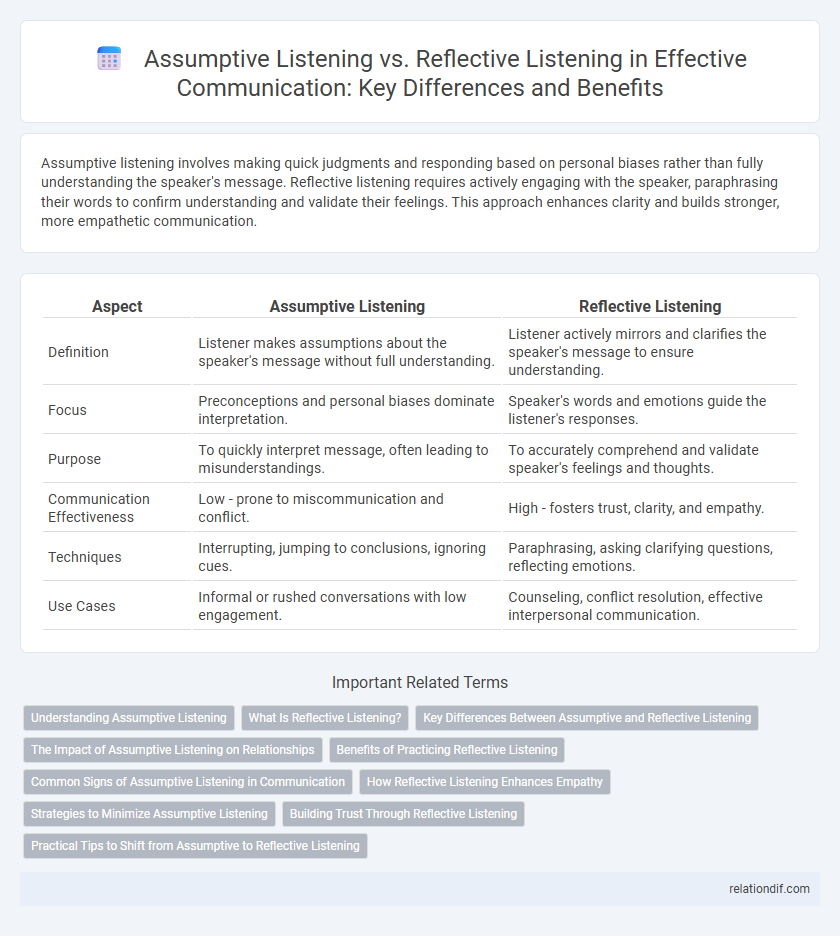
Assumptive listening involves making quick judgments and responding based on personal biases rather than fully understanding the speaker's message. Reflective listening requires actively engaging with the speaker, paraphrasing their words to confirm understanding and validate their feelings. This approach enhances clarity and builds stronger, more empathetic communication.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Assumptive Listening | Reflective Listening |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Listener makes assumptions about the speaker's message without full understanding. | Listener actively mirrors and clarifies the speaker's message to ensure understanding. |
| Focus | Preconceptions and personal biases dominate interpretation. | Speaker's words and emotions guide the listener's responses. |
| Purpose | To quickly interpret message, often leading to misunderstandings. | To accurately comprehend and validate speaker's feelings and thoughts. |
| Communication Effectiveness | Low - prone to miscommunication and conflict. | High - fosters trust, clarity, and empathy. |
| Techniques | Interrupting, jumping to conclusions, ignoring cues. | Paraphrasing, asking clarifying questions, reflecting emotions. |
| Use Cases | Informal or rushed conversations with low engagement. | Counseling, conflict resolution, effective interpersonal communication. |
Understanding Assumptive Listening
Assumptive listening involves interpreting a speaker's message based on preconceived notions or expectations rather than fully engaging with their actual words. This listening style can lead to misunderstandings as it filters communication through biases, limiting accurate comprehension. Understanding assumptive listening highlights the importance of active, reflective listening techniques to improve clarity and empathy in communication.
What Is Reflective Listening?
Reflective listening is a communication technique where the listener actively mirrors the speaker's message by paraphrasing or summarizing their words to confirm understanding. This method fosters empathy, builds trust, and clarifies emotions, enhancing overall dialogue quality. Unlike assumptive listening, reflective listening reduces misunderstandings by focusing on accurate interpretation rather than preconceived notions.
Key Differences Between Assumptive and Reflective Listening
Assumptive listening involves interpreting the speaker's message based on preconceived notions or expectations, often leading to misunderstandings and missed nuances. Reflective listening, in contrast, emphasizes accurately paraphrasing and confirming the speaker's intent, fostering clarity and empathy in communication. Key differences include assumptive listening's tendency to jump to conclusions versus reflective listening's focus on active engagement and validation of the speaker's feelings and thoughts.
The Impact of Assumptive Listening on Relationships
Assumptive listening often leads to misunderstandings and erodes trust by causing individuals to feel unheard or invalidated, which negatively impacts relationship quality. This form of listening bypasses the speaker's true message, fostering miscommunication and emotional distance between parties. In contrast, relationships thrive when active, reflective listening is practiced, as it promotes empathy and accurate understanding.
Benefits of Practicing Reflective Listening
Reflective listening enhances communication by ensuring the listener accurately understands the speaker's message, reducing misunderstandings and fostering trust. This active engagement promotes empathy and emotional connection, which are crucial for resolving conflicts and deepening relationships. Practicing reflective listening also encourages open dialogue, making conversations more meaningful and effective.
Common Signs of Assumptive Listening in Communication
Common signs of assumptive listening in communication include interrupting the speaker, finishing their sentences, and making premature judgments without fully hearing the message. This behavior often results in misunderstandings and a lack of genuine engagement, as the listener projects their own assumptions rather than focusing on the speaker's actual words. Recognizing these signs is essential to fostering more effective and respectful communication.
How Reflective Listening Enhances Empathy
Reflective listening enhances empathy by actively demonstrating understanding and validation of the speaker's emotions, which fosters trust and deeper connection in communication. This technique involves paraphrasing and mirroring feelings, allowing the listener to accurately grasp the speaker's perspective beyond surface-level words. Unlike assumptive listening, which interprets messages based on preconceived notions, reflective listening promotes emotional attunement and reduces misunderstandings.
Strategies to Minimize Assumptive Listening
Minimizing assumptive listening involves actively verifying understanding through open-ended questions and paraphrasing the speaker's message to confirm accuracy. Employing reflective listening techniques, such as summarizing key points and acknowledging emotions, ensures clearer communication and reduces misunderstandings. Consistently practicing these strategies fosters empathy and enhances the overall quality of interpersonal communication.
Building Trust Through Reflective Listening
Reflective listening fosters trust by demonstrating genuine understanding and empathy, which validates the speaker's feelings and encourages openness. This approach contrasts with assumptive listening, where the listener presumes meaning and potentially misinterprets the speaker's message, leading to misunderstandings. Prioritizing reflective listening techniques enhances communication effectiveness and strengthens interpersonal connections through active engagement and clarification.
Practical Tips to Shift from Assumptive to Reflective Listening
Assumptive listening often leads to misunderstandings due to premature conclusions, while reflective listening fosters clarity by encouraging active feedback and verification of the speaker's message. Practical tips to shift include pausing to paraphrase what the speaker has said, asking open-ended questions to invite elaboration, and maintaining nonjudgmental body language that signals attentiveness. These techniques enhance empathetic engagement, reduce miscommunication, and build stronger interpersonal connections.
Assumptive listening vs reflective listening Infographic
 relationdif.com
relationdif.com