Birth families provide biological connections and genetic heritage, shaping early identity and medical history. Adoptive families offer nurturing, stability, and a chosen environment that fosters emotional growth and belonging. Both family types contribute uniquely to a person's sense of self and support system.
Table of Comparison
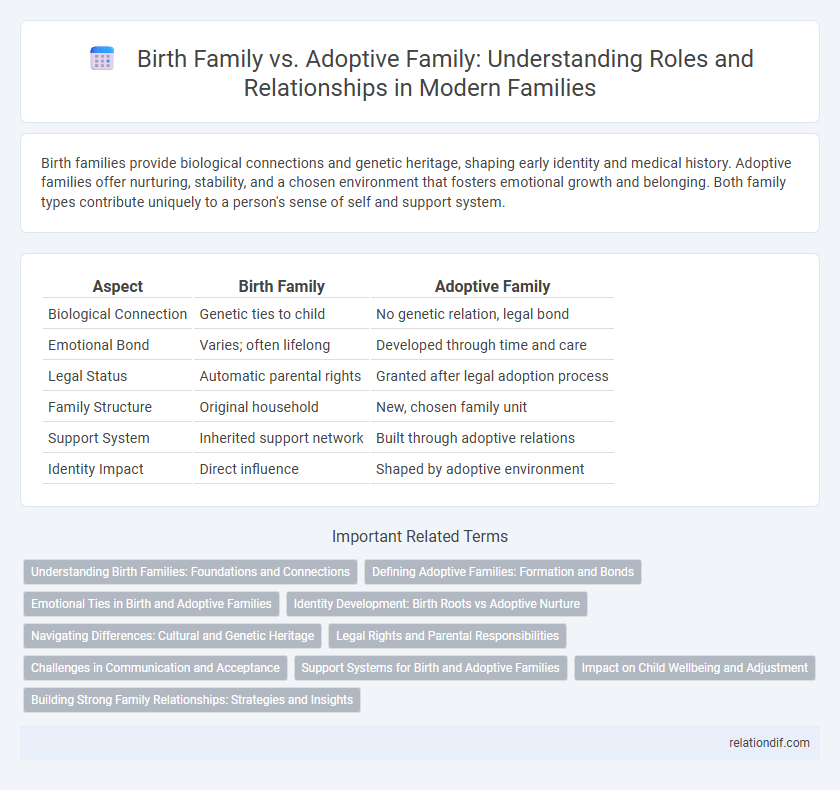
| Aspect | Birth Family | Adoptive Family |
|---|---|---|
| Biological Connection | Genetic ties to child | No genetic relation, legal bond |
| Emotional Bond | Varies; often lifelong | Developed through time and care |
| Legal Status | Automatic parental rights | Granted after legal adoption process |
| Family Structure | Original household | New, chosen family unit |
| Support System | Inherited support network | Built through adoptive relations |
| Identity Impact | Direct influence | Shaped by adoptive environment |
Understanding Birth Families: Foundations and Connections
Understanding birth families involves exploring genetic origins, cultural heritage, and early childhood experiences that shape an individual's identity. Birth families provide foundational biological ties and emotional bonds that influence attachment styles and personal development. Recognizing these connections helps adoptees navigate complexities in identity formation and fosters a comprehensive sense of self within both birth and adoptive family contexts.
Defining Adoptive Families: Formation and Bonds
Adoptive families are formed through legal processes that create permanent parent-child relationships distinct from biological ties. These families establish strong emotional bonds through shared experiences, caregiving, and commitment, often navigating challenges unique to adoption. The formation process emphasizes intentionality and legal recognition, fostering a sense of belonging and identity within the adoptive family unit.
Emotional Ties in Birth and Adoptive Families
Emotional ties in birth families often stem from biological connections and shared early experiences, fostering a deep sense of identity and belonging. In adoptive families, emotional bonds develop through intentional caregiving, trust-building, and shared life moments, creating equally strong feelings of love and security. Both family types demonstrate that emotional attachment transcends genetics, emphasizing the importance of nurturing relationships.
Identity Development: Birth Roots vs Adoptive Nurture
Identity development often involves navigating the balance between birth roots and adoptive nurture, as individuals integrate genetic heritage with the values and experiences provided by their adoptive family. Genomic influences from the birth family contribute to innate traits and predispositions, while the adoptive environment shapes social skills, emotional support, and cultural identity. Psychological studies emphasize that a cohesive sense of self emerges when both biological origins and adoptive relationships are acknowledged and reconciled.
Navigating Differences: Cultural and Genetic Heritage
Navigating the differences between birth family and adoptive family involves understanding the interplay of cultural and genetic heritage that shapes identity. Birth families provide biological roots and genetic traits, while adoptive families contribute cultural values, traditions, and emotional support critical for personal development. Embracing both heritages fosters a richer sense of belonging, aiding adoptees in reconciling diverse backgrounds.
Legal Rights and Parental Responsibilities
Legal rights and parental responsibilities in birth families typically include biological ties granting automatic custody and decision-making authority, while adoptive families receive these rights through court-approved adoption processes, conferring full parental status. Birth parents maintain inherent rights including visitation and consent under family laws unless legally terminated, whereas adoptive parents hold exclusive custody and obligations recognized by statutes post-adoption. Understanding jurisdiction-specific regulations is critical, as they define the scope of authority, guardianship, inheritance rights, and child welfare responsibilities between birth and adoptive families.
Challenges in Communication and Acceptance
Challenges in communication between birth families and adoptive families often stem from differing expectations and emotional complexities surrounding identity and belonging. Misunderstandings and varying perspectives on the child's history can create barriers to open dialogue, impacting trust and emotional connection. Acceptance requires ongoing empathy and patience to navigate feelings of loyalty, loss, and attachment for all parties involved.
Support Systems for Birth and Adoptive Families
Support systems for birth and adoptive families play a crucial role in fostering emotional well-being and stability, with birth families often relying on extended relatives and community networks to navigate challenges. Adoptive families benefit from structured support groups, counseling services, and legal resources tailored to adoption-specific issues, enhancing parental confidence and child integration. Both family types increasingly utilize social services and peer networks to address identity, attachment, and developmental concerns, highlighting the importance of comprehensive support in diverse family dynamics.
Impact on Child Wellbeing and Adjustment
Birth family relationships often provide a child with a sense of genetic identity and cultural heritage that supports emotional stability, while adoptive families contribute structured parenting and a nurturing environment essential for social development. Research indicates that children in adoptive families may face unique adjustment challenges related to identity formation and attachment, yet positive family communication and strong support systems significantly enhance wellbeing. Consistent emotional support and secure attachments within both birth and adoptive families play a critical role in promoting resilience and healthy psychological adjustment in children.
Building Strong Family Relationships: Strategies and Insights
Building strong relationships between birth families and adoptive families requires open communication, empathy, and respect for each member's unique identity and history. Establishing consistent traditions and shared experiences fosters trust and emotional connection, creating a supportive environment where all individuals feel valued. Utilizing family counseling and support groups can further enhance understanding and collaboration, promoting long-term harmony and resilience within the blended family dynamic.
birth family vs adoptive family Infographic
 relationdif.com
relationdif.com