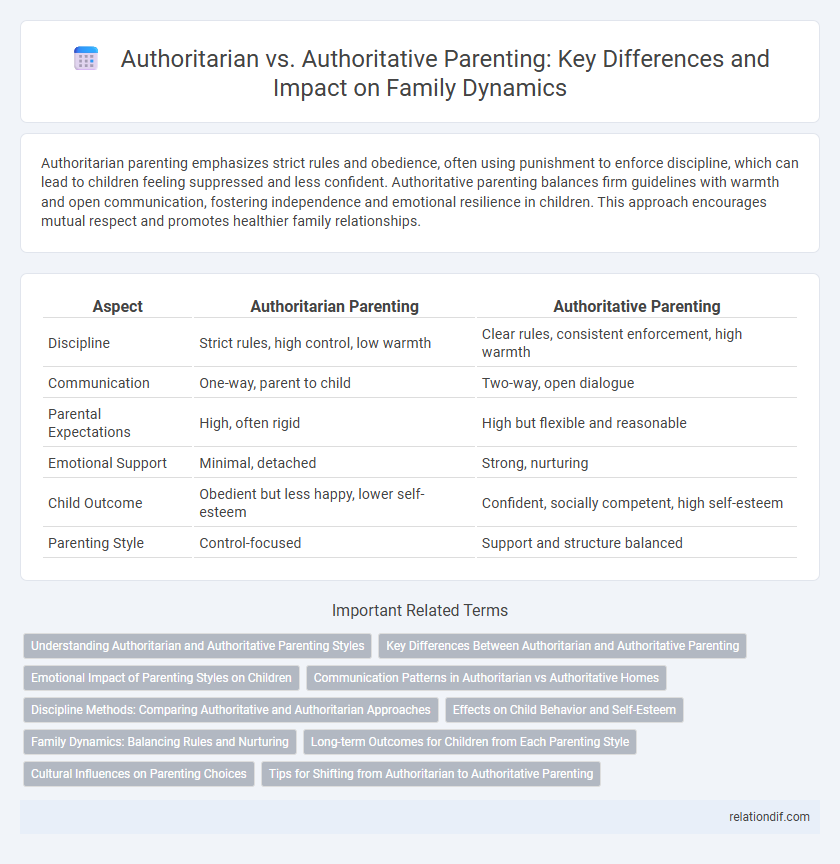
Authoritarian parenting emphasizes strict rules and obedience, often using punishment to enforce discipline, which can lead to children feeling suppressed and less confident. Authoritative parenting balances firm guidelines with warmth and open communication, fostering independence and emotional resilience in children. This approach encourages mutual respect and promotes healthier family relationships.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Authoritarian Parenting | Authoritative Parenting |
|---|---|---|
| Discipline | Strict rules, high control, low warmth | Clear rules, consistent enforcement, high warmth |
| Communication | One-way, parent to child | Two-way, open dialogue |
| Parental Expectations | High, often rigid | High but flexible and reasonable |
| Emotional Support | Minimal, detached | Strong, nurturing |
| Child Outcome | Obedient but less happy, lower self-esteem | Confident, socially competent, high self-esteem |
| Parenting Style | Control-focused | Support and structure balanced |
Understanding Authoritarian and Authoritative Parenting Styles
Authoritarian parenting is characterized by high demands, strict rules, and little warmth, often leading to obedience but limited emotional connection. In contrast, authoritative parenting balances firm expectations with nurturing support, fostering independence and strong communication. Research shows that children raised with authoritative parenting tend to have better social skills and higher self-esteem compared to those raised with authoritarian methods.
Key Differences Between Authoritarian and Authoritative Parenting
Authoritarian parenting emphasizes strict rules, obedience, and high demands with low responsiveness, often leading to obedience without open dialogue. Authoritative parenting combines high expectations with warmth and communication, fostering independence and emotional intelligence. Key differences include the level of parental responsiveness and the encouragement of child autonomy, with authoritative parents promoting supportive guidance rather than rigid control.
Emotional Impact of Parenting Styles on Children
Authoritarian parenting often leads to increased anxiety and lower self-esteem in children due to its strict, controlling nature. Authoritative parenting, characterized by warmth and structure, fosters emotional resilience and higher social competence. Research highlights that children raised with authoritative parents typically exhibit better emotional regulation and stronger mental health outcomes.
Communication Patterns in Authoritarian vs Authoritative Homes
In authoritarian homes, communication patterns are typically one-way, with parents issuing strict commands and expecting obedience without explanation, which can limit open dialogue and emotional expression. Authoritative homes foster two-way communication where parents set clear expectations but encourage children to express their thoughts and feelings, promoting mutual respect and understanding. This supportive communication style in authoritative families contributes to healthier emotional development and stronger parent-child relationships.
Discipline Methods: Comparing Authoritative and Authoritarian Approaches
Authoritative parenting employs positive discipline methods emphasizing clear communication, consistent boundaries, and reasoning to promote self-regulation and emotional growth in children. Authoritarian parenting relies on strict rules, punishment, and obedience without explanation, which can lead to compliance but often reduces emotional warmth and autonomy. Research shows authoritative discipline fosters better social skills, academic success, and psychological well-being compared to authoritarian strategies.
Effects on Child Behavior and Self-Esteem
Authoritarian parenting, characterized by strict rules and high expectations, often leads to children exhibiting lower self-esteem and increased behavioral issues such as aggression or withdrawal. In contrast, authoritative parenting, which balances firmness with warmth and open communication, fosters higher self-esteem and promotes positive social behavior and emotional regulation in children. Research indicates that children raised with authoritative parenting develop better problem-solving skills and resilience compared to those from authoritarian households.
Family Dynamics: Balancing Rules and Nurturing
Authoritarian parenting enforces strict rules and high expectations with limited emotional warmth, often leading to obedience but potentially causing resentment or low self-esteem in children. Authoritative parenting balances firm boundaries with responsive nurturing, promoting open communication, emotional support, and independence within the family. This balanced approach fosters healthier family dynamics and enhances children's social, emotional, and cognitive development.
Long-term Outcomes for Children from Each Parenting Style
Authoritarian parenting, characterized by strict rules and high demands, often leads to children exhibiting lower self-esteem and higher levels of anxiety, which can hinder social skills and academic performance in the long term. In contrast, authoritative parenting, which balances clear expectations with emotional support, is associated with children developing strong social competence, emotional regulation, and higher academic achievement. Research consistently shows that the authoritative style fosters resilience and positive psychological outcomes that benefit children's overall well-being into adulthood.
Cultural Influences on Parenting Choices
Cultural influences significantly shape parenting styles, with authoritarian parenting often prevalent in collectivist societies that emphasize obedience and respect for authority, while authoritative parenting is more common in individualistic cultures that value open communication and autonomy. Research shows that families in East Asian cultures tend to adopt authoritarian approaches rooted in Confucian values, whereas Western societies, influenced by democratic ideals, favor authoritative methods promoting reasoning and emotional support. Understanding these cultural contexts is essential for interpreting parenting behaviors and their impact on child development across diverse populations.
Tips for Shifting from Authoritarian to Authoritative Parenting
Shifting from authoritarian to authoritative parenting involves embracing empathy, open communication, and consistent but flexible boundaries to foster a nurturing family environment. Parents should practice active listening, validate children's feelings, and encourage autonomy while maintaining clear expectations and consequences. Implementing these strategies promotes mutual respect and emotional growth, leading to healthier parent-child relationships.
authoritarian parenting vs authoritative parenting Infographic
 relationdif.com
relationdif.com