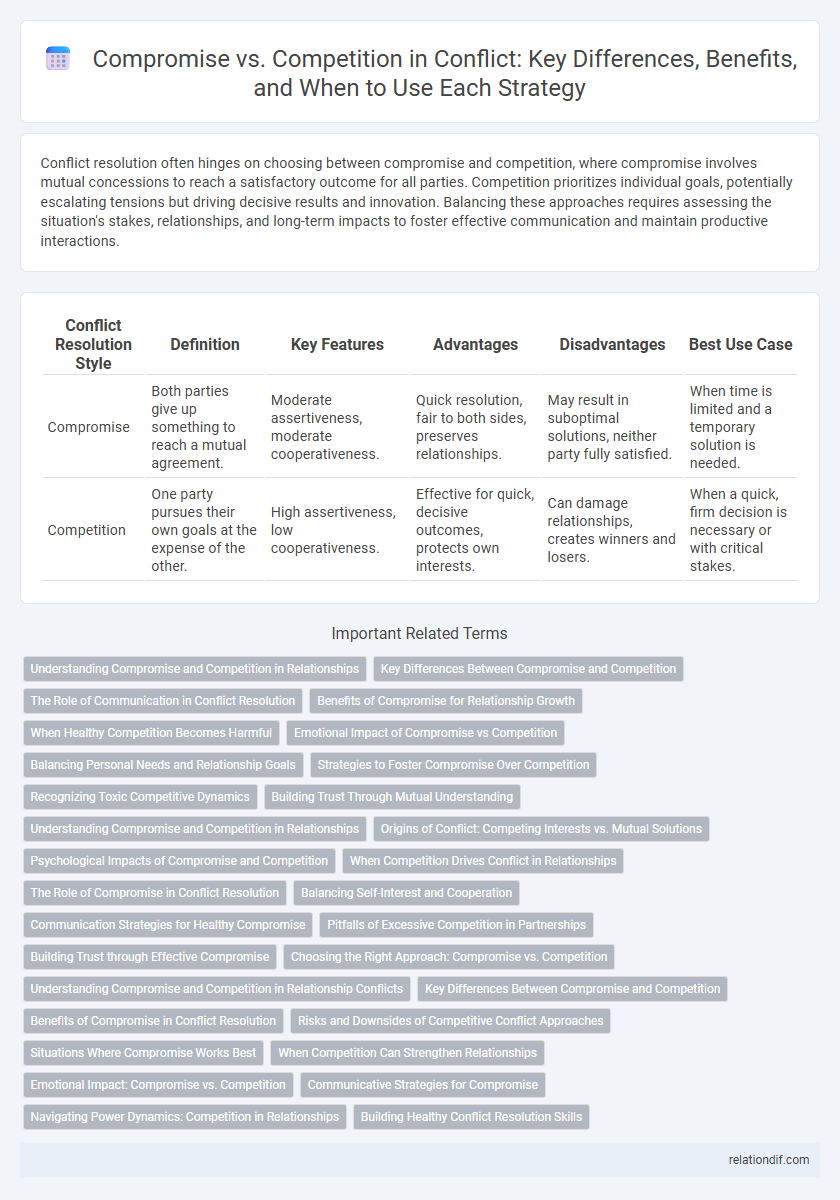
Conflict resolution often hinges on choosing between compromise and competition, where compromise involves mutual concessions to reach a satisfactory outcome for all parties. Competition prioritizes individual goals, potentially escalating tensions but driving decisive results and innovation. Balancing these approaches requires assessing the situation's stakes, relationships, and long-term impacts to foster effective communication and maintain productive interactions.
Table of Comparison
| Conflict Resolution Style | Definition | Key Features | Advantages | Disadvantages | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compromise | Both parties give up something to reach a mutual agreement. | Moderate assertiveness, moderate cooperativeness. | Quick resolution, fair to both sides, preserves relationships. | May result in suboptimal solutions, neither party fully satisfied. | When time is limited and a temporary solution is needed. |
| Competition | One party pursues their own goals at the expense of the other. | High assertiveness, low cooperativeness. | Effective for quick, decisive outcomes, protects own interests. | Can damage relationships, creates winners and losers. | When a quick, firm decision is necessary or with critical stakes. |
Understanding Compromise and Competition in Relationships
Compromise in relationships involves mutual concessions where both parties adjust their needs to achieve a balanced resolution, fostering cooperation and long-term harmony. Competition, by contrast, emphasizes winning or asserting one's own interests, often leading to tension and unresolved conflicts. Understanding when to prioritize compromise over competition can enhance communication and strengthen emotional bonds in partnerships.
Key Differences Between Compromise and Competition
Compromise involves mutual concession where conflicting parties make sacrifices to reach a shared agreement, fostering cooperation and preserving relationships. Competition emphasizes winning or outperforming the opposing party, often at the expense of collaboration and long-term harmony. Key differences lie in the goals: compromise seeks balance and consensus, while competition prioritizes individual victory and dominance.
The Role of Communication in Conflict Resolution
Effective communication plays a crucial role in conflict resolution by facilitating understanding between conflicting parties and enabling compromise, which prioritizes mutual benefit over winning. In competitive conflict scenarios, communication often escalates tensions as parties focus on asserting dominance rather than resolving issues. Clear, empathetic dialogue encourages collaboration, reduces misunderstandings, and helps transform competition into constructive negotiation.
Benefits of Compromise for Relationship Growth
Compromise fosters mutual understanding and trust, strengthening emotional bonds between parties involved in a conflict. It encourages collaborative problem-solving, allowing both sides to feel valued and respected, which promotes long-term relationship stability. This cooperative approach reduces hostility, enhances communication, and supports sustainable growth in personal and professional relationships.
When Healthy Competition Becomes Harmful
Healthy competition encourages growth and innovation, but it becomes harmful when it fosters hostility, undermines collaboration, or leads to unethical behavior. In such cases, parties prioritize winning over mutual respect and constructive dialogue, escalating conflicts unnecessarily. Recognizing when competition shifts from motivating to destructive is crucial for resolving disputes and maintaining productive relationships.
Emotional Impact of Compromise vs Competition
Compromise in conflict often reduces emotional tension by fostering feelings of cooperation and mutual respect, which can lead to lasting relationships and improved trust. In contrast, competition tends to escalate negative emotions such as frustration, anger, and anxiety due to its win-lose dynamic, potentially damaging interpersonal connections. Understanding the emotional impact helps individuals choose strategies that promote emotional well-being and effective conflict resolution.
Balancing Personal Needs and Relationship Goals
Balancing personal needs and relationship goals requires navigating the tension between compromise and competition in conflict resolution. Prioritizing open communication allows both partners to express their desires while seeking mutually beneficial solutions that respect individual boundaries. Effective conflict management strengthens trust and fosters long-term relationship satisfaction.
Strategies to Foster Compromise Over Competition
Effective conflict resolution emphasizes active listening and empathy to create a foundation for compromise rather than competition. Implementing interest-based negotiation techniques helps parties identify shared goals and mutually beneficial solutions. Establishing clear communication protocols and promoting collaborative problem-solving significantly reduce adversarial tensions and foster cooperative outcomes.
Recognizing Toxic Competitive Dynamics
Recognizing toxic competitive dynamics involves identifying patterns where rivalry escalates beyond healthy competition, leading to destructive behaviors and undermining collaboration. In such conflicts, compromise becomes essential to break cycles of hostility and foster mutual understanding, preventing long-term damage to relationships or organizational culture. Awareness of toxic competitiveness allows parties to shift focus from winning at all costs to achieving balanced, sustainable resolutions.
Building Trust Through Mutual Understanding
Building trust through mutual understanding in conflict resolution requires balancing compromise and competition effectively. Compromise fosters collaboration by encouraging parties to find middle ground, while healthy competition motivates clear expression of interests and priorities. Establishing open communication and empathy ensures that trust grows as each side acknowledges the other's perspective, leading to sustainable conflict management.
compromise vs competition Infographic
 relationdif.com
relationdif.com