Romantic love is characterized by intense passion, emotional excitement, and physical attraction, often marked by eagerness and infatuation. Companionate love centers on deep affection, trust, and enduring commitment, fostering a stable and supportive bond. Both forms contribute uniquely to meaningful relationships, with romantic love sparking initial connection and companionate love sustaining long-term partnership.
Table of Comparison
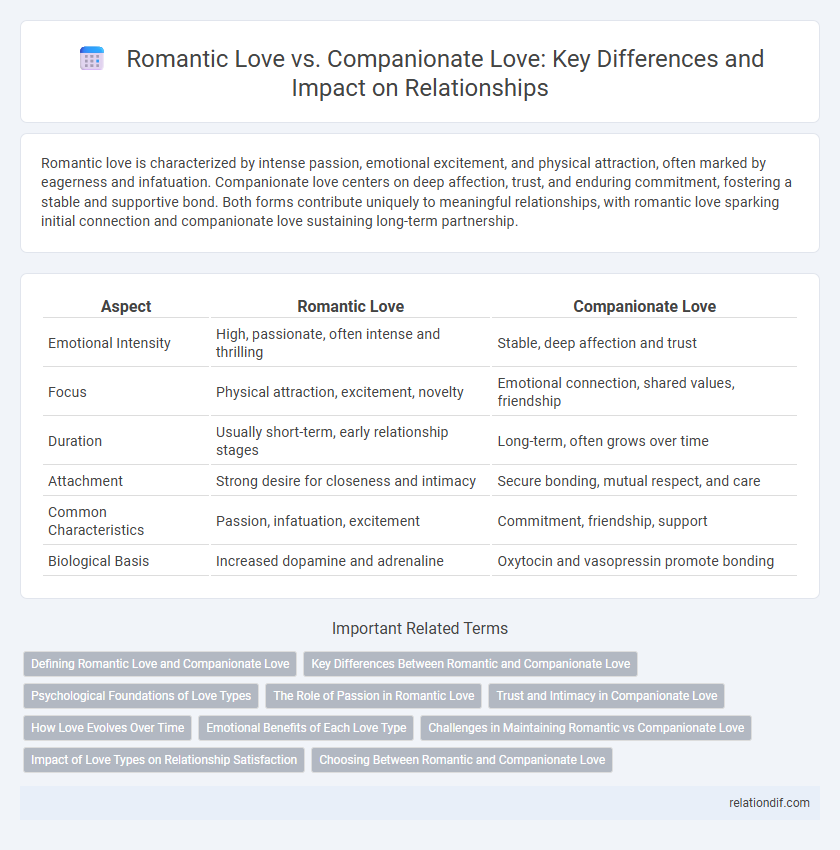
| Aspect | Romantic Love | Companionate Love |
|---|---|---|
| Emotional Intensity | High, passionate, often intense and thrilling | Stable, deep affection and trust |
| Focus | Physical attraction, excitement, novelty | Emotional connection, shared values, friendship |
| Duration | Usually short-term, early relationship stages | Long-term, often grows over time |
| Attachment | Strong desire for closeness and intimacy | Secure bonding, mutual respect, and care |
| Common Characteristics | Passion, infatuation, excitement | Commitment, friendship, support |
| Biological Basis | Increased dopamine and adrenaline | Oxytocin and vasopressin promote bonding |
Defining Romantic Love and Companionate Love
Romantic love is characterized by intense emotions, physical attraction, and passion that often mark the initial stages of a relationship, fostering excitement and desire between partners. Companionate love emphasizes deep affection, emotional intimacy, and long-term commitment, grounded in mutual respect and shared life experiences. These two forms of love represent distinct but complementary dimensions essential to sustaining meaningful romantic relationships.
Key Differences Between Romantic and Companionate Love
Romantic love is characterized by intense passion, emotional arousal, and physical attraction, often sparking excitement and desire in early relationship stages. Companionate love centers on deep affection, mutual respect, and long-term commitment, typically evolving through shared experiences and emotional intimacy. The key differences lie in romantic love's emphasis on passion and novelty, while companionate love prioritizes stability, trust, and enduring connection.
Psychological Foundations of Love Types
Romantic love is characterized by intense emotional arousal, passion, and physical attraction, driven by brain regions such as the ventral tegmental area and caudate nucleus, which release dopamine and foster reward-seeking behavior. Companionate love involves deep attachment, mutual respect, and long-term commitment, supported by oxytocin and vasopressin that promote bonding and emotional security. Psychological foundations distinguish romantic love's focus on novelty and excitement from companionate love's emphasis on stability and trust in enduring relationships.
The Role of Passion in Romantic Love
Passion plays a central role in romantic love, characterized by intense emotions, physical attraction, and a desire for union. This passionate intensity often distinguishes romantic love from companionate love, which emphasizes deep affection, trust, and commitment without the same level of arousal or urgency. Neurochemical factors such as elevated dopamine and adrenaline levels contribute to the fiery and exhilarating nature of romantic love's passionate experience.
Trust and Intimacy in Companionate Love
Companionate love is characterized by deep trust and enduring intimacy, fostering a stable emotional bond that supports long-term relationships. Trust in companionate love is built through consistent reliability and mutual respect, creating a secure environment for emotional openness. This intimacy extends beyond physical attraction, encompassing shared values, experiences, and a profound sense of emotional connection.
How Love Evolves Over Time
Romantic love often ignites with intense passion and emotional arousal, driven by dopamine and adrenaline in the early stages of relationships. Over time, this passionate intensity typically transitions into companionate love, characterized by deep affection, trust, and mutual support, underpinned by oxytocin and vasopressin release. The evolution from romantic to companionate love reflects a shift from infatuation to a stable, enduring bond that prioritizes partnership and emotional intimacy.
Emotional Benefits of Each Love Type
Romantic love typically provides intense emotional highs, passion, and excitement, fostering a deep sense of connection and physical attraction that enhances personal happiness. Companionate love offers stability, trust, and mutual respect, promoting long-lasting emotional security and a strong sense of partnership. Both love types contribute to psychological well-being by fulfilling different emotional needs, with romantic love emphasizing novelty and desire, and companionate love emphasizing comfort and support.
Challenges in Maintaining Romantic vs Companionate Love
Romantic love often faces challenges such as sustaining passion and managing intense emotional fluctuations, which can lead to conflicts and misunderstandings over time. In contrast, companionate love requires ongoing efforts to nurture deep trust, mutual respect, and shared goals, with difficulties arising from complacency and reduced emotional intensity. Both forms of love demand communication and adaptability to overcome obstacles and maintain a fulfilling connection.
Impact of Love Types on Relationship Satisfaction
Romantic love, characterized by passion and intense emotions, often sparks initial attraction and excitement, significantly boosting early relationship satisfaction. Companionate love, marked by deep affection, trust, and commitment, sustains long-term relationship stability and emotional fulfillment. Studies show couples experiencing a balanced blend of romantic and companionate love report higher overall satisfaction and resilience in their relationships.
Choosing Between Romantic and Companionate Love
Choosing between romantic love, characterized by intense passion and emotional arousal, and companionate love, defined by deep affection and commitment, depends on individual needs and relationship goals. Romantic love often triggers physiological responses such as increased dopamine and serotonin levels, fostering excitement and desire, whereas companionate love emphasizes long-term stability through trust and mutual respect. Prioritizing either form involves assessing personal values regarding intimacy, emotional connection, and relationship durability.
Romantic Love vs Companionate Love Infographic
 relationdif.com
relationdif.com