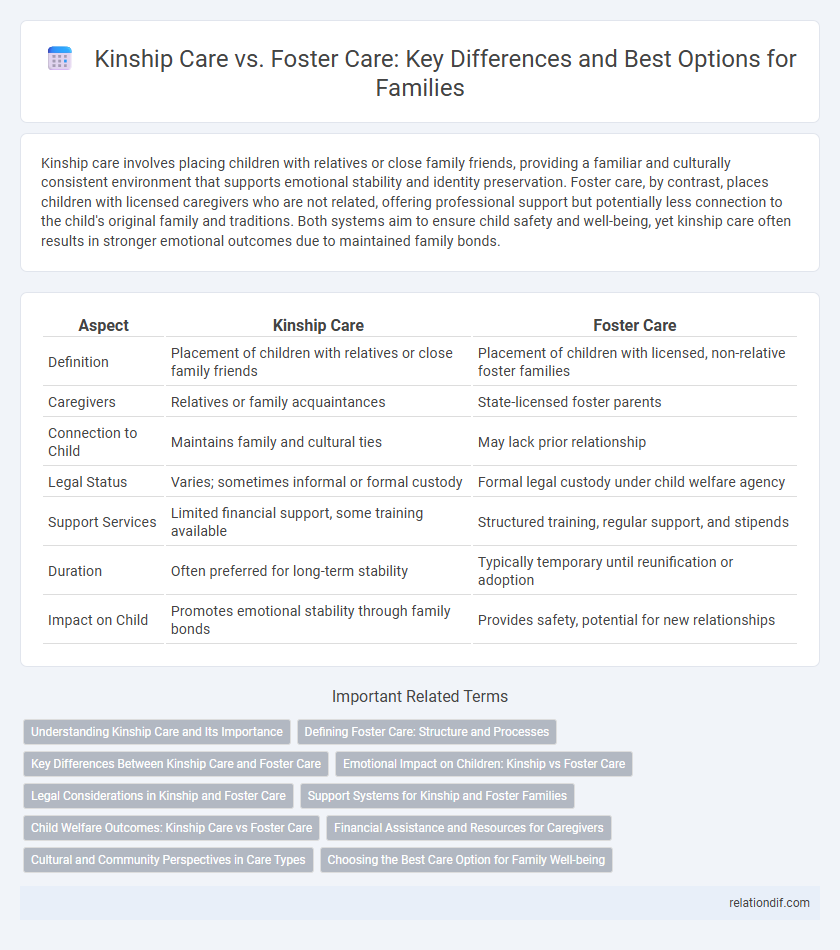
Kinship care involves placing children with relatives or close family friends, providing a familiar and culturally consistent environment that supports emotional stability and identity preservation. Foster care, by contrast, places children with licensed caregivers who are not related, offering professional support but potentially less connection to the child's original family and traditions. Both systems aim to ensure child safety and well-being, yet kinship care often results in stronger emotional outcomes due to maintained family bonds.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Kinship Care | Foster Care |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Placement of children with relatives or close family friends | Placement of children with licensed, non-relative foster families |
| Caregivers | Relatives or family acquaintances | State-licensed foster parents |
| Connection to Child | Maintains family and cultural ties | May lack prior relationship |
| Legal Status | Varies; sometimes informal or formal custody | Formal legal custody under child welfare agency |
| Support Services | Limited financial support, some training available | Structured training, regular support, and stipends |
| Duration | Often preferred for long-term stability | Typically temporary until reunification or adoption |
| Impact on Child | Promotes emotional stability through family bonds | Provides safety, potential for new relationships |
Understanding Kinship Care and Its Importance
Kinship care involves placing children with relatives or close family friends when their parents are unable to provide care, ensuring stability and preserving family connections. Research shows that children in kinship care experience fewer behavioral issues and maintain stronger cultural and familial ties compared to foster care settings. Understanding the benefits of kinship care highlights its vital role in supporting child well-being and promoting permanent family relationships.
Defining Foster Care: Structure and Processes
Foster care involves placing children with certified caregivers who provide temporary homes while the state ensures their safety and well-being through structured assessments and ongoing supervision. This system requires caregivers to meet specific licensing criteria, including background checks and training, to support children's emotional and developmental needs. Caseworkers collaborate closely with foster families to facilitate reunification with birth families or other permanent arrangements.
Key Differences Between Kinship Care and Foster Care
Kinship care involves placing children with relatives or close family friends, prioritizing maintaining family connections and cultural continuity, while foster care places children with licensed non-relative caregivers often through state agencies. Kinship caregivers typically receive less financial support and training compared to foster parents, impacting the resources available to care for the child. Legal custody often remains with birth parents or relatives in kinship care, whereas foster care usually involves state custody with the goal of reunification or adoption.
Emotional Impact on Children: Kinship vs Foster Care
Children in kinship care often experience greater emotional stability and a stronger sense of identity due to familiar connections, which supports healthier attachment patterns. Foster care children may face challenges related to emotional trauma and attachment disruptions, increasing the risk of behavioral and psychological issues. Studies show kinship care reduces feelings of loss and abandonment, promoting improved mental well-being compared to traditional foster placements.
Legal Considerations in Kinship and Foster Care
Legal considerations in kinship care often involve expedited placement processes and prioritized permanency plans due to preexisting family bonds, which can facilitate more stable custody arrangements. Foster care requires formal licensing and adherence to state-specific regulations, including regular home evaluations and compliance with foster parent training mandates. Both systems necessitate legal guardianship or custody transfers, but kinship care typically emphasizes kin rights and family preservation within the child welfare framework.
Support Systems for Kinship and Foster Families
Kinship care offers familial support networks that promote cultural continuity and emotional stability, often involving extended family members who provide caregiving with fewer disruptions to the child's sense of identity. Foster care systems typically feature structured support through social services, including access to training, counseling, and financial resources aimed at meeting the diverse needs of children and foster families. Both kinship and foster care emphasize the importance of comprehensive support systems to enhance the well-being and development of children in out-of-home care settings.
Child Welfare Outcomes: Kinship Care vs Foster Care
Kinship care often results in better child welfare outcomes compared to foster care, including higher rates of placement stability and stronger emotional bonds due to familiar family connections. Children in kinship care typically experience fewer behavioral problems and improved mental health, contributing to a more positive developmental environment. Research shows that kinship caregivers provide more consistent cultural and familial continuity, which supports overall well-being and permanency for children.
Financial Assistance and Resources for Caregivers
Kinship care often provides more stable financial assistance through government benefits such as Temporary Assistance for Needy Families (TANF) and Supplemental Security Income (SSI), tailored to support relatives raising children. Foster care typically offers broader resource access, including monthly stipends for basic needs, healthcare coverage, and training programs designed to equip non-relative caregivers. Both systems aim to alleviate financial burdens but differ in eligibility criteria and the scope of support services available to caregivers.
Cultural and Community Perspectives in Care Types
Kinship care preserves cultural identity by placing children with relatives, reinforcing community bonds and traditional values crucial for emotional stability. Foster care often lacks this cultural continuity, potentially leading to identity disruption and community alienation. Prioritizing kinship care supports heritage preservation and strengthens social networks within minority and indigenous populations.
Choosing the Best Care Option for Family Well-being
Kinship care provides children with stability by placing them with relatives, preserving family bonds and cultural identity, which promotes emotional well-being. Foster care offers professional support and resources for children whose relatives are unavailable, ensuring safety and structured care environments. Evaluating a child's emotional needs, family availability, and long-term support options is essential for selecting the best care solution that enhances overall family well-being.
Kinship care vs Foster care Infographic
 relationdif.com
relationdif.com