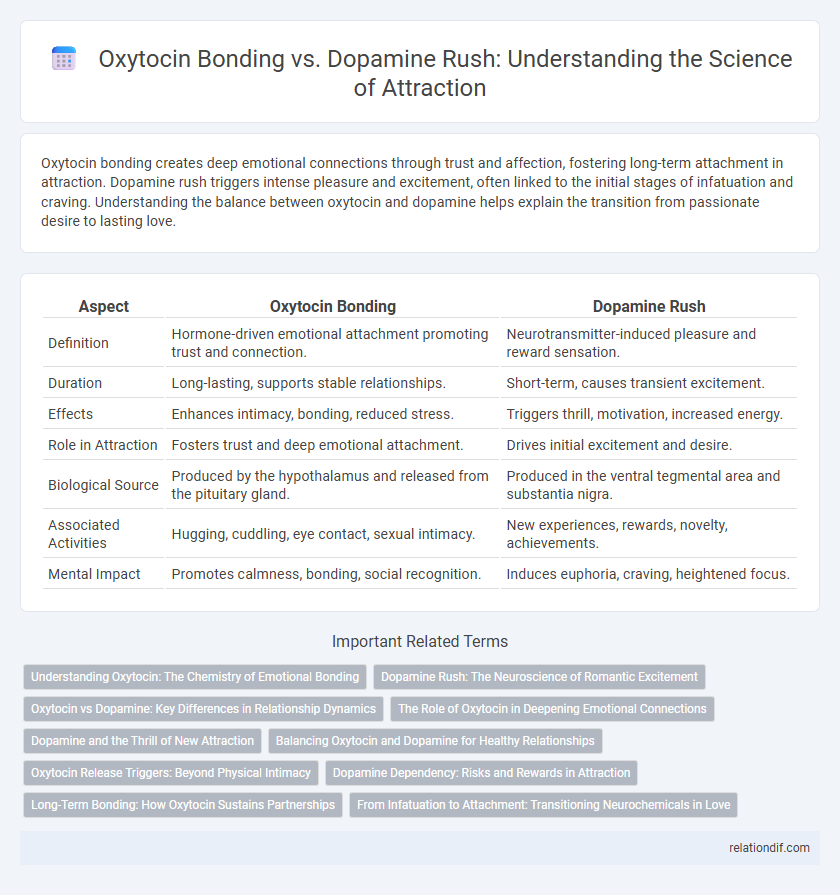
Oxytocin bonding creates deep emotional connections through trust and affection, fostering long-term attachment in attraction. Dopamine rush triggers intense pleasure and excitement, often linked to the initial stages of infatuation and craving. Understanding the balance between oxytocin and dopamine helps explain the transition from passionate desire to lasting love.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Oxytocin Bonding | Dopamine Rush |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Hormone-driven emotional attachment promoting trust and connection. | Neurotransmitter-induced pleasure and reward sensation. |
| Duration | Long-lasting, supports stable relationships. | Short-term, causes transient excitement. |
| Effects | Enhances intimacy, bonding, reduced stress. | Triggers thrill, motivation, increased energy. |
| Role in Attraction | Fosters trust and deep emotional attachment. | Drives initial excitement and desire. |
| Biological Source | Produced by the hypothalamus and released from the pituitary gland. | Produced in the ventral tegmental area and substantia nigra. |
| Associated Activities | Hugging, cuddling, eye contact, sexual intimacy. | New experiences, rewards, novelty, achievements. |
| Mental Impact | Promotes calmness, bonding, social recognition. | Induces euphoria, craving, heightened focus. |
Understanding Oxytocin: The Chemistry of Emotional Bonding
Oxytocin, often dubbed the "love hormone," plays a pivotal role in emotional bonding by enhancing trust, empathy, and social connection between individuals. Unlike dopamine, which triggers short-lived pleasure and excitement during initial attraction, oxytocin fosters long-term attachment by promoting feelings of safety and intimacy. This neuropeptide is released during close physical contact, such as hugging or intimate moments, solidifying deeper, more meaningful relationships.
Dopamine Rush: The Neuroscience of Romantic Excitement
Dopamine rush in romantic excitement activates the brain's reward system, intensifying feelings of pleasure and motivation that drive attraction. This neurotransmitter surge heightens focus on a partner, reinforcing the desire for social connection and novel experiences. Unlike oxytocin bonding, which fosters long-term attachment, dopamine creates the exhilarating, addictive sensations characteristic of early-stage romance.
Oxytocin vs Dopamine: Key Differences in Relationship Dynamics
Oxytocin, often called the "bonding hormone," promotes long-term attachment and trust in relationships by enhancing emotional intimacy and stability. Dopamine triggers intense pleasure and reward sensations, driving the excitement and novelty of new romantic encounters but often fading as the relationship matures. Understanding the balance between oxytocin's calming influence and dopamine's stimulating effects is crucial for sustaining healthy and fulfilling romantic relationships.
The Role of Oxytocin in Deepening Emotional Connections
Oxytocin plays a crucial role in deepening emotional connections by promoting trust, empathy, and intimacy between individuals, which strengthens long-term bonding in relationships. Unlike the transient dopamine rush associated with initial attraction and excitement, oxytocin supports sustained feelings of attachment and security. This neuropeptide's release during physical touch, eye contact, and shared experiences helps to solidify meaningful emotional bonds essential for lasting partnerships.
Dopamine and the Thrill of New Attraction
Dopamine plays a crucial role in the thrill of new attraction by triggering intense feelings of pleasure, excitement, and motivation, often linked to the anticipation of romantic encounters. This neurotransmitter fuels the initial rush and heightened focus on a new partner, creating a powerful drive to pursue and explore the budding relationship. Unlike oxytocin bonding, which fosters long-term emotional connection and trust, dopamine spikes deliver the exhilarating, sometimes addictive sensation of fresh attraction.
Balancing Oxytocin and Dopamine for Healthy Relationships
Balancing oxytocin and dopamine is essential for nurturing healthy relationships, as oxytocin fosters deep emotional bonds and trust while dopamine drives excitement and pleasure. Prioritizing sustained oxytocin release through meaningful interactions counters the often fleeting dopamine rushes associated with novelty and infatuation. Establishing equilibrium between these neurochemicals supports lasting intimacy and emotional stability, crucial for relationship resilience.
Oxytocin Release Triggers: Beyond Physical Intimacy
Oxytocin release extends beyond physical intimacy to include activities such as deep conversations, eye contact, and shared experiences, which strengthen emotional bonds and trust. This hormone plays a crucial role in long-term attachment by fostering feelings of security and connection, contrasting with dopamine's short-lived pleasure spikes during initial attraction. Understanding oxytocin triggers helps cultivate meaningful relationships grounded in emotional closeness rather than transient excitement.
Dopamine Dependency: Risks and Rewards in Attraction
Dopamine dependency in attraction triggers intense pleasure and motivation but often leads to volatile emotional highs and lows, increasing the risk of addiction to the excitement of new connections. While dopamine-fueled relationships can enhance attraction by promoting novelty and reward-seeking behavior, they may also result in unstable bonds due to reliance on constant stimulation. Balancing dopamine-driven excitement with deeper oxytocin-based bonding fosters healthier, more sustainable romantic attachments.
Long-Term Bonding: How Oxytocin Sustains Partnerships
Oxytocin plays a crucial role in long-term bonding by promoting trust, emotional intimacy, and social connection between partners, which strengthens relationship stability over time. Unlike the short-lived dopamine rush that triggers excitement and attraction, oxytocin fosters sustained attachment by enhancing feelings of security and mutual care. Research indicates that oxytocin release during physical touch, eye contact, and shared experiences supports enduring partnerships and emotional resilience.
From Infatuation to Attachment: Transitioning Neurochemicals in Love
Oxytocin, often called the "bonding hormone," strengthens long-term attachment by promoting trust and emotional connection between partners. Dopamine drives the intense pleasure and motivation associated with early-stage infatuation, fueling desire and excitement. The transition from dopamine-driven passion to oxytocin-mediated attachment marks the neurochemical shift that sustains enduring romantic relationships.
Oxytocin Bonding vs Dopamine Rush Infographic
 relationdif.com
relationdif.com