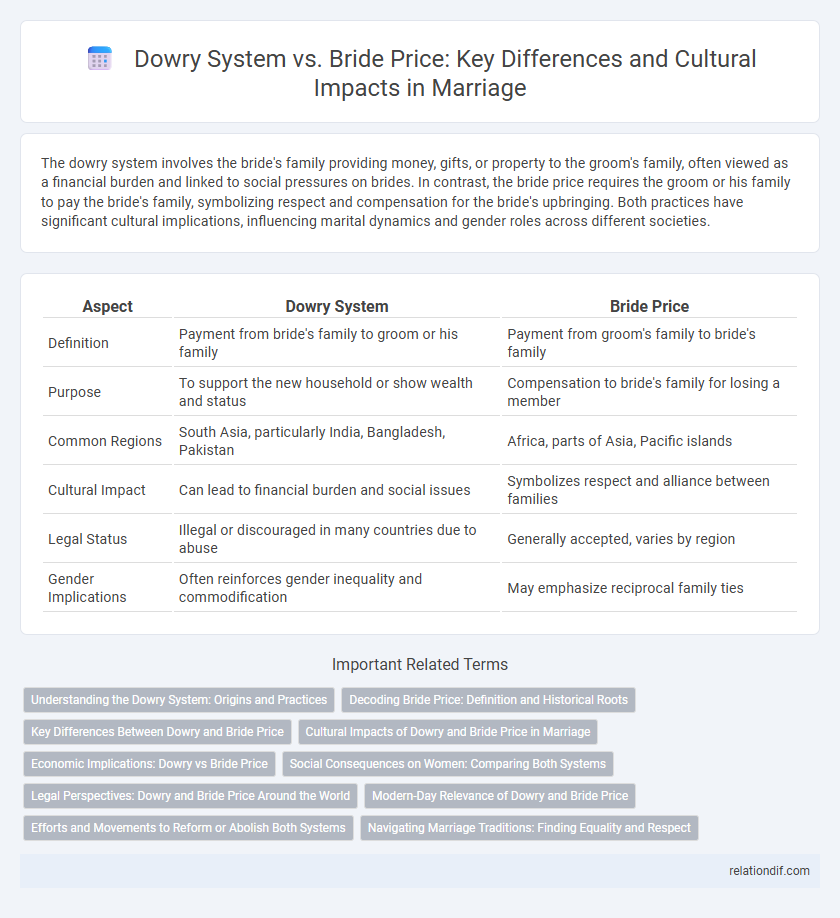
The dowry system involves the bride's family providing money, gifts, or property to the groom's family, often viewed as a financial burden and linked to social pressures on brides. In contrast, the bride price requires the groom or his family to pay the bride's family, symbolizing respect and compensation for the bride's upbringing. Both practices have significant cultural implications, influencing marital dynamics and gender roles across different societies.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Dowry System | Bride Price |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Payment from bride's family to groom or his family | Payment from groom's family to bride's family |
| Purpose | To support the new household or show wealth and status | Compensation to bride's family for losing a member |
| Common Regions | South Asia, particularly India, Bangladesh, Pakistan | Africa, parts of Asia, Pacific islands |
| Cultural Impact | Can lead to financial burden and social issues | Symbolizes respect and alliance between families |
| Legal Status | Illegal or discouraged in many countries due to abuse | Generally accepted, varies by region |
| Gender Implications | Often reinforces gender inequality and commodification | May emphasize reciprocal family ties |
Understanding the Dowry System: Origins and Practices
The dowry system originated as a cultural tradition where the bride's family provided money, goods, or property to the groom's family, serving as financial security for the bride. This practice varies significantly across regions, often reflecting social, economic, and religious influences, with some communities emphasizing lavish gifts while others maintain modest exchanges. Understanding dowry requires examining its transformation from a supportive gesture to a source of social tension and legal regulation in many countries.
Decoding Bride Price: Definition and Historical Roots
Bride price, defined as a payment made by the groom or his family to the bride's family, has deep historical roots across many cultures, symbolizing respect, alliance, and compensation for the bride's upbringing. Unlike the dowry system, where the bride's family provides wealth to the groom, bride price represents a reversal of economic exchange reflective of social customs and marital negotiations. Its origins can be traced to ancient societies where marriage transactions reinforced familial bonds, property rights, and social status.
Key Differences Between Dowry and Bride Price
Dowry involves the transfer of parental property, gifts, or money from the bride's family to the groom or his family at marriage, often emphasizing social status and financial security. Bride price is a payment made by the groom or his family to the bride's family, symbolizing compensation for the bride's loss to her natal family and securing marital rights. Key differences lie in the direction of transfer, cultural significance, and their impact on gender dynamics within various societies.
Cultural Impacts of Dowry and Bride Price in Marriage
Dowry systems often reinforce patriarchal norms by commodifying brides and placing financial burdens on their families, which can lead to social inequities and domestic violence. Bride price practices may elevate the bride's perceived value but also risk commodification, impacting gender dynamics and power structures within marriage. Both systems shape cultural attitudes toward marriage, influencing family relationships, social status, and gender roles across various societies.
Economic Implications: Dowry vs Bride Price
The dowry system often places a significant financial burden on the bride's family, leading to economic stress and potential indebtedness, whereas the bride price transfers wealth from the groom's family to the bride's family, sometimes enhancing her economic security. Dowry demands can exacerbate gender inequality and poverty by commodifying women and triggering competition among families, while bride price may reinforce male authority but also serve as a form of compensation for the bride's kin. Both practices impact local economies and social structures, influencing household wealth distribution and marriage market dynamics.
Social Consequences on Women: Comparing Both Systems
The dowry system often leads to increased financial burden and violence against women, perpetuating gender inequality and social stigma. In contrast, the bride price system can commodify women, reinforcing patriarchal control and limiting their autonomy within marriage. Both practices contribute to societal norms that undermine women's rights and empowerment in different cultural contexts.
Legal Perspectives: Dowry and Bride Price Around the World
Legal perspectives on dowry and bride price vary significantly worldwide, with many countries enforcing strict laws against dowry to curb related abuses, such as India's Dowry Prohibition Act, 1961. Conversely, bride price practices are legally recognized or regulated in various African and Pacific Island nations, where they serve as cultural rites of passage, though some jurisdictions address exploitation concerns through specific legislation. International human rights bodies advocate for the abolition or reform of both systems to protect women's rights and promote gender equality in marriage.
Modern-Day Relevance of Dowry and Bride Price
The dowry system and bride price remain influential in shaping marriage customs across various cultures, with dowry often representing a transfer of wealth from the bride's family and bride price involving payments from the groom's family. In modern society, dowry practices have faced criticism for perpetuating gender inequality and financial burdens, whereas bride price can symbolize respect and commitment but sometimes lead to commodification of relationships. Contemporary reform efforts target the eradication of exploitative practices while promoting equitable marriage traditions that respect individual rights and cultural values.
Efforts and Movements to Reform or Abolish Both Systems
Efforts to reform or abolish the dowry system and bride price have gained momentum through legislative measures, awareness campaigns, and grassroots activism aimed at promoting gender equality and reducing financial burdens on families. Organizations and governments in countries like India and Nigeria have implemented strict laws, such as the Dowry Prohibition Act and anti-bride price statutes, to penalize exploitative practices. Social movements emphasize education, women's empowerment, and cultural shifts to eradicate these customs and foster equitable marriage practices worldwide.
Navigating Marriage Traditions: Finding Equality and Respect
Navigating marriage traditions such as the dowry system and bride price requires a focus on equality and mutual respect between partners and families. Emphasizing transparent communication and shared decision-making helps dismantle practices that reinforce gender imbalances and financial burdens. Couples fostering respect and partnership promote healthier, more equitable marital foundations across diverse cultural contexts.
Dowry System vs Bride Price Infographic
 relationdif.com
relationdif.com