Cohabitation offers couples flexibility and a trial period to understand compatibility without the legal obligations tied to marriage. Legal marriage provides formal recognition, granting spouses rights such as inheritance, tax benefits, and healthcare decision-making authority. Understanding the distinctions between cohabitation and marriage is essential for making informed decisions about long-term commitment and legal protection.
Table of Comparison
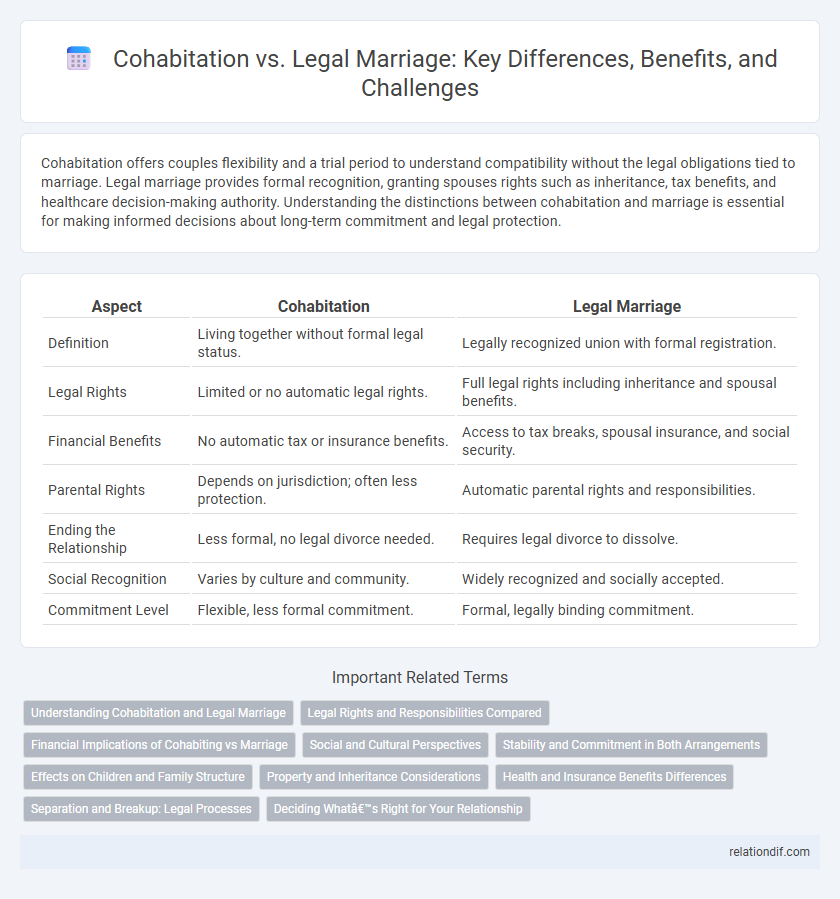
| Aspect | Cohabitation | Legal Marriage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Living together without formal legal status. | Legally recognized union with formal registration. |
| Legal Rights | Limited or no automatic legal rights. | Full legal rights including inheritance and spousal benefits. |
| Financial Benefits | No automatic tax or insurance benefits. | Access to tax breaks, spousal insurance, and social security. |
| Parental Rights | Depends on jurisdiction; often less protection. | Automatic parental rights and responsibilities. |
| Ending the Relationship | Less formal, no legal divorce needed. | Requires legal divorce to dissolve. |
| Social Recognition | Varies by culture and community. | Widely recognized and socially accepted. |
| Commitment Level | Flexible, less formal commitment. | Formal, legally binding commitment. |
Understanding Cohabitation and Legal Marriage
Cohabitation involves partners living together without formal legal recognition, often lacking the same rights and protections as married couples concerning property, inheritance, and decision-making. Legal marriage provides a recognized contract between spouses, granting comprehensive legal benefits, such as spousal support, tax advantages, and parental rights. Understanding these differences helps individuals make informed choices about their relationship structure and the legal implications involved.
Legal Rights and Responsibilities Compared
Legal marriage grants couples formal rights such as inheritance, tax benefits, and spousal decision-making authority that cohabitation does not automatically provide. Married partners are legally obligated to support each other financially and emotionally, with specific responsibilities defined by law. Cohabiting couples may need to establish contracts to protect their rights, as many jurisdictions do not recognize cohabitation as equivalent to marriage in terms of legal protections.
Financial Implications of Cohabiting vs Marriage
Cohabiting couples often face limited legal protections in areas like property division, inheritance, and spousal support compared to legally married spouses, which can lead to financial vulnerability during separations or a partner's death. Married couples benefit from tax advantages, access to spousal benefits such as Social Security and health insurance, and clearer legal frameworks governing asset ownership and debt responsibility. Financial planning for marriage typically involves formal agreements and state-recognized rights that provide greater security, while cohabitants may need to rely on private contracts or risk uncertainty.
Social and Cultural Perspectives
Cohabitation and legal marriage carry distinct social and cultural connotations that vary across societies. Legal marriage often symbolizes formal commitment and social recognition, while cohabitation may challenge traditional norms and reflect evolving attitudes toward relationships. Social acceptance and cultural values influence the perceived legitimacy and stability of these unions in different communities.
Stability and Commitment in Both Arrangements
Legal marriage provides a formal and enforceable commitment offering greater stability through legally binding rights and responsibilities, including property division and spousal support protections. Cohabitation, while reflecting emotional commitment, lacks these legal safeguards, often resulting in less predictable outcomes during separation. Studies indicate married couples generally experience higher relationship stability due to societal, legal, and financial reinforcement not guaranteed in cohabitation.
Effects on Children and Family Structure
Cohabitation before marriage influences children's stability differently compared to legal marriage, with studies indicating higher risks of behavioral issues and instability in cohabiting households. Legal marriage tends to provide a more structured family environment, contributing to better emotional and financial security for children. Family structure in married couples often results in clearer parental roles and consistent support systems, which positively affect child development.
Property and Inheritance Considerations
Cohabitation without legal marriage often leaves partners without automatic property rights or inheritance claims, making legal agreements essential to protect shared assets. Married couples benefit from statutory protections, including joint ownership presumption and spousal inheritance rights without a will. Understanding the legal distinctions in property division and inheritance ensures fair outcomes, especially in the absence of formal documentation for cohabiting partners.
Health and Insurance Benefits Differences
Legal marriage often provides more comprehensive health and insurance benefits compared to cohabitation, including spousal health insurance coverage, eligibility for family health plans, and access to spousal benefits such as Social Security and Medicaid. Cohabiting partners may face challenges obtaining joint health insurance policies or survivor benefits, as many insurers and government programs require a legal marriage certificate to grant coverage and benefits. Studies show married couples typically experience better health outcomes due to increased access to healthcare resources, spousal support, and insurance advantages not commonly available to unmarried cohabitants.
Separation and Breakup: Legal Processes
Separation and breakup processes differ significantly between cohabitation and legal marriage, with legal marriages requiring formal divorce proceedings overseen by courts that address asset division, child custody, and alimony. Cohabiting couples often lack standardized legal protections, leading to complex disputes resolved through civil litigation or negotiated agreements without the benefit of established family law frameworks. Legal marriage offers clearer statutory guidelines for separation, while cohabitation separations depend heavily on cohabitation agreements or local jurisdictional laws.
Deciding What’s Right for Your Relationship
Deciding between cohabitation and legal marriage depends on factors such as financial stability, legal protections, and personal values. Cohabitation offers flexibility and fewer legal obligations, while marriage provides comprehensive legal rights including inheritance, tax benefits, and healthcare decisions. Evaluating long-term goals and consulting with a family law expert can help determine the best choice for your relationship's unique needs.
Cohabitation vs Legal Marriage Infographic
 relationdif.com
relationdif.com