Biological parents provide genetic heritage and early bonding essential for a child's identity development, while adoptive parents offer nurturing, stability, and unconditional love that shape emotional well-being. Both types of parents play crucial roles in fostering a secure, supportive environment where children can thrive regardless of biological ties. The strength of family lies in commitment and care rather than genetic connection alone.
Table of Comparison
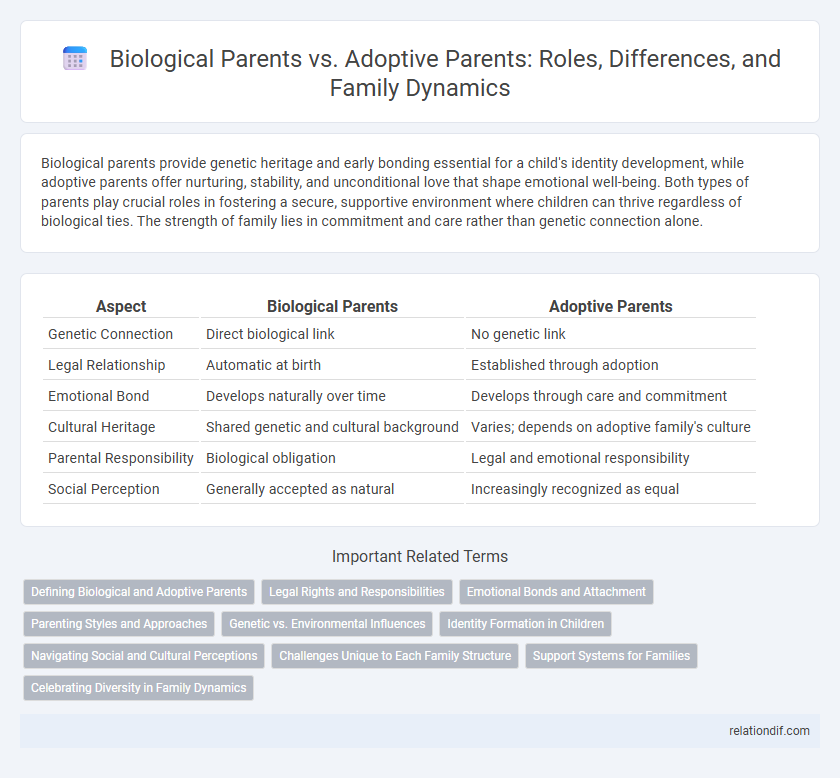
| Aspect | Biological Parents | Adoptive Parents |
|---|---|---|
| Genetic Connection | Direct biological link | No genetic link |
| Legal Relationship | Automatic at birth | Established through adoption |
| Emotional Bond | Develops naturally over time | Develops through care and commitment |
| Cultural Heritage | Shared genetic and cultural background | Varies; depends on adoptive family's culture |
| Parental Responsibility | Biological obligation | Legal and emotional responsibility |
| Social Perception | Generally accepted as natural | Increasingly recognized as equal |
Defining Biological and Adoptive Parents
Biological parents are individuals who contribute genetically to a child through conception, establishing a biological connection that influences the child's hereditary traits. Adoptive parents legally assume parental responsibilities and rights, providing emotional support, care, and upbringing without a genetic link. Both biological and adoptive parents play crucial roles in a child's development, shaping identity, values, and familial bonds.
Legal Rights and Responsibilities
Biological parents retain inherent legal rights and responsibilities including custody, child support, and decision-making unless legally terminated. Adoptive parents assume all parental rights and obligations upon finalization of adoption, gaining full authority over the child's welfare and legal matters. Courts prioritize the child's best interests when addressing conflicts between biological and adoptive parental rights.
Emotional Bonds and Attachment
Emotional bonds and attachment between children and their biological parents are often rooted in early physical and genetic connections, fostering a deep sense of identity and security. Adoptive parents, through consistent care, affection, and support, can establish equally strong and resilient attachments that fulfill the child's emotional needs effectively. Research in developmental psychology highlights that the quality of caregiving and emotional responsiveness are the primary determinants of secure attachment, regardless of biological relation.
Parenting Styles and Approaches
Biological parents often rely on instinctual and genetically influenced parenting styles, shaping their child's development through inherited behaviors and emotional bonds. Adoptive parents typically adopt more intentional and flexible approaches, emphasizing communication, nurture, and building trust to create strong family connections. Both parenting styles prioritize the child's emotional well-being, cognitive growth, and social skills, adapting strategies to meet individual needs.
Genetic vs. Environmental Influences
Biological parents contribute genetic material that shapes a child's physical traits, predispositions, and potential health risks, embedding hereditary influences into development. Adoptive parents provide the environmental framework--nurture, education, values, and social support--that profoundly affects emotional wellbeing and personality growth. Understanding the interplay of genetic inheritance and environmental factors helps clarify complex identity formation within family dynamics.
Identity Formation in Children
Biological parents contribute genetic heritage that shapes a child's innate traits and predispositions, influencing early identity development. Adoptive parents provide intentional socialization, emotional support, and environmental stability, which are crucial for the child's sense of belonging and self-concept. Both biological and adoptive parental roles interact dynamically to form a child's integrated identity through nature and nurture factors.
Navigating Social and Cultural Perceptions
Navigating social and cultural perceptions of family often involves understanding the unique roles of biological and adoptive parents in a child's life. Biological parents are frequently associated with genetic ties and heritage, while adoptive parents emphasize chosen commitment and nurturing. Society's evolving acceptance highlights the importance of love and support over biological connection in defining family bonds.
Challenges Unique to Each Family Structure
Biological parents often face challenges related to managing genetic predispositions and navigating biological health histories, while adoptive parents encounter unique legal complexities and the emotional task of building attachment without shared genetics. Both family structures require addressing identity development and addressing potential societal biases that affect their children. Effective communication and support networks are essential for overcoming these distinct obstacles.
Support Systems for Families
Biological parents often provide genetic connections and a deep understanding of inherited health conditions, which can be crucial for medical support within families. Adoptive parents create strong emotional bonds and nurture resilience by offering stable environments and unconditional love, serving as vital support systems. Both biological and adoptive parents contribute uniquely to family support networks, promoting child development and well-being through diverse nurturing approaches.
Celebrating Diversity in Family Dynamics
Biological parents and adoptive parents both play crucial roles in nurturing and supporting children, each offering unique perspectives and strengths that enrich family life. Celebrating diversity in family dynamics highlights the importance of love, commitment, and stability over genetic connections, fostering inclusive environments where children thrive emotionally and socially. Recognizing the value of varied family structures strengthens community bonds and promotes acceptance across cultures and societies.
biological parents vs adoptive parents Infographic
 relationdif.com
relationdif.com