A cohabitation agreement and a marriage contract both establish legal rights and responsibilities for couples living together, but they differ in scope and formality. Cohabitation agreements are designed primarily for unmarried couples, outlining property division and financial arrangements without affecting marital status. Marriage contracts, often incorporated into prenuptial agreements, address asset protection, spousal support, and other obligations specifically tied to the legal institution of marriage.
Table of Comparison
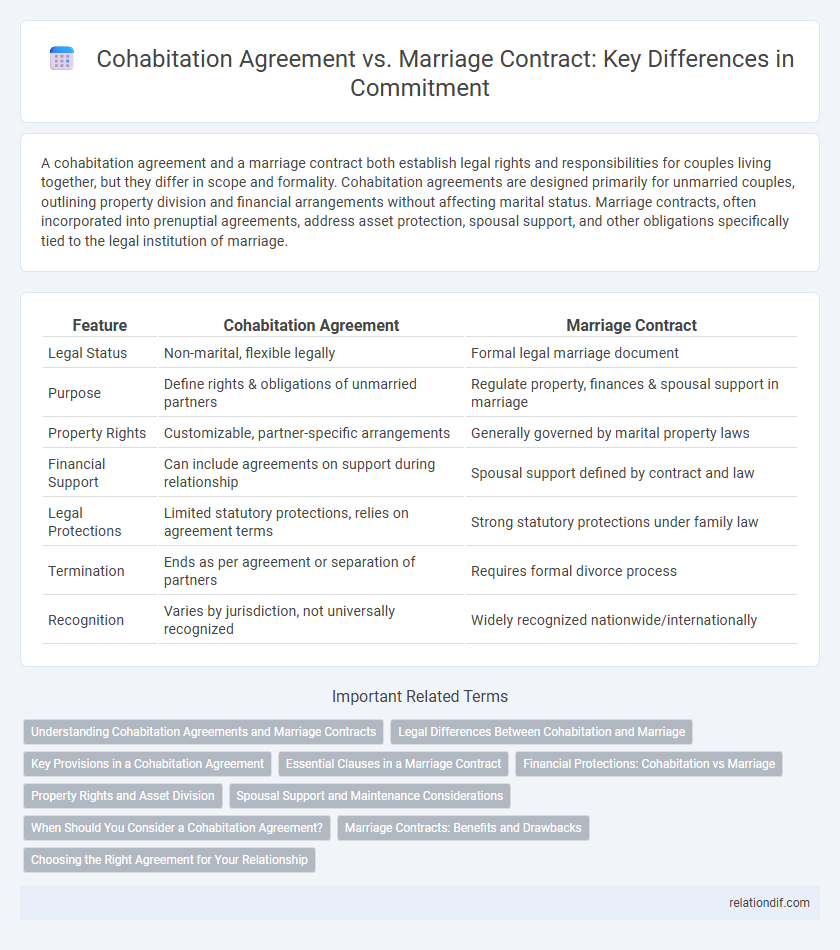
| Feature | Cohabitation Agreement | Marriage Contract |
|---|---|---|
| Legal Status | Non-marital, flexible legally | Formal legal marriage document |
| Purpose | Define rights & obligations of unmarried partners | Regulate property, finances & spousal support in marriage |
| Property Rights | Customizable, partner-specific arrangements | Generally governed by marital property laws |
| Financial Support | Can include agreements on support during relationship | Spousal support defined by contract and law |
| Legal Protections | Limited statutory protections, relies on agreement terms | Strong statutory protections under family law |
| Termination | Ends as per agreement or separation of partners | Requires formal divorce process |
| Recognition | Varies by jurisdiction, not universally recognized | Widely recognized nationwide/internationally |
Understanding Cohabitation Agreements and Marriage Contracts
Cohabitation agreements outline property rights, financial responsibilities, and dispute resolution methods for unmarried couples living together, providing legal clarity without formal marriage. Marriage contracts, commonly known as prenuptial agreements, govern asset division, spousal support, and debt liabilities in the event of divorce or separation within a legally recognized marriage. Understanding the distinct legal enforceability and scope of each agreement helps couples protect their interests based on their commitment status.
Legal Differences Between Cohabitation and Marriage
A cohabitation agreement primarily addresses property rights, financial responsibilities, and dispute resolution for couples living together without formal marriage, providing limited legal protection compared to marriage. Marriage contracts confer extensive legal obligations and rights, including inheritance, tax benefits, spousal support, and decision-making authority during emergencies. Unlike a cohabitation agreement, marriage requires statutory compliance and government registration, granting broader legal recognition and enforceability.
Key Provisions in a Cohabitation Agreement
Key provisions in a cohabitation agreement typically include property division, financial responsibilities, and dispute resolution methods tailored for unmarried couples. These agreements outline each partner's rights and obligations concerning assets, debts, and living expenses, ensuring clarity without the legal bindings of marriage contracts. Protecting personal property and addressing support commitments are essential elements that differentiate cohabitation agreements from traditional marriage contracts.
Essential Clauses in a Marriage Contract
Essential clauses in a marriage contract typically cover property division, spousal support, inheritance rights, and dispute resolution to safeguard both parties' interests. Unlike cohabitation agreements, marriage contracts often include provisions for child custody and financial responsibilities during and after the marriage. Clear articulation of these clauses ensures legal certainty and helps prevent conflicts in the event of separation or divorce.
Financial Protections: Cohabitation vs Marriage
Cohabitation agreements provide tailored financial protections addressing asset division, debt responsibility, and support obligations for unmarried couples, but may lack uniform legal recognition across jurisdictions. Marriage contracts, including prenuptial agreements, benefit from established legal frameworks ensuring clearer enforcement of spousal support, property rights, and inheritance entitlements. Understanding state-specific laws is crucial for couples to maximize financial security whether choosing cohabitation or marriage contracts.
Property Rights and Asset Division
Cohabitation agreements specifically outline property rights and asset division for unmarried couples, ensuring clear ownership and financial responsibilities during and after the relationship. Marriage contracts, or prenuptial agreements, provide a comprehensive legal framework that governs asset division and property rights in the event of divorce or death, often including spousal support provisions. Both agreements serve to protect individual assets but differ in legal recognition and enforceability depending on jurisdiction.
Spousal Support and Maintenance Considerations
Cohabitation agreements often provide specific terms for spousal support that differ from those in marriage contracts, typically reflecting the non-marital status of the partners. Marriage contracts usually include more comprehensive provisions for maintenance, influenced by state laws that recognize spousal support obligations during and after marriage. Understanding the distinctions in these agreements is crucial for managing financial responsibilities and securing spousal support rights in both cohabitation and marital relationships.
When Should You Consider a Cohabitation Agreement?
Consider a cohabitation agreement when living together without marriage to clearly outline property rights, financial responsibilities, and support obligations. Cohabitation agreements are essential for protecting individual assets and reducing potential legal disputes in case of separation. This contract is particularly important for couples with significant assets, children from previous relationships, or inconsistent income streams.
Marriage Contracts: Benefits and Drawbacks
Marriage contracts provide legal clarity and financial protection by outlining asset division, spousal support, and debt responsibilities in the event of divorce or separation. They safeguard individual property rights and reduce potential disputes, offering peace of mind for couples entering marriage with significant assets or children from previous relationships. However, marriage contracts can be perceived as undermining emotional commitment and may require negotiation that challenges trust between partners.
Choosing the Right Agreement for Your Relationship
Choosing the right legal agreement depends on the level of commitment and financial planning desired within the relationship. Cohabitation agreements typically address property rights and responsibilities for couples living together without marriage, emphasizing flexibility and individual asset protection. Marriage contracts, or prenuptial agreements, often involve more comprehensive financial arrangements and spousal support terms, reflecting the formal legal status and long-term obligations of marriage.
cohabitation agreement vs marriage contract Infographic
 relationdif.com
relationdif.com