building and Nurturing a Deep Bond
Building and nurturing a deep bond involves consistent emotional intimacy, trust, and open communication, which create a foundation far stronger than the initial excitement of a crush. Unlike fleeting attraction, deep bonds grow through shared experiences, vulnerability, and mutual support over time. Prioritizing empathy and active listening enhances connection, transforming surface-level infatuation into lasting emotional attachment.
Emotional Impact: Crush vs Deep Attachment
A crush triggers intense but fleeting emotions characterized by excitement and idealization, often influenced by physical attraction and surface-level interactions. Deep attachment involves profound emotional connection, trust, and understanding, resulting in lasting security and empathy between individuals. While a crush may cause emotional highs and anxiety due to uncertainty, deep attachment fosters emotional stability and resilience over time.
Navigating Transitions: From Crush to Deep Bond
Navigating the transition from crush to deep bond requires recognizing the shift from infatuation based on physical attraction to developing emotional intimacy and mutual trust. Building a deep bond involves consistent communication, vulnerability, and shared experiences that reinforce connection beyond initial excitement. Understanding this progression helps individuals foster lasting relationships rooted in genuine affection rather than fleeting admiration.
Crush vs Deep Bond Infographic
 relationdif.com
relationdif.com