Monogamous intimacy centers on deep emotional and physical connection between two partners, fostering trust and exclusivity that strengthens the bond. Polyamorous intimacy involves cultivating meaningful relationships with multiple partners, emphasizing communication, consent, and emotional honesty to navigate complex dynamics. Both forms prioritize intimacy but differ in structure and the way affection and commitment are expressed within relationships.
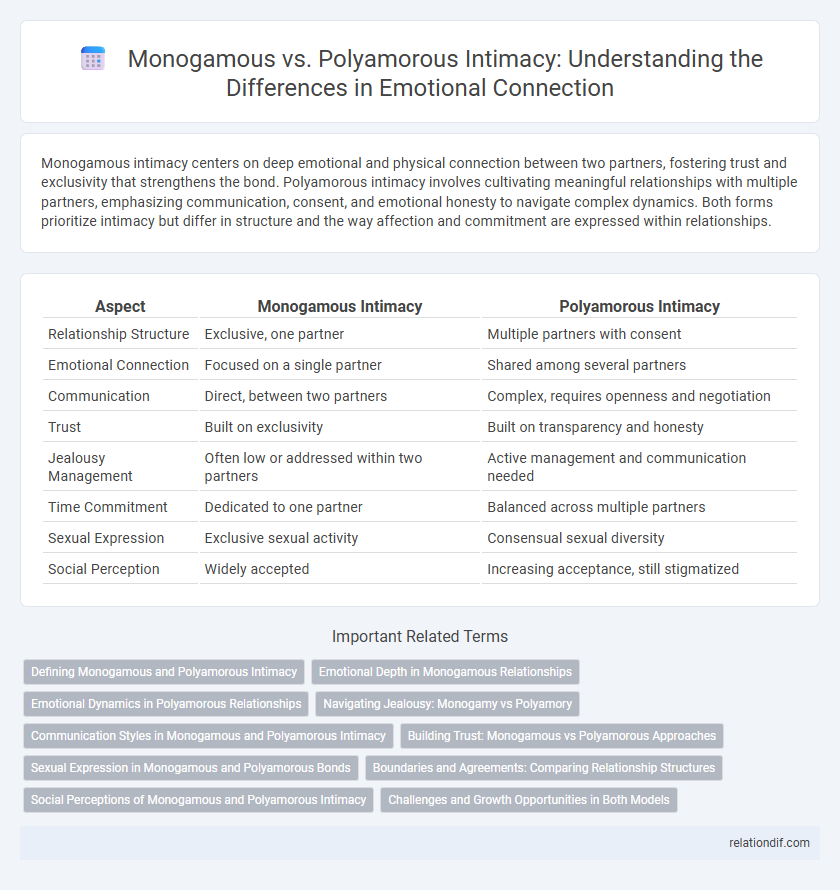
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Monogamous Intimacy | Polyamorous Intimacy |
|---|---|---|
| Relationship Structure | Exclusive, one partner | Multiple partners with consent |
| Emotional Connection | Focused on a single partner | Shared among several partners |
| Communication | Direct, between two partners | Complex, requires openness and negotiation |
| Trust | Built on exclusivity | Built on transparency and honesty |
| Jealousy Management | Often low or addressed within two partners | Active management and communication needed |
| Time Commitment | Dedicated to one partner | Balanced across multiple partners |
| Sexual Expression | Exclusive sexual activity | Consensual sexual diversity |
| Social Perception | Widely accepted | Increasing acceptance, still stigmatized |
Defining Monogamous and Polyamorous Intimacy
Monogamous intimacy centers on exclusive emotional and physical connections between two partners, emphasizing trust, commitment, and deep relational bonding. In contrast, polyamorous intimacy involves consensual, simultaneous relationships with multiple partners, prioritizing communication, transparency, and negotiated boundaries. Both forms of intimacy require mutual respect and emotional attunement but differ fundamentally in structure and expectations.
Emotional Depth in Monogamous Relationships
Monogamous intimacy often fosters profound emotional depth through exclusive, focused connection and consistent mutual vulnerability, enhancing trust and security between partners. This singular attachment facilitates deep emotional bonding, enabling partners to explore complex feelings and shared experiences over time. Research indicates that the concentrated attention in monogamous relationships can result in heightened emotional satisfaction and stability compared to polyamorous arrangements.
Emotional Dynamics in Polyamorous Relationships
Polyamorous intimacy involves complex emotional dynamics characterized by multiple simultaneous attachments that require heightened communication, trust, and boundary-setting compared to monogamous relationships. Participants often engage in emotional negotiation to balance jealousy, compersion, and individual needs, fostering personal growth and relational resilience. Emotional transparency and active consent are key factors that support the sustainable development of polyamorous bonds.
Navigating Jealousy: Monogamy vs Polyamory
Navigating jealousy in monogamous intimacy often involves exclusive emotional and physical connection, relying on trust and strong communication to mitigate feelings of insecurity. Polyamorous intimacy requires managing multiple romantic bonds simultaneously, emphasizing transparency, boundary-setting, and active negotiation to address jealousy constructively. Both relational structures benefit from emotional self-awareness and open dialogue to foster healthy intimacy.
Communication Styles in Monogamous and Polyamorous Intimacy
Monogamous intimacy often relies on direct, exclusive communication focused on nurturing a single partnership, emphasizing clarity and consistency to build trust and emotional security. In contrast, polyamorous intimacy requires complex communication strategies to navigate multiple relationships, involving heightened transparency, frequent check-ins, and explicit boundary-setting to manage diverse emotional needs and prevent misunderstandings. Effective communication in both styles hinges on active listening, emotional honesty, and mutual respect to maintain healthy, fulfilling connections.
Building Trust: Monogamous vs Polyamorous Approaches
Building trust in monogamous intimacy often revolves around exclusivity and consistent emotional availability, fostering security through clear boundaries and mutual commitment. Polyamorous intimacy requires trust in communication, transparency, and consent, emphasizing negotiation and emotional agility among multiple partners. Both approaches prioritize honesty and respect but differ significantly in structure, with monogamy focusing on dyadic trust and polyamory on networked trust dynamics.
Sexual Expression in Monogamous and Polyamorous Bonds
Sexual expression in monogamous intimacy often centers on exclusivity, fostering deep emotional connection and trust between two partners while prioritizing fidelity. In polyamorous bonds, sexual expression embraces diversity and multiple consensual relationships, promoting communication, honesty, and negotiation of boundaries among all involved. Both approaches require emotional intelligence and mutual respect but differ fundamentally in how sexual needs and desires are navigated and fulfilled.
Boundaries and Agreements: Comparing Relationship Structures
Monogamous intimacy typically relies on clear, exclusive boundaries where partners agree to emotional and physical exclusivity, fostering trust through predictability and singular commitment. Polyamorous intimacy involves negotiated agreements that accommodate multiple romantic or sexual connections, emphasizing communication, consent, and flexible boundaries tailored to each relationship. The key difference lies in how boundaries are maintained and redefined to balance individual autonomy with mutual respect across diverse relational structures.
Social Perceptions of Monogamous and Polyamorous Intimacy
Monogamous intimacy is often socially perceived as the normative standard, associated with traditional values of exclusivity and lifelong commitment, which influences legal and cultural recognition. Polyamorous intimacy challenges these conventions by emphasizing multiple consensual relationships, facing mixed social acceptance and frequent misconceptions about legitimacy and stability. Social perceptions impact relationship visibility, support systems, and societal integration, shaping the experiences of individuals practicing monogamous or polyamorous intimacy.
Challenges and Growth Opportunities in Both Models
Monogamous intimacy often faces challenges like maintaining long-term exclusivity and managing expectations of emotional and sexual fidelity, which can foster deep trust and commitment over time. Polyamorous intimacy requires navigating complex communication, boundary-setting, and jealousy management, offering growth opportunities in emotional intelligence and interpersonal skills. Both models encourage personal development and relationship resilience through distinct pathways of vulnerability and connection.
monogamous intimacy vs polyamorous intimacy Infographic
 relationdif.com
relationdif.com