A blended family consists of members from previous relationships, creating a diverse household with unique challenges and opportunities for bonding. In contrast, a nuclear family typically includes two parents and their biological children, often reflecting traditional family dynamics. Understanding the differences helps support effective communication and emotional connection in both family types.
Table of Comparison
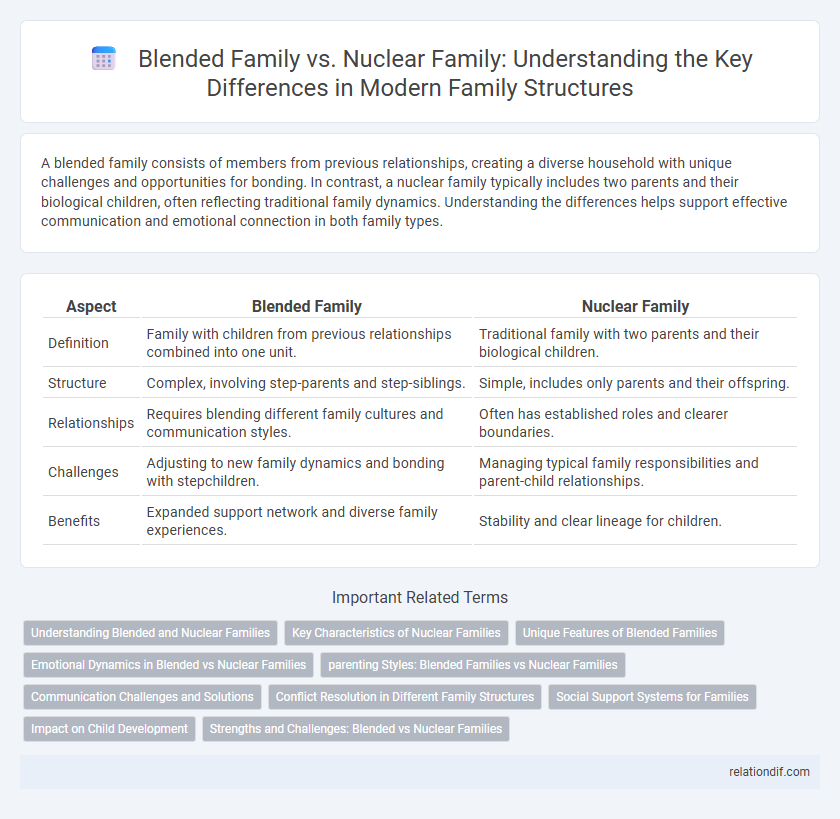
| Aspect | Blended Family | Nuclear Family |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Family with children from previous relationships combined into one unit. | Traditional family with two parents and their biological children. |
| Structure | Complex, involving step-parents and step-siblings. | Simple, includes only parents and their offspring. |
| Relationships | Requires blending different family cultures and communication styles. | Often has established roles and clearer boundaries. |
| Challenges | Adjusting to new family dynamics and bonding with stepchildren. | Managing typical family responsibilities and parent-child relationships. |
| Benefits | Expanded support network and diverse family experiences. | Stability and clear lineage for children. |
Understanding Blended and Nuclear Families
Blended families consist of partners and children from previous relationships, creating a dynamic of diverse relationships and shared responsibilities. Nuclear families typically include two parents and their biological or adopted children living under one roof with more traditional roles and clearer family boundaries. Understanding the unique challenges and strengths of blended versus nuclear families helps promote effective communication and emotional support within the household.
Key Characteristics of Nuclear Families
Nuclear families are characterized by a core unit consisting of two parents and their biological or adopted children living together in a single household. This family structure often emphasizes close-knit relationships, clear parental roles, and stability in daily routines. Compared to blended families, nuclear families typically experience fewer complexities related to household dynamics and legal family ties.
Unique Features of Blended Families
Blended families are characterized by the merging of two previously separate family units, often including step-parents, step-siblings, and half-siblings, creating a complex relational dynamic. Unique features include managing diverse family traditions, navigating co-parenting arrangements with non-custodial parents, and fostering relationships between step-relatives while balancing loyalty to biological family components. These families often require adaptive communication strategies and conflict resolution skills to maintain harmony and support individual family members' emotional needs.
Emotional Dynamics in Blended vs Nuclear Families
Blended families often experience complex emotional dynamics due to the integration of step-parents and step-siblings, which can lead to challenges in establishing trust and belonging compared to nuclear families. Nuclear families typically benefit from more stable emotional bonds, as relationships develop from birth without the need for adjustment to new family members. Emotional support patterns differ, with blended families requiring intentional communication strategies to navigate loyalty conflicts and rebuild family cohesion.
parenting Styles: Blended Families vs Nuclear Families
Parenting styles in blended families often require increased flexibility and communication to navigate relationships between stepparents and stepchildren, compared to nuclear families where roles tend to be more clearly defined and consistent. Blended families frequently adopt adaptive and collaborative approaches to establish authority and cohesion, while nuclear families typically follow more traditional, hierarchical parenting patterns. Effective co-parenting strategies in blended families emphasize negotiation and empathy to balance the needs of all family members.
Communication Challenges and Solutions
Blended families often face complex communication challenges due to differing parenting styles, loyalty conflicts, and the need to establish new family roles, whereas nuclear families generally have more straightforward communication patterns. Effective solutions include open dialogue practices, family meetings to address concerns, and professional counseling to develop mutual understanding and trust. Utilizing active listening and empathy strengthens bonds and helps blend diverse family dynamics into a cohesive unit.
Conflict Resolution in Different Family Structures
Blended families often face unique challenges in conflict resolution due to the presence of stepparents and stepsiblings, requiring adaptive communication strategies and flexibility. Nuclear families typically rely on established routines and direct parental authority, which can simplify the resolution process but may limit perspectives on conflict management. Understanding these structural differences enhances tailored approaches to fostering harmony and effective conflict resolution in diverse family environments.
Social Support Systems for Families
Blended families often benefit from diversified social support systems, as connections extend across multiple households, creating a broader network of emotional and practical assistance. Nuclear families typically rely on a more concentrated support system, primarily involving immediate family members and close friends, which can foster strong, focused bonds but may limit the range of perspectives available. Access to varied social networks in blended families enhances resilience and resource-sharing during family transitions and challenges.
Impact on Child Development
Blended families often provide children with diverse role models and greater adaptability skills, fostering emotional resilience and social flexibility. Nuclear families typically offer stability and consistent routines, which can enhance a child's sense of security and well-being. The impact on child development varies with family dynamics, communication quality, and parental involvement in each family structure.
Strengths and Challenges: Blended vs Nuclear Families
Blended families offer diverse support systems and opportunities for children to develop adaptability and resilience, yet they often face challenges related to complex relationships and co-parenting dynamics. Nuclear families typically benefit from stability and clear roles, providing a controlled environment conducive to consistent parenting, but may encounter limitations in social diversity and support networks. Understanding these distinct strengths and challenges helps tailor effective strategies for fostering healthy family dynamics.
blended family vs nuclear family Infographic
 relationdif.com
relationdif.com