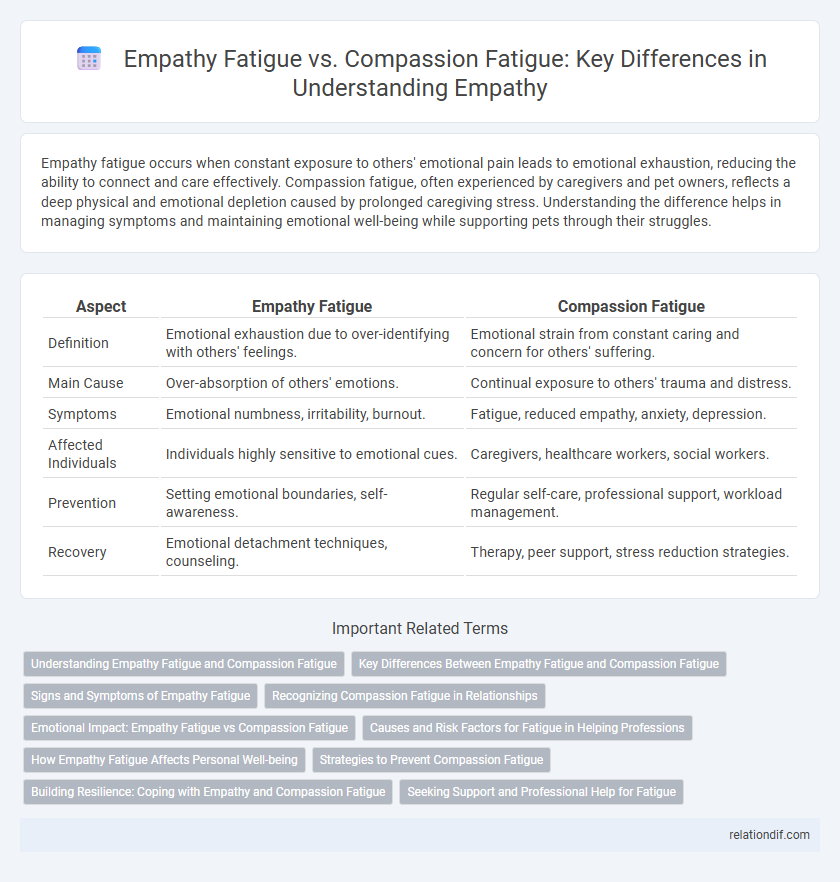
Empathy fatigue occurs when constant exposure to others' emotional pain leads to emotional exhaustion, reducing the ability to connect and care effectively. Compassion fatigue, often experienced by caregivers and pet owners, reflects a deep physical and emotional depletion caused by prolonged caregiving stress. Understanding the difference helps in managing symptoms and maintaining emotional well-being while supporting pets through their struggles.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Empathy Fatigue | Compassion Fatigue |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Emotional exhaustion due to over-identifying with others' feelings. | Emotional strain from constant caring and concern for others' suffering. |
| Main Cause | Over-absorption of others' emotions. | Continual exposure to others' trauma and distress. |
| Symptoms | Emotional numbness, irritability, burnout. | Fatigue, reduced empathy, anxiety, depression. |
| Affected Individuals | Individuals highly sensitive to emotional cues. | Caregivers, healthcare workers, social workers. |
| Prevention | Setting emotional boundaries, self-awareness. | Regular self-care, professional support, workload management. |
| Recovery | Emotional detachment techniques, counseling. | Therapy, peer support, stress reduction strategies. |
Understanding Empathy Fatigue and Compassion Fatigue
Empathy fatigue occurs when prolonged exposure to others' emotional distress leads to emotional exhaustion, reducing the ability to empathize effectively. Compassion fatigue, often seen in caregivers and healthcare professionals, involves a deeper sense of emotional depletion and burnout caused by continuous feelings of helplessness in alleviating others' suffering. Recognizing the distinctions between empathy fatigue and compassion fatigue is crucial for implementing targeted self-care strategies and maintaining emotional resilience in emotionally demanding roles.
Key Differences Between Empathy Fatigue and Compassion Fatigue
Empathy fatigue results from excessive emotional involvement in others' distress, leading to feeling overwhelmed and emotionally drained, while compassion fatigue stems from prolonged exposure to suffering, causing a reduced capacity to care and emotional numbness. Empathy fatigue primarily affects emotional resonance and sensitivity, whereas compassion fatigue impacts professional efficacy and emotional resilience. Distinguishing these conditions is crucial for implementing targeted strategies to maintain mental health in caregiving professions.
Signs and Symptoms of Empathy Fatigue
Empathy fatigue manifests through emotional exhaustion, decreased ability to feel compassion, and a sense of numbness towards others' suffering. Individuals may experience irritability, withdrawal, and difficulty concentrating, alongside physical symptoms such as headaches and sleep disturbances. Recognizing these signs is critical for timely intervention and maintaining emotional well-being in caregiving or high-empathy professions.
Recognizing Compassion Fatigue in Relationships
Recognizing compassion fatigue in relationships involves identifying emotional exhaustion, reduced empathy, and increased irritability stemming from prolonged caring for others' suffering. This fatigue often leads to withdrawal and decreased ability to provide support, contrasting with empathy fatigue, which primarily refers to the overload of feeling others' emotions. Effective strategies for detection include monitoring changes in patience levels, communication breakdowns, and persistent feelings of being overwhelmed or detached.
Emotional Impact: Empathy Fatigue vs Compassion Fatigue
Empathy fatigue arises from prolonged exposure to others' emotions, causing emotional exhaustion due to constant emotional engagement. Compassion fatigue results from the ongoing stress of caregiving roles, leading to a diminished capacity to feel sympathy or compassion for others. Both conditions affect emotional resilience, but empathy fatigue primarily stems from emotional overload, whereas compassion fatigue involves burnout linked to sustained caregiving stressors.
Causes and Risk Factors for Fatigue in Helping Professions
Empathy fatigue arises from prolonged exposure to others' emotional distress, often driven by continuous emotional engagement and lack of adequate recovery time. Compassion fatigue results from repeated compassion-related stress, frequently linked to secondary traumatic stress and burnout in helping professionals. Risk factors include high caseloads, insufficient social support, personal trauma histories, and organizational pressures demanding constant emotional labor.
How Empathy Fatigue Affects Personal Well-being
Empathy fatigue leads to emotional exhaustion and decreased ability to connect with others, significantly impacting personal well-being by fostering stress and burnout. Unlike compassion fatigue, which specifically results from exposure to others' suffering, empathy fatigue arises from prolonged emotional involvement and overload. This condition often causes withdrawal, reduced emotional resilience, and impaired mental health, emphasizing the need for self-care and boundary-setting in empathetic interactions.
Strategies to Prevent Compassion Fatigue
Implementing self-care routines, setting clear professional boundaries, and seeking peer support are essential strategies to prevent compassion fatigue. Regular mindfulness practices and professional counseling can help maintain emotional resilience in caregivers. Organizations should promote a culture of open communication and provide resources that support mental well-being to reduce the risk of burnout.
Building Resilience: Coping with Empathy and Compassion Fatigue
Building resilience to manage empathy fatigue and compassion fatigue involves developing effective coping strategies such as mindfulness, self-care routines, and boundary setting to prevent emotional exhaustion. Recognizing symptoms like chronic stress, irritability, and emotional numbness early allows individuals to implement restorative practices that replenish mental and emotional resources. Incorporating professional support, peer consultation, and regular debriefing promotes sustained empathy without compromising personal well-being.
Seeking Support and Professional Help for Fatigue
Empathy fatigue and compassion fatigue both demand proactive seeking of support and professional help to maintain emotional well-being. Engaging with mental health professionals, such as therapists specializing in trauma or caregiver stress, offers tailored strategies to manage exhaustion and prevent burnout. Peer support groups also provide valuable shared experiences that reinforce resilience and coping mechanisms in emotionally demanding roles.
Empathy fatigue vs compassion fatigue Infographic
 relationdif.com
relationdif.com