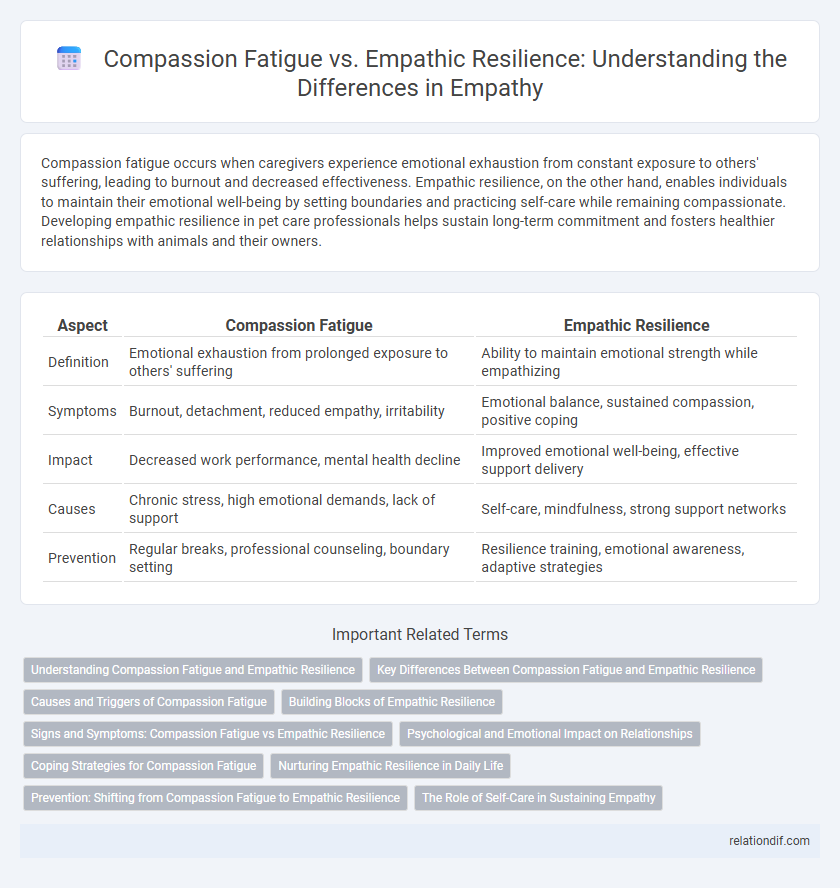
Compassion fatigue occurs when caregivers experience emotional exhaustion from constant exposure to others' suffering, leading to burnout and decreased effectiveness. Empathic resilience, on the other hand, enables individuals to maintain their emotional well-being by setting boundaries and practicing self-care while remaining compassionate. Developing empathic resilience in pet care professionals helps sustain long-term commitment and fosters healthier relationships with animals and their owners.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Compassion Fatigue | Empathic Resilience |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Emotional exhaustion from prolonged exposure to others' suffering | Ability to maintain emotional strength while empathizing |
| Symptoms | Burnout, detachment, reduced empathy, irritability | Emotional balance, sustained compassion, positive coping |
| Impact | Decreased work performance, mental health decline | Improved emotional well-being, effective support delivery |
| Causes | Chronic stress, high emotional demands, lack of support | Self-care, mindfulness, strong support networks |
| Prevention | Regular breaks, professional counseling, boundary setting | Resilience training, emotional awareness, adaptive strategies |
Understanding Compassion Fatigue and Empathic Resilience
Compassion fatigue emerges from prolonged exposure to others' suffering, leading to emotional exhaustion, decreased empathy, and burnout, especially among caregivers and healthcare professionals. Empathic resilience involves cultivating emotional boundaries and self-care strategies that enable individuals to maintain compassion without becoming overwhelmed by distress. Recognizing the signs of compassion fatigue and actively building empathic resilience are essential for sustaining effective, compassionate engagement in emotionally demanding roles.
Key Differences Between Compassion Fatigue and Empathic Resilience
Compassion fatigue results from prolonged exposure to others' suffering, leading to emotional exhaustion and reduced capacity for empathy, while empathic resilience enables individuals to maintain emotional strength and sensitivity without becoming overwhelmed. Key differences include how compassion fatigue diminishes empathetic engagement and contributes to burnout, whereas empathic resilience promotes recovery and sustained compassionate care. Understanding these contrasts helps professionals implement strategies to foster resilience and prevent emotional depletion.
Causes and Triggers of Compassion Fatigue
Compassion fatigue arises primarily from prolonged exposure to others' trauma and chronic emotional stress, often seen in healthcare providers, social workers, and first responders. Key triggers include continuous caregiving without adequate rest, emotional boundary erosion, and secondary traumatic stress from witnessing suffering. Empathic resilience develops through self-care strategies, supportive environments, and maintaining emotional detachment to prevent burnout and sustain compassionate engagement.
Building Blocks of Empathic Resilience
Empathic resilience is built on key components such as self-awareness, emotional regulation, and boundary setting, which help individuals maintain emotional balance while engaging deeply with others' suffering. Unlike compassion fatigue, which depletes emotional resources, empathic resilience fosters sustainable caring through practices like mindfulness, social support, and purposeful self-care. Developing these building blocks enhances one's capacity to stay connected without becoming overwhelmed by the emotional demands of caregiving or helping professions.
Signs and Symptoms: Compassion Fatigue vs Empathic Resilience
Compassion fatigue manifests through persistent emotional exhaustion, reduced empathy, and feelings of helplessness, often leading to burnout and decreased professional efficacy. Empathic resilience, on the other hand, is characterized by the capacity to maintain emotional balance, recover swiftly from stress, and sustain a compassionate engagement without becoming overwhelmed. Recognizing signs like chronic fatigue and detachment can help differentiate compassion fatigue from empathic resilience, which promotes sustained well-being and effective caregiving.
Psychological and Emotional Impact on Relationships
Compassion fatigue often leads to emotional exhaustion and diminished capacity for empathy, resulting in strained personal and professional relationships due to decreased emotional availability and increased irritability. In contrast, empathic resilience enhances psychological well-being by fostering self-awareness and emotional regulation, which strengthens interpersonal connections and promotes healthier communication. Understanding the balance between these states is crucial for maintaining supportive relationships and preventing burnout in caregiving roles.
Coping Strategies for Compassion Fatigue
Coping strategies for compassion fatigue include establishing strong boundaries, practicing regular self-care activities like mindfulness and physical exercise, and seeking professional support such as counseling or peer support groups. Developing empathic resilience involves cultivating emotional awareness, engaging in reflective practices, and balancing empathy with self-preservation to maintain mental well-being. Implementing these strategies reduces burnout risk and sustains the capacity for compassionate caregiving in high-stress environments.
Nurturing Empathic Resilience in Daily Life
Nurturing empathic resilience involves setting clear emotional boundaries and practicing self-care to prevent compassion fatigue, which depletes an individual's ability to connect empathetically. Techniques such as mindfulness meditation, regular debriefing sessions, and engaging in restorative activities enhance emotional regulation and sustain empathy over time. Building a supportive community emphasizes shared experiences and mutual encouragement, strengthening one's capacity to maintain compassion without burnout.
Prevention: Shifting from Compassion Fatigue to Empathic Resilience
Preventing compassion fatigue requires intentional strategies that foster empathic resilience through self-care, boundary-setting, and mindfulness practices. Empathic resilience builds emotional strength by recognizing personal limits while maintaining deep connection to others' experiences. Integrating regular reflection and support systems enhances the capacity to sustain empathy without burnout.
The Role of Self-Care in Sustaining Empathy
Compassion fatigue occurs when continuous exposure to others' suffering depletes emotional resources, leading to burnout and reduced empathy. Empathic resilience is cultivated through consistent self-care practices such as mindfulness, regular rest, and boundary-setting, which replenish emotional energy and sustain empathetic engagement. Prioritizing self-care enables caregivers to maintain compassion without experiencing emotional exhaustion, reinforcing long-term empathetic strength.
compassion fatigue vs empathic resilience Infographic
 relationdif.com
relationdif.com