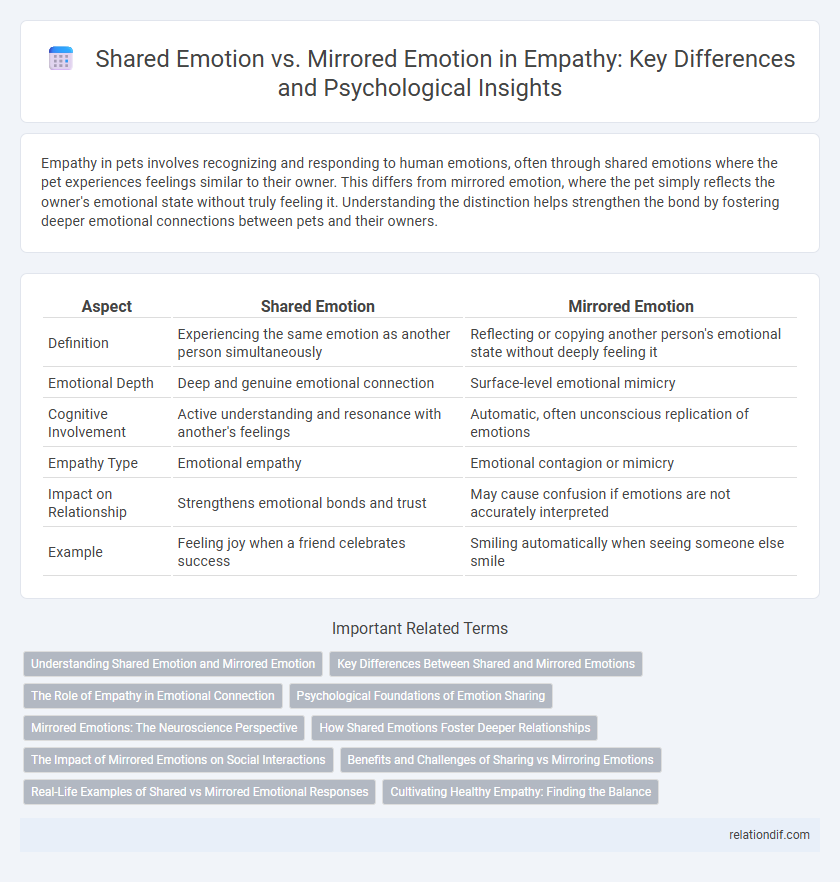
Empathy in pets involves recognizing and responding to human emotions, often through shared emotions where the pet experiences feelings similar to their owner. This differs from mirrored emotion, where the pet simply reflects the owner's emotional state without truly feeling it. Understanding the distinction helps strengthen the bond by fostering deeper emotional connections between pets and their owners.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Shared Emotion | Mirrored Emotion |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Experiencing the same emotion as another person simultaneously | Reflecting or copying another person's emotional state without deeply feeling it |
| Emotional Depth | Deep and genuine emotional connection | Surface-level emotional mimicry |
| Cognitive Involvement | Active understanding and resonance with another's feelings | Automatic, often unconscious replication of emotions |
| Empathy Type | Emotional empathy | Emotional contagion or mimicry |
| Impact on Relationship | Strengthens emotional bonds and trust | May cause confusion if emotions are not accurately interpreted |
| Example | Feeling joy when a friend celebrates success | Smiling automatically when seeing someone else smile |
Understanding Shared Emotion and Mirrored Emotion
Shared emotion involves experiencing feelings that align with another person's emotional state through genuine connection and mutual understanding. Mirrored emotion occurs when an individual unconsciously reflects another's emotional expression without fully internalizing or comprehending the underlying experience. Understanding the distinction between shared and mirrored emotions enhances emotional intelligence and strengthens interpersonal relationships by promoting authentic empathy.
Key Differences Between Shared and Mirrored Emotions
Shared emotions involve a collective experience where individuals simultaneously feel the same emotion, fostering a sense of unity and mutual understanding. Mirrored emotions occur when one person unconsciously replicates another's emotional expressions, often through neural mechanisms like mirror neurons, without necessarily sharing the subjective feeling. The key difference lies in shared emotions requiring concurrent emotional states among people, while mirrored emotions reflect automatic emotional reflections without identical internal experiences.
The Role of Empathy in Emotional Connection
Empathy facilitates emotional connection by enabling individuals to experience shared emotions, where one person genuinely feels another's emotional state, fostering deep understanding and trust. Mirrored emotions, in contrast, involve reflecting observable feelings without internalizing them, serving as a social cue rather than true emotional resonance. This distinction highlights empathy's crucial role in forming authentic bonds through mutual emotional experience rather than mere imitation.
Psychological Foundations of Emotion Sharing
Shared emotion involves the interpersonal experience where individuals genuinely feel the same emotion simultaneously, rooted in neural mechanisms such as mirror neurons facilitating emotional resonance. Mirrored emotion refers to the automatic mimicry and internal simulation of another's emotional state without fully adopting the subjective feeling, often linked to affective empathy processes. Psychological foundations of emotion sharing encompass cognitive appraisal, emotional contagion, and neurobiological substrates including the insula and anterior cingulate cortex that enable synchronized emotional experiences.
Mirrored Emotions: The Neuroscience Perspective
Mirrored emotions arise from the brain's mirror neuron system, which enables individuals to subconsciously replicate and experience others' emotional states. Neuroscientific studies reveal that areas such as the anterior insula and anterior cingulate cortex become activated both during firsthand emotional experiences and when observing others in similar states. This neural mirroring mechanism facilitates empathy by allowing for automatic emotional resonance without necessarily involving conscious emotional sharing.
How Shared Emotions Foster Deeper Relationships
Shared emotions create a mutual understanding by allowing individuals to experience feelings collectively, which strengthens emotional bonds and trust. Unlike mirrored emotions that simply reflect another's feelings, shared emotions involve an active emotional exchange, promoting deeper connection and empathy. This dynamic fosters resilience in relationships by enhancing communication and emotional support.
The Impact of Mirrored Emotions on Social Interactions
Mirrored emotions intensify social interactions by creating a dynamic feedback loop that enhances emotional connection and understanding between individuals. This phenomenon activates neural mirroring systems, fostering empathy and strengthening group cohesion through synchronized emotional experiences. The amplification of shared feelings through mirrored emotions can improve communication effectiveness and promote prosocial behavior in various social contexts.
Benefits and Challenges of Sharing vs Mirroring Emotions
Shared emotion fosters deeper connections by allowing individuals to experience feelings collectively, enhancing mutual understanding and emotional support. Mirrored emotion involves reflecting another's feelings, which can validate their experience but risks emotional fatigue or misunderstanding if boundaries are unclear. Balancing sharing and mirroring emotions promotes empathy while maintaining emotional well-being and clear communication.
Real-Life Examples of Shared vs Mirrored Emotional Responses
Shared emotions involve a mutual, genuine experience of feelings, such as consoling a friend grieving a loss where both individuals feel sadness. Mirrored emotions occur when one person unconsciously imitates another's emotional expression without deeply experiencing the emotion, like smiling reflexively when someone else smiles. Real-life examples include healthcare providers who share patients' pain to offer genuine support versus coworkers who mirror excitement during a team celebration to maintain social harmony.
Cultivating Healthy Empathy: Finding the Balance
Cultivating healthy empathy requires distinguishing between shared emotion, where individuals genuinely experience the emotions of others, and mirrored emotion, which involves reflecting feelings without internalizing them. Balancing this differentiation helps maintain emotional boundaries, reducing the risk of burnout and emotional overwhelm. Effective empathy supports compassionate connection while preserving individual emotional well-being.
Shared emotion vs mirrored emotion Infographic
 relationdif.com
relationdif.com