Nuclear families consist of two parents and their children living together, fostering close-knit relationships and ease of mobility. Extended families include multiple generations under one roof or in close proximity, providing a broader support system and shared responsibilities. Both family structures influence emotional bonds, resource distribution, and social dynamics within households.
Table of Comparison
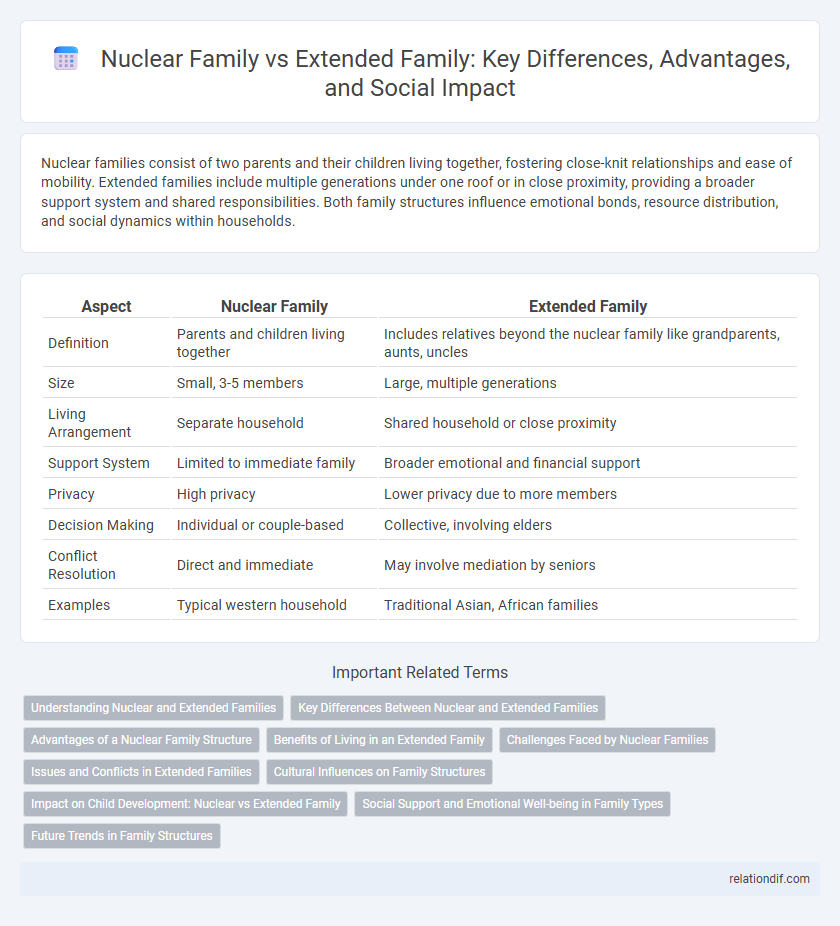
| Aspect | Nuclear Family | Extended Family |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Parents and children living together | Includes relatives beyond the nuclear family like grandparents, aunts, uncles |
| Size | Small, 3-5 members | Large, multiple generations |
| Living Arrangement | Separate household | Shared household or close proximity |
| Support System | Limited to immediate family | Broader emotional and financial support |
| Privacy | High privacy | Lower privacy due to more members |
| Decision Making | Individual or couple-based | Collective, involving elders |
| Conflict Resolution | Direct and immediate | May involve mediation by seniors |
| Examples | Typical western household | Traditional Asian, African families |
Understanding Nuclear and Extended Families
Nuclear families consist of two parents and their children, emphasizing a more compact household structure that supports economic independence and privacy. Extended families include multiple generations living together or maintaining close relationships, fostering strong social bonds and shared resources. Understanding these family types highlights varying cultural values and social support systems crucial for child development and caregiving.
Key Differences Between Nuclear and Extended Families
Nuclear families consist of two parents and their children living together, emphasizing a more private and independent household structure, while extended families include multiple generations and relatives under one roof, promoting shared responsibilities and close-knit relationships. The nuclear family often enables quicker decision-making and mobility, whereas the extended family provides broader social support and cultural continuity. Economic resources tend to be pooled in extended families, contrasting with the more individualized financial management seen in nuclear families.
Advantages of a Nuclear Family Structure
A nuclear family structure offers advantages such as greater privacy and independence, allowing members to make decisions without external influence. It facilitates closer emotional bonds between parents and children, promoting a supportive and stable environment. Financial management and resource allocation often become more efficient due to the smaller group size and shared responsibilities.
Benefits of Living in an Extended Family
Living in an extended family fosters strong intergenerational bonds, providing a robust support system for childcare, emotional guidance, and shared responsibilities. Access to diverse perspectives and collective wisdom benefits problem-solving and decision-making within the household. Financial advantages arise through pooled resources, reducing individual economic burdens and enhancing overall family stability.
Challenges Faced by Nuclear Families
Nuclear families often face challenges such as limited emotional support and childcare assistance compared to extended families, increasing stress for parents. Balancing work-life responsibilities becomes harder without the backup of grandparents or relatives, leading to potential burnout. Financial pressures also tend to be more intense, as expenses fall solely on the immediate family unit without shared resources from a larger household.
Issues and Conflicts in Extended Families
Extended families often experience conflicts due to overlapping roles and responsibilities, leading to blurred boundaries and power struggles among members. Financial disputes and differences in parenting styles contribute to ongoing tension, complicating decision-making processes. Communication breakdowns and generational gaps further exacerbate misunderstandings, impacting family cohesion.
Cultural Influences on Family Structures
Cultural influences profoundly shape family structures, determining whether nuclear or extended family models prevail in a society. In collectivist cultures, extended families often dominate, emphasizing intergenerational support and shared responsibilities, while individualistic cultures prioritize nuclear families, valuing independence and self-sufficiency. These cultural norms impact social roles, caregiving practices, and familial obligations, reflecting the community's broader values and traditions.
Impact on Child Development: Nuclear vs Extended Family
Nuclear families often provide children with concentrated parental attention and greater emotional stability, fostering independence and self-reliance. Extended families offer diverse role models and social support, enhancing children's social skills and cultural identity through multi-generational interactions. Both family structures uniquely influence cognitive development, emotional well-being, and social competence in children.
Social Support and Emotional Well-being in Family Types
Nuclear families offer concentrated social support through close-knit bonds between parents and children, fostering emotional stability and individualized attention. Extended families provide a broader network of relatives, enhancing emotional well-being by sharing caregiving responsibilities and cultural traditions across generations. Studies indicate that the presence of extended kinship networks often correlates with increased resilience and reduced stress during family crises.
Future Trends in Family Structures
Future trends in family structures indicate a growing prevalence of nuclear families due to urbanization, increased mobility, and changing economic conditions. Despite this shift, extended families remain important in many cultures for providing emotional support and shared resources, especially in multigenerational households. Advances in technology and evolving social norms are fostering more flexible and hybrid family forms that combine elements of both nuclear and extended family systems.
nuclear family vs extended family Infographic
 relationdif.com
relationdif.com