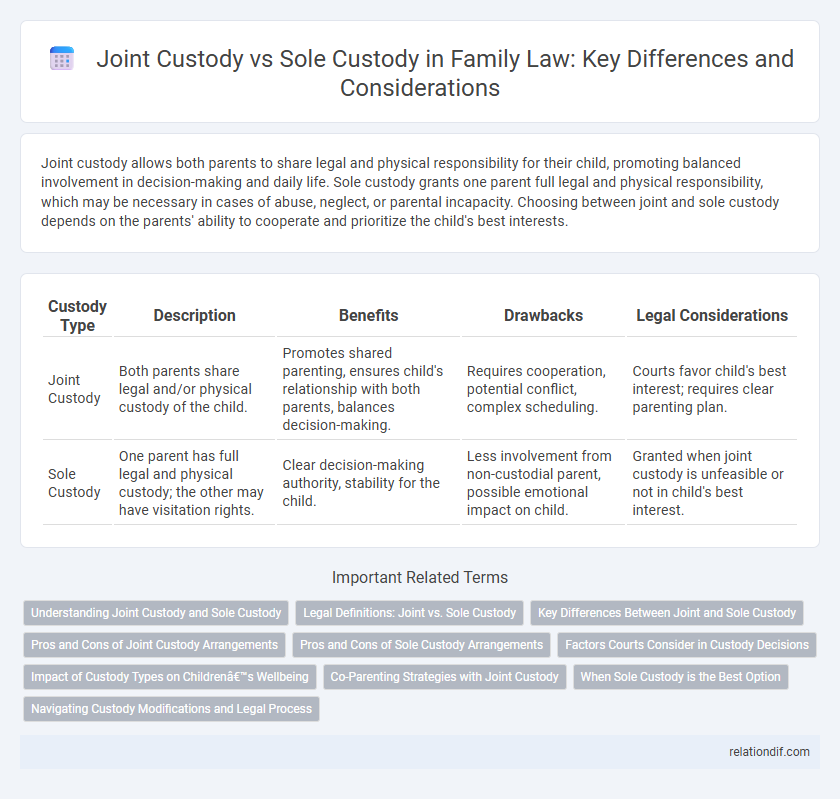
Joint custody allows both parents to share legal and physical responsibility for their child, promoting balanced involvement in decision-making and daily life. Sole custody grants one parent full legal and physical responsibility, which may be necessary in cases of abuse, neglect, or parental incapacity. Choosing between joint and sole custody depends on the parents' ability to cooperate and prioritize the child's best interests.
Table of Comparison
| Custody Type | Description | Benefits | Drawbacks | Legal Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Joint Custody | Both parents share legal and/or physical custody of the child. | Promotes shared parenting, ensures child's relationship with both parents, balances decision-making. | Requires cooperation, potential conflict, complex scheduling. | Courts favor child's best interest; requires clear parenting plan. |
| Sole Custody | One parent has full legal and physical custody; the other may have visitation rights. | Clear decision-making authority, stability for the child. | Less involvement from non-custodial parent, possible emotional impact on child. | Granted when joint custody is unfeasible or not in child's best interest. |
Understanding Joint Custody and Sole Custody
Joint custody allows both parents to share legal and physical custody, promoting active involvement in decision-making and child-rearing, while sole custody grants one parent exclusive rights and responsibilities. Legal custody pertains to decisions about the child's education, health, and welfare, whereas physical custody involves the child's living arrangements. Courts prioritize the child's best interests, often favoring joint custody to maintain strong parental bonds unless circumstances necessitate sole custody.
Legal Definitions: Joint vs. Sole Custody
Joint custody legally grants both parents shared rights and responsibilities for decision-making regarding the child's welfare, education, and health, fostering cooperative parenting. Sole custody awards one parent exclusive legal and physical custody, granting them the primary authority over major decisions and the child's living arrangements. Understanding these legal definitions is crucial for navigating custody agreements and ensuring the child's best interests are prioritized in family law.
Key Differences Between Joint and Sole Custody
Joint custody involves both parents sharing legal and/or physical custody of their child, ensuring collaborative decision-making regarding the child's upbringing, health, and education. Sole custody grants one parent exclusive authority and physical custody, with the other typically having visitation rights but limited decision-making power. The primary distinction lies in the distribution of parental responsibilities, affecting the child's routine and parental involvement post-separation.
Pros and Cons of Joint Custody Arrangements
Joint custody allows both parents to share decision-making responsibilities, promoting balanced involvement in a child's life and supporting emotional stability through continued contact with both parents. However, it can lead to conflicts or confusion if parents have differing parenting styles or struggle with communication, potentially causing stress for the child. Sole custody offers clear decision-making authority and may provide a more stable environment when one parent is unfit or unavailable, but it can limit the child's access to the other parent, affecting emotional bonds and support.
Pros and Cons of Sole Custody Arrangements
Sole custody grants one parent full legal and physical custody of the child, ensuring consistent decision-making and stability in the child's living environment. This arrangement can reduce conflicts between parents but may limit the child's relationship with the non-custodial parent, potentially impacting emotional well-being. Sole custody requires the custodial parent to shoulder all parenting responsibilities, which can be challenging without support from the other parent.
Factors Courts Consider in Custody Decisions
Courts prioritize the best interests of the child when deciding between joint custody and sole custody, evaluating factors such as each parent's ability to provide a stable environment, the child's emotional and developmental needs, and the quality of each parent's relationship with the child. The court also considers the parents' willingness to cooperate and communicate effectively, the presence of any history of abuse or neglect, and the child's preference when age-appropriate. Custody decisions are guided by ensuring the child's safety, continuity, and overall well-being above all.
Impact of Custody Types on Children’s Wellbeing
Joint custody often promotes emotional stability and stronger parent-child relationships by ensuring consistent involvement from both parents. Sole custody can lead to feelings of abandonment or loyalty conflicts in children, potentially affecting their psychological wellbeing. Studies reveal that children with joint custody arrangements tend to exhibit better social adjustment and academic performance compared to those in sole custody settings.
Co-Parenting Strategies with Joint Custody
Effective co-parenting strategies with joint custody involve clear communication, consistent schedules, and mutual respect to prioritize the child's well-being. Utilizing parenting plans that detail visitation, decision-making responsibilities, and conflict resolution reduces misunderstandings and fosters cooperative parenting. Emphasizing flexibility and prioritizing the child's needs helps both parents maintain a stable environment despite living separately.
When Sole Custody is the Best Option
Sole custody is the best option when one parent is unfit due to abuse, neglect, substance abuse, or severe mental illness, ensuring the child's safety and well-being. Courts prioritize the child's stability and may grant sole custody if the other parent poses a risk or is unwilling to cooperate in co-parenting. This arrangement provides a consistent environment, crucial for children who require clear boundaries and protection from conflict.
Navigating Custody Modifications and Legal Process
Navigating custody modifications involves understanding the legal criteria for changing joint custody agreements versus sole custody arrangements, often requiring clear evidence of substantial changes in circumstances affecting the child's best interests. Courts prioritize the stability and welfare of the child, evaluating petitions through comprehensive assessments including parental fitness, child's preference, and living environments. Legal processes typically demand filing formal motions, attending hearings, and sometimes mediation, with outcomes heavily influenced by state-specific family law statutes.
joint custody vs sole custody Infographic
 relationdif.com
relationdif.com