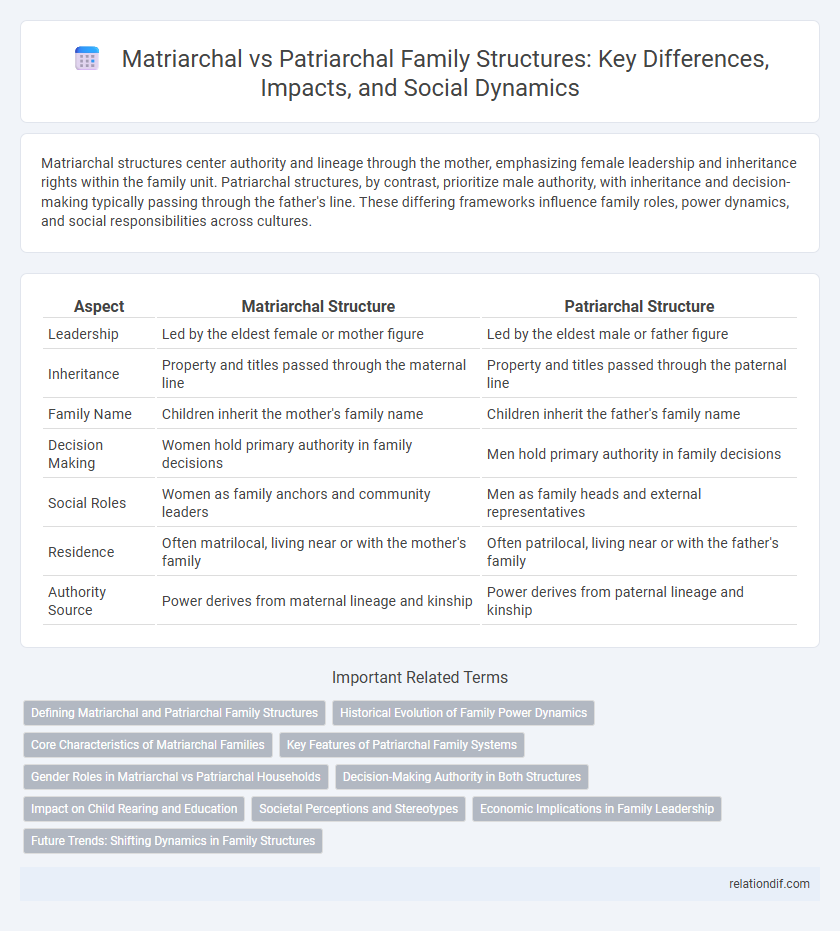
Matriarchal structures center authority and lineage through the mother, emphasizing female leadership and inheritance rights within the family unit. Patriarchal structures, by contrast, prioritize male authority, with inheritance and decision-making typically passing through the father's line. These differing frameworks influence family roles, power dynamics, and social responsibilities across cultures.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Matriarchal Structure | Patriarchal Structure |
|---|---|---|
| Leadership | Led by the eldest female or mother figure | Led by the eldest male or father figure |
| Inheritance | Property and titles passed through the maternal line | Property and titles passed through the paternal line |
| Family Name | Children inherit the mother's family name | Children inherit the father's family name |
| Decision Making | Women hold primary authority in family decisions | Men hold primary authority in family decisions |
| Social Roles | Women as family anchors and community leaders | Men as family heads and external representatives |
| Residence | Often matrilocal, living near or with the mother's family | Often patrilocal, living near or with the father's family |
| Authority Source | Power derives from maternal lineage and kinship | Power derives from paternal lineage and kinship |
Defining Matriarchal and Patriarchal Family Structures
Matriarchal family structures center authority around the eldest female, often emphasizing maternal lineage, inheritance, and decision-making within the household. Patriarchal family structures prioritize male authority, typically vesting power in the eldest male who oversees family decisions, inheritance, and social order. These contrasting systems shape the distribution of roles, responsibilities, and cultural values within families across societies.
Historical Evolution of Family Power Dynamics
Matriarchal and patriarchal family structures have evolved through distinct historical trajectories, reflecting broader socio-cultural shifts in power dynamics. Matriarchal systems, often observed in indigenous and ancient societies, centered authority around elder women, highlighting lineage and inheritance through the maternal line. Patriarchal structures, dominant in most modern civilizations, institutionalized male authority, influencing legal, economic, and social frameworks that shaped family roles and intergenerational power distribution.
Core Characteristics of Matriarchal Families
Matriarchal families center around female authority, where the eldest woman typically holds leadership and decision-making power within the household. These structures emphasize communal living, prioritizing cooperation, nurturing roles, and inheritance through the maternal line. Emotional support and child-rearing responsibilities are often shared collectively among women, reinforcing strong kinship bonds and social cohesion.
Key Features of Patriarchal Family Systems
Patriarchal family systems prioritize male authority, where the father or eldest male holds primary decision-making power and inheritance passes through the male lineage. This structure often emphasizes traditional gender roles, with men as breadwinners and women responsible for homemaking and child-rearing. Social norms within patriarchal families reinforce male dominance and limit women's participation in external economic and political activities.
Gender Roles in Matriarchal vs Patriarchal Households
Matriarchal households center authority and decision-making around women, often assigning nurturing and leadership roles to mothers and grandmothers, which challenges traditional gender roles seen in patriarchal families where men dominate public and financial spheres. Gender roles in patriarchal structures emphasize male authority, with women primarily responsible for domestic duties and child-rearing, reinforcing a hierarchical division of labor based on gender. Studies show that matriarchal families promote gender equality by distributing responsibilities more evenly and valuing cooperative dynamics over rigid gender-based expectations.
Decision-Making Authority in Both Structures
In matriarchal family structures, decision-making authority predominantly resides with women, often the eldest female, who influences key matters regarding family welfare, resource distribution, and social relationships. In patriarchal structures, men, typically the eldest male or father figure, hold primary control over decisions, guiding the family's economic activities, conflict resolution, and long-term planning. These distinct frameworks impact power dynamics, inheritance patterns, and the social roles assigned within the family unit.
Impact on Child Rearing and Education
Matriarchal structures often emphasize collaborative decision-making and emotional support, fostering a nurturing environment that enhances children's social and academic development. Patriarchal families typically prioritize authority and discipline, which can instill respect and responsibility but may limit open communication and emotional expression. The contrasting dynamics in these family systems significantly influence children's cognitive growth, self-esteem, and educational achievement.
Societal Perceptions and Stereotypes
Matriarchal structures often face societal stereotypes that portray women as overly dominant or emotional leaders, while patriarchal structures are commonly perceived as natural or traditional models of authority. These perceptions influence family roles and expectations, reinforcing gender norms that affect decision-making power and social status within the household. Studies show that media representation and cultural narratives play crucial roles in shaping and perpetuating these biased views.
Economic Implications in Family Leadership
Matriarchal family structures often emphasize communal resource management and shared economic responsibilities, fostering financial stability through collaborative decision-making. In contrast, patriarchal structures typically centralize economic control within male leadership, potentially limiting diverse income sources but streamlining financial authority. The economic implications influence wealth distribution, access to resources, and long-term family prosperity in each system.
Future Trends: Shifting Dynamics in Family Structures
Emerging future trends indicate a gradual shift from traditional patriarchal structures towards more matriarchal and egalitarian family models, driven by increasing gender equality and changing societal values. Data from global studies reveal a rise in female-headed households and shared parental responsibilities, reflecting evolving power dynamics within families. Technological advancements and economic independence further empower women to assume leadership roles, reshaping family hierarchies and decision-making processes.
Matriarchal Structure vs Patriarchal Structure Infographic
 relationdif.com
relationdif.com