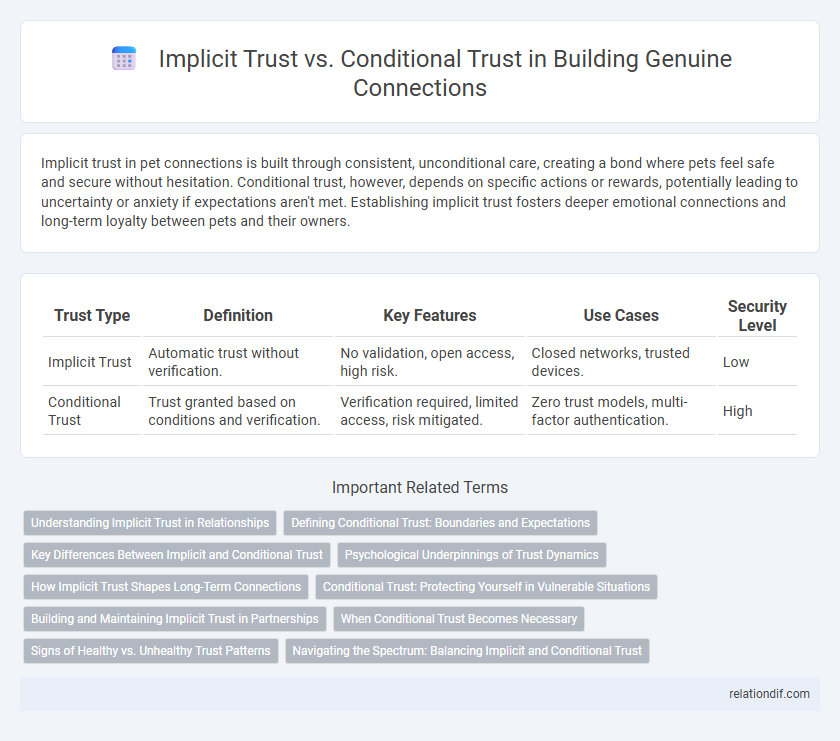
Implicit trust in pet connections is built through consistent, unconditional care, creating a bond where pets feel safe and secure without hesitation. Conditional trust, however, depends on specific actions or rewards, potentially leading to uncertainty or anxiety if expectations aren't met. Establishing implicit trust fosters deeper emotional connections and long-term loyalty between pets and their owners.
Table of Comparison
| Trust Type | Definition | Key Features | Use Cases | Security Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Implicit Trust | Automatic trust without verification. | No validation, open access, high risk. | Closed networks, trusted devices. | Low |
| Conditional Trust | Trust granted based on conditions and verification. | Verification required, limited access, risk mitigated. | Zero trust models, multi-factor authentication. | High |
Understanding Implicit Trust in Relationships
Implicit trust in relationships involves a deep, automatic confidence where individuals rely on each other's integrity and intentions without constant verification, fostering emotional security and stronger bonds. This form of trust is often built through shared experiences and consistent positive interactions that reinforce an unspoken assurance. Understanding implicit trust allows partners to navigate challenges smoothly, promoting resilience and long-term connection.
Defining Conditional Trust: Boundaries and Expectations
Conditional trust establishes clear boundaries and specific expectations between parties, ensuring reliability based on demonstrated actions and consistent behavior. Unlike implicit trust, which assumes goodwill without proof, conditional trust requires ongoing verification to maintain confidence and protect interests. This approach enhances connection security by promoting accountability and transparency within the relationship.
Key Differences Between Implicit and Conditional Trust
Implicit trust is an automatic, unquestioned belief in someone's reliability based on emotional bonds or familiarity, whereas conditional trust depends on specific behaviors, performance, or evidence before being granted. Implicit trust often emerges in close relationships without explicit verification, while conditional trust requires ongoing validation and may fluctuate with circumstances. Understanding these key differences helps organizations and individuals manage expectations and build stronger, more resilient connections.
Psychological Underpinnings of Trust Dynamics
Implicit trust arises from deep psychological mechanisms such as attachment styles and early relational experiences that shape automatic, unconscious expectations of reliability and safety. Conditional trust develops through conscious evaluation of others' behaviors, driven by cognitive processes assessing consistency, competence, and benevolence within specific contexts. Understanding these trust dynamics reveals how implicit trust fosters seamless social bonds while conditional trust allows adaptive, cautious connections in complex interpersonal environments.
How Implicit Trust Shapes Long-Term Connections
Implicit trust fosters deeper emotional bonds by enabling vulnerability and consistent support without explicit demands, creating a foundation for enduring relationships. This inherent confidence accelerates communication efficiency and resilience, as parties anticipate positive intentions even in uncertain situations. Over time, such trust solidifies commitment and loyalty, distinguishing long-term connections from superficial or conditional interactions.
Conditional Trust: Protecting Yourself in Vulnerable Situations
Conditional trust establishes boundaries that safeguard individuals in vulnerable situations by requiring evidence of reliability before granting full confidence. This approach minimizes risks by allowing trust to develop gradually, based on consistent actions and transparency. Implementing conditional trust enhances personal security and emotional resilience in relationships and professional interactions.
Building and Maintaining Implicit Trust in Partnerships
Building and maintaining implicit trust in partnerships requires consistent transparency, reliability, and open communication that fosters unspoken confidence between parties. Implicit trust grows from shared values and demonstrated integrity, reducing the need for explicit agreements or constant oversight. Strong emotional bonds and mutual understanding reinforce this trust, enabling smoother collaboration and resilience during conflicts.
When Conditional Trust Becomes Necessary
Conditional trust becomes necessary when repeated interactions reveal inconsistencies or risks that implicit trust cannot address, ensuring accountability in relationships. Establishing boundaries and criteria for trust validity protects parties from potential breaches or misunderstandings. This approach enhances connection stability by aligning expectations with observable behavior rather than assumptions.
Signs of Healthy vs. Unhealthy Trust Patterns
Signs of healthy trust patterns include consistent transparency, mutual respect, and reliable communication, fostering strong and lasting connections. Unhealthy trust patterns often manifest through secrecy, frequent doubts, and inconsistent behavior, leading to vulnerability and emotional distance. Recognizing these signs enables individuals to cultivate implicit trust rather than conditional trust, enhancing relationship stability.
Navigating the Spectrum: Balancing Implicit and Conditional Trust
Navigating the spectrum between implicit and conditional trust requires understanding the nuanced dynamics that influence relationship stability and growth. Implicit trust relies on inherent confidence and shared values, fostering seamless collaboration, while conditional trust depends on demonstrated reliability and situational assessments to mitigate risks. Balancing these trust forms enhances connection resilience by adapting to context-specific needs and promoting transparent communication.
implicit trust vs conditional trust Infographic
 relationdif.com
relationdif.com