Direct communication ensures clarity by conveying messages explicitly, reducing misunderstandings and fostering transparency. Indirect communication often relies on context and nonverbal cues, which can preserve harmony but may lead to ambiguity. Choosing between direct and indirect methods depends on cultural norms and the specific needs of the interaction.
Table of Comparison
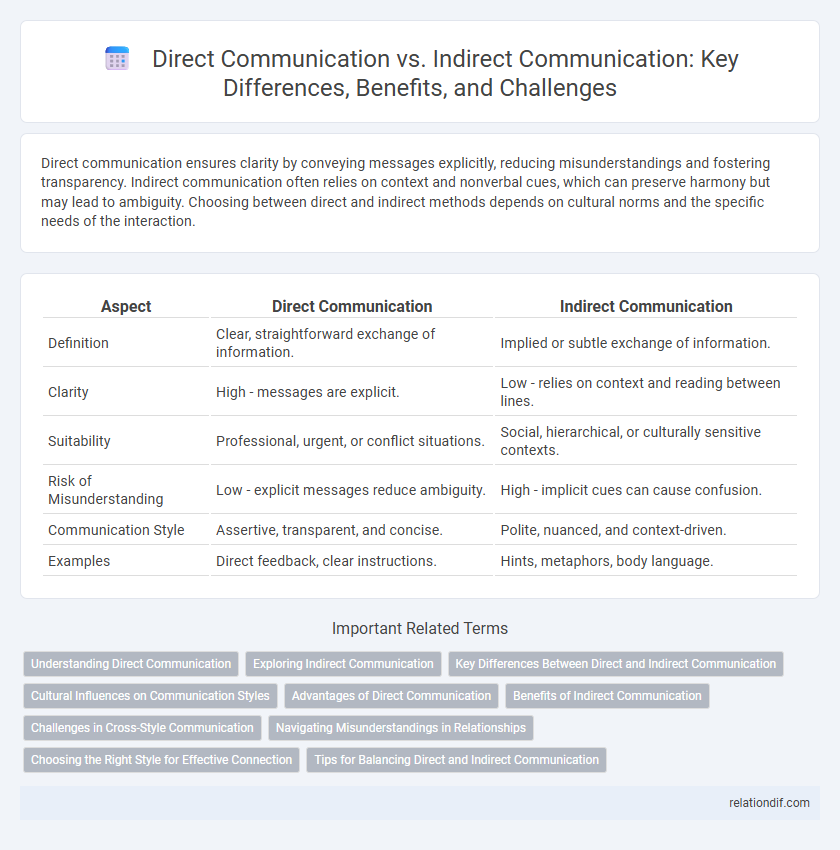
| Aspect | Direct Communication | Indirect Communication |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Clear, straightforward exchange of information. | Implied or subtle exchange of information. |
| Clarity | High - messages are explicit. | Low - relies on context and reading between lines. |
| Suitability | Professional, urgent, or conflict situations. | Social, hierarchical, or culturally sensitive contexts. |
| Risk of Misunderstanding | Low - explicit messages reduce ambiguity. | High - implicit cues can cause confusion. |
| Communication Style | Assertive, transparent, and concise. | Polite, nuanced, and context-driven. |
| Examples | Direct feedback, clear instructions. | Hints, metaphors, body language. |
Understanding Direct Communication
Direct communication involves clear, explicit messages where the speaker's intentions and meanings are openly expressed without ambiguity. It enhances understanding by reducing misunderstandings and fostering transparency between parties. This straightforward approach is particularly effective in professional settings and cultures valuing honesty and efficiency.
Exploring Indirect Communication
Indirect communication relies on context, nonverbal cues, and implied meanings to convey messages subtly, often prioritizing harmony and relationship preservation. It is prevalent in high-context cultures where understanding depends on shared experiences and unspoken assumptions. Mastering indirect communication enhances interpretation skills and fosters nuanced interactions in diverse social or professional settings.
Key Differences Between Direct and Indirect Communication
Direct communication involves explicit, clear, and straightforward messages aimed at delivering information unambiguously, while indirect communication relies on context, tone, and nonverbal cues to convey meaning subtly. Direct communicators prioritize transparency and efficiency, often using concise language and explicit requests, whereas indirect communicators emphasize harmony, politeness, and relationship maintenance by avoiding confrontation or overt statements. Understanding these key differences enhances cross-cultural communication, conflict resolution, and interpersonal effectiveness in diverse environments.
Cultural Influences on Communication Styles
Direct communication emphasizes explicit verbal expression and clarity, commonly found in Western cultures like the United States and Germany, where straightforwardness is valued. Indirect communication, prevalent in many East Asian and Middle Eastern cultures such as Japan and Saudi Arabia, relies heavily on context, non-verbal cues, and implicit messages to maintain harmony and avoid confrontation. Cultural influences shape whether individuals prioritize explicit clarity or relational sensitivity in their communication styles, impacting cross-cultural understanding and interaction effectiveness.
Advantages of Direct Communication
Direct communication enhances clarity and reduces misunderstandings by conveying messages explicitly, which improves overall efficiency in professional and personal interactions. It fosters transparency and trust, enabling quicker decision-making and problem-solving through straightforward exchanges. Clear, concise communication also minimizes ambiguity, leading to stronger collaboration and more effective teamwork.
Benefits of Indirect Communication
Indirect communication enhances relationship harmony by allowing speakers to convey messages subtly, reducing the risk of conflict or offense. It enables the use of context, tone, and nonverbal cues to express sensitivity and respect, fostering mutual understanding in diverse cultural settings. This approach supports diplomatic interactions and preserves social hierarchy, making it effective in professional and interpersonal environments.
Challenges in Cross-Style Communication
Cross-style communication between direct and indirect communicators often leads to misunderstandings due to differing expectations in message clarity and context reliance. Direct communicators prioritize explicit language and straightforwardness, while indirect communicators depend on nuance and nonverbal cues, causing ambiguity. These contrasting approaches can challenge effective collaboration, requiring heightened cultural sensitivity and adaptive communication strategies.
Navigating Misunderstandings in Relationships
Direct communication reduces the risk of misunderstandings by clearly expressing thoughts and feelings without ambiguity. Indirect communication often relies on context and nonverbal cues, which can lead to misinterpretations and unresolved conflicts in relationships. Training in both verbal clarity and active listening improves navigation of misunderstandings, fostering healthier interpersonal connections.
Choosing the Right Style for Effective Connection
Direct communication fosters clarity and immediacy, enabling straightforward exchange of ideas and reducing misunderstandings, which is essential in high-stakes environments like corporate meetings or emergency situations. Indirect communication, often characterized by nuanced language and context-driven cues, benefits relationships where preserving harmony and respecting social hierarchies is critical, such as in multicultural teams or diplomatic interactions. Selecting the appropriate communication style requires evaluating the audience, cultural context, and desired outcomes to ensure effective connection and mutual understanding.
Tips for Balancing Direct and Indirect Communication
Balancing direct and indirect communication requires assessing the cultural context and the relationship dynamics to choose the appropriate style. Use clear and concise language when clarity is crucial, while employing subtle cues and diplomacy to preserve harmony and avoid misunderstandings. Practicing active listening and seeking feedback ensures messages are understood as intended, enhancing effective interpersonal communication.
direct communication vs indirect communication Infographic
 relationdif.com
relationdif.com