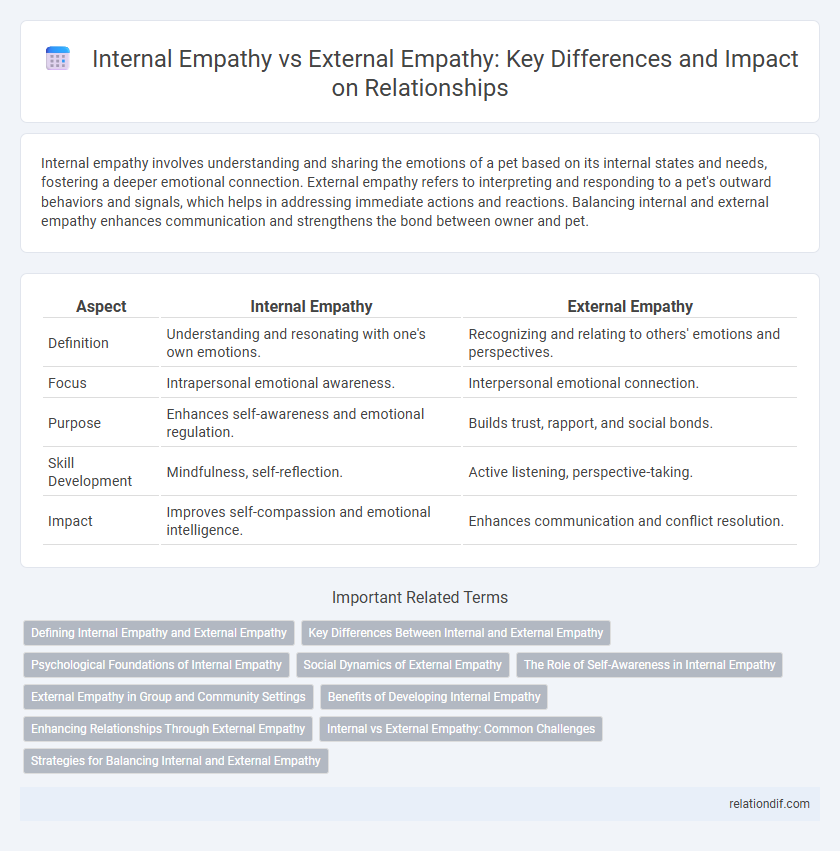
Internal empathy involves understanding and sharing the emotions of a pet based on its internal states and needs, fostering a deeper emotional connection. External empathy refers to interpreting and responding to a pet's outward behaviors and signals, which helps in addressing immediate actions and reactions. Balancing internal and external empathy enhances communication and strengthens the bond between owner and pet.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Internal Empathy | External Empathy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Understanding and resonating with one's own emotions. | Recognizing and relating to others' emotions and perspectives. |
| Focus | Intrapersonal emotional awareness. | Interpersonal emotional connection. |
| Purpose | Enhances self-awareness and emotional regulation. | Builds trust, rapport, and social bonds. |
| Skill Development | Mindfulness, self-reflection. | Active listening, perspective-taking. |
| Impact | Improves self-compassion and emotional intelligence. | Enhances communication and conflict resolution. |
Defining Internal Empathy and External Empathy
Internal empathy refers to the ability to understand and share one's own emotions and experiences, fostering self-awareness and emotional regulation. External empathy involves recognizing and responding to the emotions and perspectives of others, facilitating social connection and effective communication. Both internal and external empathy are essential components of emotional intelligence and interpersonal relationships.
Key Differences Between Internal and External Empathy
Internal empathy involves recognizing and understanding one's own emotions, enhancing self-awareness and emotional regulation, while external empathy focuses on perceiving and resonating with the emotions of others to build social connections. Key differences include the direction of emotional focus--internal empathy is inward, promoting self-compassion and personal growth, whereas external empathy is outward, facilitating interpersonal relationships and social support. Neural pathways also differ, with internal empathy engaging brain areas related to self-reflection, and external empathy activating regions linked to social cognition and perspective-taking.
Psychological Foundations of Internal Empathy
Internal empathy is rooted in the psychological capacity to recognize and understand one's own emotions and mental states, which relies heavily on self-awareness and introspection. This form of empathy is grounded in neural mechanisms involving the medial prefrontal cortex and anterior insula, areas associated with self-referential processing and emotional regulation. Mastery of internal empathy enhances emotional resilience and promotes a deeper connection to personal experiences, which subsequently informs more authentic social interactions.
Social Dynamics of External Empathy
External empathy drives social dynamics by enabling individuals to accurately perceive and respond to others' emotions in group settings, fostering trust and cooperation. It involves active listening, perspective-taking, and emotional regulation, which enhance interpersonal communication and collective problem-solving. This form of empathy strengthens social bonds, reduces conflicts, and promotes inclusive environments critical for community resilience and organizational success.
The Role of Self-Awareness in Internal Empathy
Self-awareness plays a crucial role in internal empathy by enabling individuals to recognize and understand their own emotions, which forms the foundation for accurately interpreting others' feelings. This introspective capacity enhances emotional regulation and deepens empathy by fostering a genuine connection with one's internal experiences before projecting understanding externally. Developing self-awareness through mindfulness practices and reflective exercises significantly strengthens internal empathy and improves interpersonal relationships.
External Empathy in Group and Community Settings
External empathy in group and community settings involves understanding and responding to the emotions and perspectives of others beyond one's immediate circle. It facilitates social cohesion by promoting active listening, validation of diverse experiences, and collective problem-solving. This form of empathy strengthens community bonds and enhances cooperative efforts towards shared goals.
Benefits of Developing Internal Empathy
Developing internal empathy enhances self-awareness by fostering a deeper understanding of one's emotions and motivations, which leads to improved emotional regulation and mental resilience. It enables individuals to identify personal triggers and biases, promoting healthier decision-making and reducing stress-related behaviors. Strengthening internal empathy ultimately cultivates a foundation for authentic self-compassion, driving better relationships and overall psychological well-being.
Enhancing Relationships Through External Empathy
External empathy enhances relationships by actively tuning into others' feelings and perspectives, creating deeper connections and trust. It involves observing nonverbal cues, asking thoughtful questions, and validating emotions to foster understanding beyond one's own experience. Practicing external empathy cultivates emotional intelligence, improves communication, and strengthens social bonds in personal and professional environments.
Internal vs External Empathy: Common Challenges
Internal empathy involves understanding and managing one's own emotions, frequently hindered by self-awareness gaps and emotional regulation difficulties. External empathy requires accurately perceiving and responding to others' emotions, often challenged by biases, misinterpretations, and lack of active listening skills. Balancing internal and external empathy is crucial for effective emotional intelligence, yet barriers like personal stress and cultural differences commonly disrupt this equilibrium.
Strategies for Balancing Internal and External Empathy
Balancing internal and external empathy involves cultivating self-awareness to understand one's own emotions while actively listening to others' experiences. Techniques such as mindfulness practices help regulate internal empathy by fostering emotional clarity, whereas perspective-taking exercises enhance external empathy by appreciating different viewpoints. Integrating journaling for self-reflection with empathetic communication skills training creates a dynamic approach that supports both self-compassion and authentic connection with others.
internal empathy vs external empathy Infographic
 relationdif.com
relationdif.com