Deep listening involves fully engaging with a pet's vocalizations, body language, and energy to understand their needs and emotions, fostering a strong bond and trust. Passive hearing merely registers sounds without interpreting meaning, often leading to missed cues and misunderstandings. Prioritizing deep listening enhances communication and strengthens the connection between owner and pet.
Table of Comparison
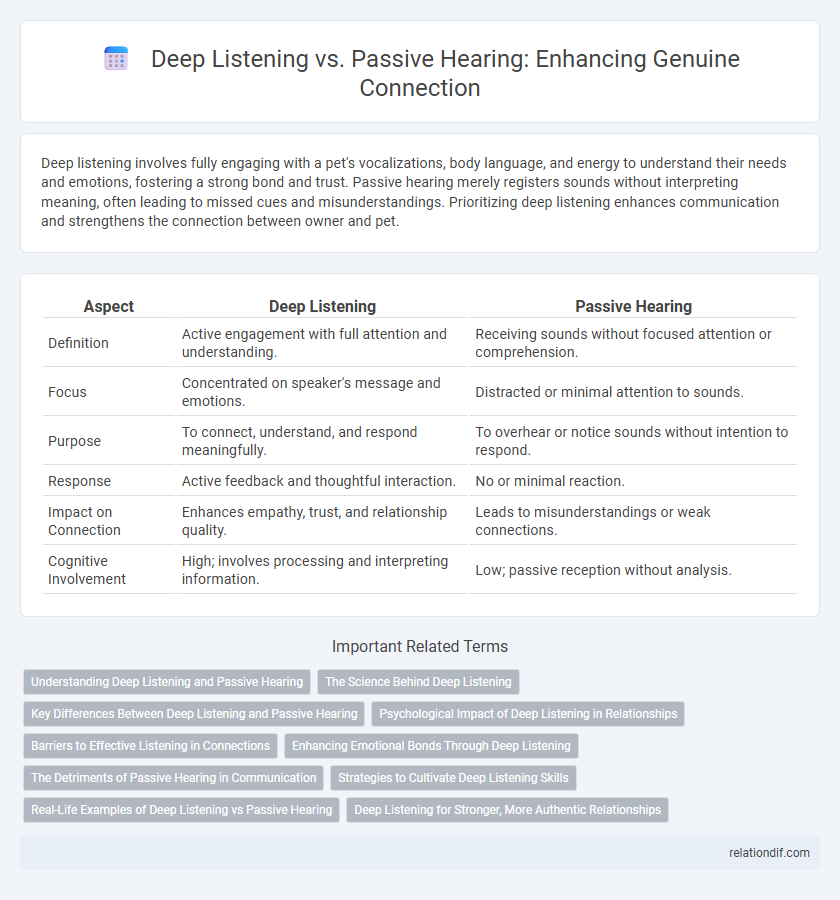
| Aspect | Deep Listening | Passive Hearing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Active engagement with full attention and understanding. | Receiving sounds without focused attention or comprehension. |
| Focus | Concentrated on speaker's message and emotions. | Distracted or minimal attention to sounds. |
| Purpose | To connect, understand, and respond meaningfully. | To overhear or notice sounds without intention to respond. |
| Response | Active feedback and thoughtful interaction. | No or minimal reaction. |
| Impact on Connection | Enhances empathy, trust, and relationship quality. | Leads to misunderstandings or weak connections. |
| Cognitive Involvement | High; involves processing and interpreting information. | Low; passive reception without analysis. |
Understanding Deep Listening and Passive Hearing
Deep listening involves fully engaging with the speaker, interpreting emotions, intentions, and unspoken cues to foster genuine connection. Passive hearing merely registers sounds without processing or responding to the underlying message, often leading to misunderstandings. Understanding this distinction enhances communication effectiveness and strengthens interpersonal relationships.
The Science Behind Deep Listening
Deep listening activates specific brain regions such as the auditory cortex and prefrontal cortex, enhancing cognitive processing and emotional regulation. Neuroscientific studies reveal that deep listening improves neural plasticity and strengthens synaptic connections, facilitating better communication and empathy. This heightened neural engagement distinguishes deep listening from passive hearing, which involves minimal cognitive involvement and limited emotional connection.
Key Differences Between Deep Listening and Passive Hearing
Deep listening involves fully engaging with the speaker, interpreting verbal and non-verbal cues, and responding empathetically to build meaningful connections. Passive hearing occurs when sounds are perceived without conscious attention or emotional involvement, often leading to misunderstandings or missed information. The key difference lies in the level of active mental presence and intentionality, with deep listening fostering trust and clarity, while passive hearing results in superficial or incomplete communication.
Psychological Impact of Deep Listening in Relationships
Deep listening enhances emotional intimacy by promoting empathy and trust, which strengthens relationship bonds and reduces misunderstandings. Engaging attentively with a partner's verbal and nonverbal cues activates neural pathways associated with emotional regulation and social connection. This psychological impact fosters greater communication satisfaction and resilience against relational conflicts.
Barriers to Effective Listening in Connections
Barriers to effective listening in connections include distractions, preconceived notions, and emotional biases that hinder deep listening. Passive hearing often results from focusing only on words without engaging with the speaker's intent or emotions. Overcoming these obstacles requires active attention, empathy, and minimizing internal and external interruptions to foster genuine understanding.
Enhancing Emotional Bonds Through Deep Listening
Deep listening involves fully engaging with and interpreting the speaker's emotions and intentions, which strengthens emotional bonds by fostering empathy and trust. Passive hearing merely registers sounds without processing the underlying feelings or messages, leading to superficial interactions. By practicing deep listening, individuals create meaningful connections that support emotional intimacy and mutual understanding.
The Detriments of Passive Hearing in Communication
Passive hearing undermines communication by limiting true understanding and emotional engagement, often leading to misunderstandings and weakened relationships. It impairs the ability to process information critically, causing important details to be overlooked or misinterpreted. Deep listening enhances connection by fostering empathy, clarity, and responsive interaction, whereas passive hearing perpetuates disconnection and conflict.
Strategies to Cultivate Deep Listening Skills
Effective strategies to cultivate deep listening skills include practicing active engagement by maintaining eye contact, minimizing distractions, and providing reflective feedback to ensure understanding. Mindfulness techniques, such as focused breathing and present-moment awareness, enhance attention and reduce habitual internal dialogue during conversations. Regularly summarizing key points and asking open-ended questions fosters a deeper connection and facilitates meaningful communication.
Real-Life Examples of Deep Listening vs Passive Hearing
Deep listening is demonstrated in therapy sessions where counselors actively engage with clients, interpreting emotions beyond spoken words, while passive hearing occurs during crowded events when background conversations are unnoticed. In classrooms, teachers practicing deep listening respond thoughtfully to student questions, enhancing learning, contrasting with passive hearing where instructions are merely heard but not fully processed. Corporate meetings showcase deep listening when executives analyze nuanced feedback to make strategic decisions, as opposed to passive hearing which often leads to miscommunication and missed opportunities.
Deep Listening for Stronger, More Authentic Relationships
Deep listening fosters genuine connection by fully engaging with the speaker's emotions and intentions, enhancing empathy and trust. This active approach strengthens relationships through meaningful understanding and authentic communication. Being present and attentive during conversations cultivates deeper bonds and mutual respect.
deep listening vs passive hearing Infographic
 relationdif.com
relationdif.com