Half-siblings share one biological parent, creating a genetic link that often influences family dynamics and inheritance rights. Step-siblings are related through the marriage of their respective parents, lacking a biological connection but forming bonds through blended family relationships. Understanding these distinctions helps navigate emotional connections and legal considerations in modern families.
Table of Comparison
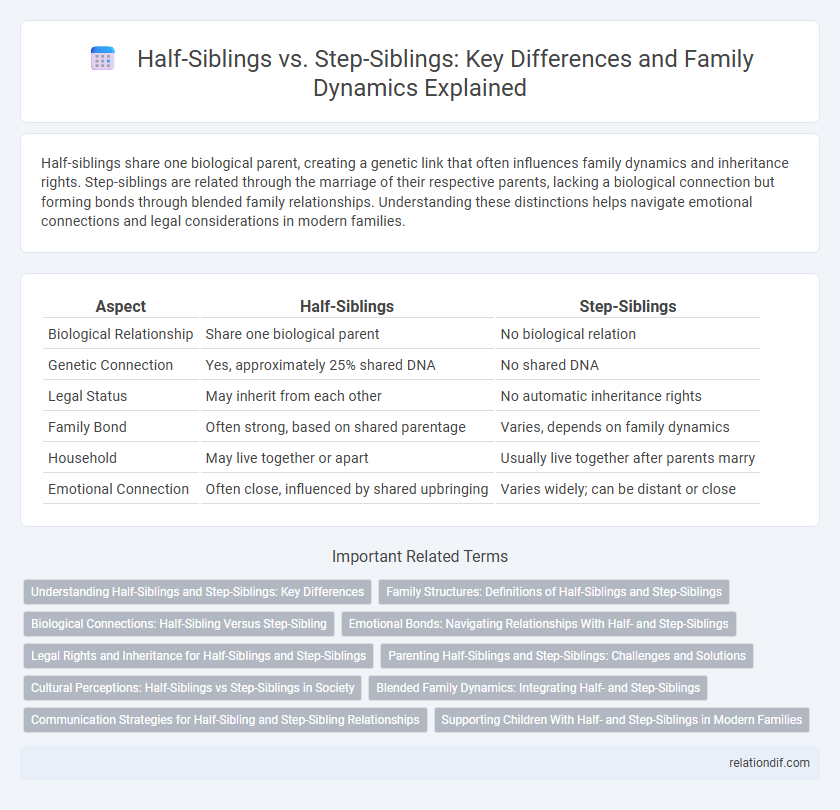
| Aspect | Half-Siblings | Step-Siblings |
|---|---|---|
| Biological Relationship | Share one biological parent | No biological relation |
| Genetic Connection | Yes, approximately 25% shared DNA | No shared DNA |
| Legal Status | May inherit from each other | No automatic inheritance rights |
| Family Bond | Often strong, based on shared parentage | Varies, depends on family dynamics |
| Household | May live together or apart | Usually live together after parents marry |
| Emotional Connection | Often close, influenced by shared upbringing | Varies widely; can be distant or close |
Understanding Half-Siblings and Step-Siblings: Key Differences
Half-siblings share one biological parent, either mother or father, resulting in a genetic connection that influences family dynamics and inheritance. Step-siblings are related through marriage with no shared biological parents, often forming bonds through blended family relationships and shared household experiences. Understanding these distinctions highlights the varying emotional and legal implications in family structures.
Family Structures: Definitions of Half-Siblings and Step-Siblings
Half-siblings share one biological parent, either a mother or a father, resulting in a genetic connection that influences family dynamics and inheritance rights. Step-siblings, formed through the marriage or partnership of two individuals with children from previous relationships, have no biological relation but often develop familial bonds through cohabitation and shared experiences. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for legal, social, and emotional aspects within blended family structures.
Biological Connections: Half-Sibling Versus Step-Sibling
Half-siblings share approximately 25% of their DNA due to having one common biological parent, establishing a direct genetic link that influences traits and hereditary conditions. Step-siblings have no biological connection, as their relationship is formed through the marriage or partnership of their respective parents. Understanding these distinctions helps clarify the varying degrees of genetic relatedness and social dynamics within blended families.
Emotional Bonds: Navigating Relationships With Half- and Step-Siblings
Emotional bonds between half-siblings often stem from shared genetic heritage and overlapping family history, fostering a unique sense of kinship and identity. Step-sibling relationships require intentional effort to build trust and connection, as they are formed through blended family dynamics rather than biology. Navigating these relationships successfully depends on communication, mutual respect, and understanding individual experiences within the family structure.
Legal Rights and Inheritance for Half-Siblings and Step-Siblings
Half-siblings share biological parents and often possess legal rights to inheritance under intestate succession laws, ensuring they are recognized as legitimate heirs without a will. Step-siblings, who are related only through the marriage of their parents, generally do not have automatic legal rights to inherit unless explicitly included in a will or legal agreement. Estate planning often requires clear documentation to define inheritance rights among step-siblings to avoid disputes, as their claims are not recognized by default in most jurisdictions.
Parenting Half-Siblings and Step-Siblings: Challenges and Solutions
Parenting half-siblings involves addressing shared genetics, which can influence identity and emotional bonds, whereas step-siblings require fostering connections without biological ties, often demanding deliberate relationship-building efforts. Challenges include managing jealousy, loyalty conflicts, and differing parenting styles, which necessitate open communication and consistent discipline strategies to create a harmonious environment. Solutions emphasize setting clear boundaries, promoting individual attention, and encouraging inclusive family activities to strengthen sibling relationships and support blended family dynamics.
Cultural Perceptions: Half-Siblings vs Step-Siblings in Society
Cultural perceptions of half-siblings often emphasize biological connections, leading to a stronger sense of shared identity and familial obligation in many societies. Step-siblings, whose bonds are formed through marriage rather than blood, may face varied acceptance depending on cultural norms and family dynamics, sometimes being perceived as less integral to the family unit. Social attitudes influence legal rights, inheritance, and emotional closeness, shaping the distinct experiences of half-siblings versus step-siblings across cultural contexts.
Blended Family Dynamics: Integrating Half- and Step-Siblings
Blended family dynamics often involve the integration of half-siblings, who share a biological parent, and step-siblings, who are related through marriage without shared genetics. Establishing strong relationships requires navigating distinct emotional bonds and identity challenges unique to each sibling type. Effective communication and mutual respect are essential for fostering harmony and a cohesive family environment.
Communication Strategies for Half-Sibling and Step-Sibling Relationships
Effective communication strategies for half-sibling and step-sibling relationships emphasize active listening and empathy to bridge differing family experiences. Establishing open dialogues about boundaries, feelings, and expectations helps foster trust and mutual understanding in blended families. Consistent, respectful communication reduces conflict and strengthens the emotional bonds between half and step-siblings.
Supporting Children With Half- and Step-Siblings in Modern Families
Supporting children with half-siblings and step-siblings involves recognizing the unique dynamics created by shared and non-shared parents, which influence attachment and identity formation. Effective communication and establishing clear boundaries help navigate loyalty conflicts and foster positive relationships among siblings. Providing consistent emotional support and encouraging inclusive family activities enhance bonding and stability in blended families.
half-siblings vs step-siblings Infographic
 relationdif.com
relationdif.com