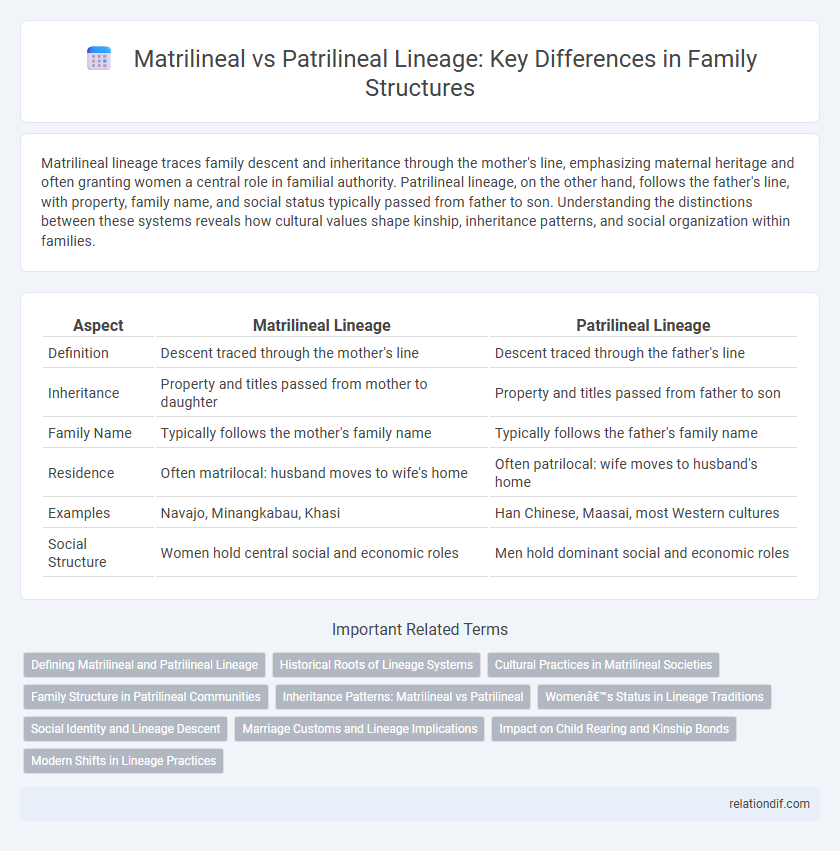
Matrilineal lineage traces family descent and inheritance through the mother's line, emphasizing maternal heritage and often granting women a central role in familial authority. Patrilineal lineage, on the other hand, follows the father's line, with property, family name, and social status typically passed from father to son. Understanding the distinctions between these systems reveals how cultural values shape kinship, inheritance patterns, and social organization within families.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Matrilineal Lineage | Patrilineal Lineage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Descent traced through the mother's line | Descent traced through the father's line |
| Inheritance | Property and titles passed from mother to daughter | Property and titles passed from father to son |
| Family Name | Typically follows the mother's family name | Typically follows the father's family name |
| Residence | Often matrilocal: husband moves to wife's home | Often patrilocal: wife moves to husband's home |
| Examples | Navajo, Minangkabau, Khasi | Han Chinese, Maasai, most Western cultures |
| Social Structure | Women hold central social and economic roles | Men hold dominant social and economic roles |
Defining Matrilineal and Patrilineal Lineage
Matrilineal lineage traces family descent and inheritance through the mother's line, emphasizing maternal ancestors and their roles in heritage and property rights. Patrilineal lineage follows the father's line, prioritizing paternal ancestors for the transmission of family name, assets, and social status. These distinct systems shape kinship, cultural identity, and social organization within various societies worldwide.
Historical Roots of Lineage Systems
Matrilineal lineage systems, historically prevalent among societies such as the Akan of Ghana and the Minangkabau of Indonesia, trace descent through the mother's line, emphasizing inheritance and social identity via maternal ancestry. In contrast, patrilineal lineage systems, dominant in many Eurasian and African cultures, determine lineage, inheritance, and clan membership through the father's line, reinforcing patriarchal family structures. These lineage frameworks significantly shaped social organization, property rights, and kinship roles across diverse civilizations throughout history.
Cultural Practices in Matrilineal Societies
In matrilineal societies, cultural practices emphasize inheritance and descent through the mother's lineage, often granting women significant authority in family decisions and property rights. Rituals, ceremonies, and social roles are frequently centered around maternal kin, reinforcing the importance of the mother's clan in maintaining social cohesion. These practices contrast sharply with patrilineal traditions where lineage and inheritance typically follow the father's line, highlighting diverse family structures globally.
Family Structure in Patrilineal Communities
Patrilineal communities trace descent and inheritance through the male line, emphasizing the father's family as the central unit in family structure. This system often results in patriarchal authority, where males hold primary power and property passes from father to son, influencing kinship ties and social roles. Such family arrangements reinforce male lineage continuity, shaping social identity and community cohesion around paternal ancestry.
Inheritance Patterns: Matrilineal vs Patrilineal
Inheritance patterns in matrilineal lineages trace property and titles through the mother's side, often granting women and their descendants significant rights and familial authority. Patrilineal inheritance, common worldwide, passes assets, surnames, and social status through the father's line, emphasizing male heirs for continuity. These contrasting systems influence family structure, wealth distribution, and social roles within communities.
Women’s Status in Lineage Traditions
Matrilineal lineage traditions often elevate women's status by positioning them as primary bearers of family identity and inheritance, fostering stronger social authority and influence within the clan. In contrast, patrilineal systems typically emphasize male lineage, limiting women's roles to marriage alliances and offspring production, which can restrict their social and economic power. The evolution of women's status in family lineage reflects broader cultural dynamics influencing gender roles and intergenerational inheritance patterns.
Social Identity and Lineage Descent
Matrilineal lineage traces descent through the mother's line, significantly shaping social identity by emphasizing maternal heritage and inherited status. Patrilineal lineage passes descent through the father's line, often establishing inheritance rights, family name, and social roles tied to paternal ancestors. These systems influence kinship structures, property transmission, and cultural continuity differently, impacting individual identity and community organization.
Marriage Customs and Lineage Implications
Matrilineal lineage emphasizes descent and inheritance through the mother's family, influencing marriage customs where husbands may integrate into the wife's household, establishing residence patterns that strengthen maternal kin ties. Patrilineal lineage traces ancestry through the father's line, often resulting in marriage customs where wives join the husband's family, reinforcing paternal lineage and inheritance structures. These differing systems impact family authority, inheritance rights, and social obligations, shaping the dynamics of kinship and identity within various cultures.
Impact on Child Rearing and Kinship Bonds
Matrilineal lineage often strengthens maternal kinship bonds, fostering a family environment where child-rearing responsibilities and inheritances pass through the mother's side, which can enhance children's sense of security and communal support. In contrast, patrilineal lineage emphasizes paternal descent, typically centralizing authority and resource allocation within the father's lineage, influencing children's identity and social roles through male relatives. These differing systems shape children's emotional attachments and social networks by prioritizing distinct familial connections and caregiving structures.
Modern Shifts in Lineage Practices
Modern shifts in lineage practices reveal a growing acceptance of matrilineal systems alongside traditional patrilineal ones, influenced by changing gender roles and legal reforms. Urbanization and increased female workforce participation contribute to the recognition of maternal lineage in inheritance and family identity. Digital platforms also enable diverse family narratives, expanding beyond conventional patrilineal frameworks to accommodate contemporary kinship dynamics.
matrilineal lineage vs patrilineal lineage Infographic
 relationdif.com
relationdif.com