Endogamy involves marrying within a specific social, cultural, or ethnic group, reinforcing shared values and traditions while maintaining community cohesion. Exogamy requires individuals to marry outside their immediate social group, promoting genetic diversity and expanding social networks. These contrasting marriage practices play a significant role in shaping family structures and cultural identity across societies.
Table of Comparison
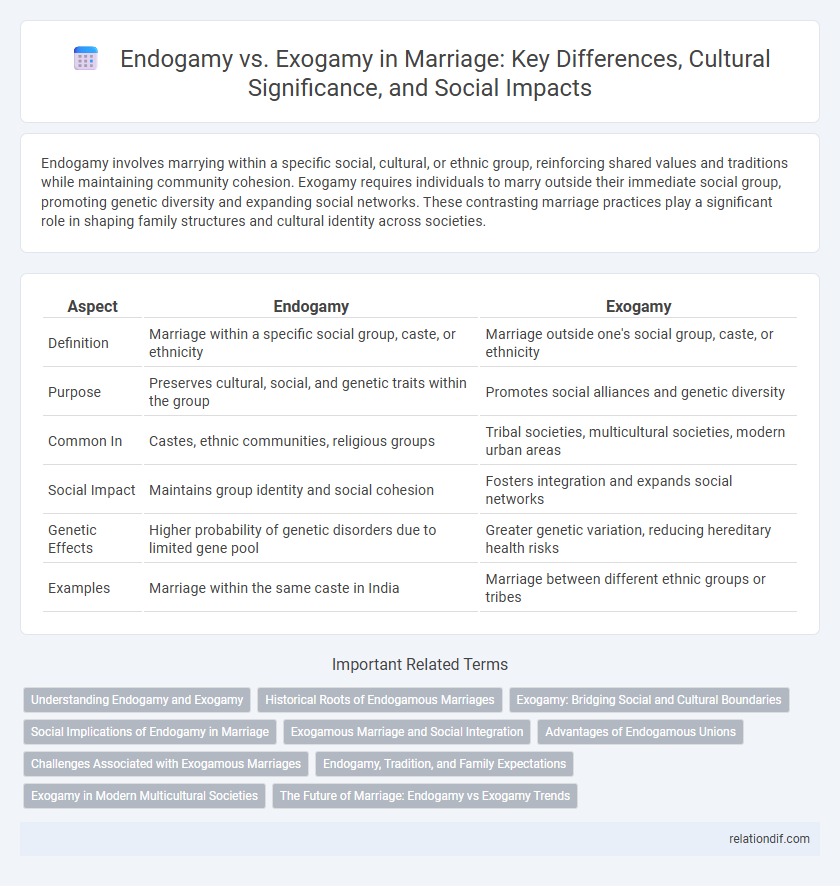
| Aspect | Endogamy | Exogamy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Marriage within a specific social group, caste, or ethnicity | Marriage outside one's social group, caste, or ethnicity |
| Purpose | Preserves cultural, social, and genetic traits within the group | Promotes social alliances and genetic diversity |
| Common In | Castes, ethnic communities, religious groups | Tribal societies, multicultural societies, modern urban areas |
| Social Impact | Maintains group identity and social cohesion | Fosters integration and expands social networks |
| Genetic Effects | Higher probability of genetic disorders due to limited gene pool | Greater genetic variation, reducing hereditary health risks |
| Examples | Marriage within the same caste in India | Marriage between different ethnic groups or tribes |
Understanding Endogamy and Exogamy
Endogamy refers to the practice of marrying within a specific social, cultural, ethnic, or religious group, maintaining group boundaries and preserving cultural heritage. Exogamy involves marrying outside one's social group, promoting genetic diversity and fostering social alliances between different communities. Understanding endogamy and exogamy highlights how these marriage patterns shape social structure, identity, and cohesion in various societies.
Historical Roots of Endogamous Marriages
Endogamous marriages have deep historical roots in many societies, serving to preserve cultural identity, social status, and economic wealth within specific groups or communities. Ancient civilizations such as India, Egypt, and tribal societies often enforced endogamy to maintain hereditary lines and reinforce caste or clan structures. This practice was especially prevalent in societies where social cohesion and continuity depended on strict marital boundaries within defined ethnic, religious, or social classes.
Exogamy: Bridging Social and Cultural Boundaries
Exogamy promotes marriage outside one's social, cultural, or ethnic group, fostering diversity and cross-cultural understanding. By encouraging unions beyond immediate communities, exogamy helps bridge social boundaries and create wider social networks. This practice often leads to increased social cohesion and the blending of distinct cultural traditions.
Social Implications of Endogamy in Marriage
Endogamy in marriage reinforces social cohesion by encouraging unions within specific cultural, religious, or ethnic groups, preserving traditions and group identity. This practice often limits genetic diversity and may contribute to social stratification, affecting community integration and mobility. Endogamous marriages can also impact social networks by maintaining alliances within the group but potentially excluding broader social interactions.
Exogamous Marriage and Social Integration
Exogamous marriage, which involves selecting a spouse outside one's social group, plays a critical role in fostering social integration by bridging diverse communities and promoting cultural exchange. This practice helps to break down social barriers and creates networks of kinship that extend beyond immediate groups, enhancing social cohesion and reducing conflict. By encouraging alliances across different social, ethnic, or religious groups, exogamy strengthens societal stability and diversity.
Advantages of Endogamous Unions
Endogamous unions foster cultural cohesion and strengthen community identity by promoting marriages within a specific social, ethnic, or religious group. These marriages often enhance social support networks and ensure the preservation of shared traditions and values across generations. Maintaining genetic homogeneity through endogamy can also reduce social conflict by reinforcing a common sense of belonging and solidarity.
Challenges Associated with Exogamous Marriages
Exogamous marriages often face challenges such as cultural clashes, differing religious beliefs, and social acceptance issues. Partners may struggle with integrating diverse family traditions, leading to communication barriers and potential conflicts. Navigating societal expectations and resistance from extended families can create stress that impacts the stability of the relationship.
Endogamy, Tradition, and Family Expectations
Endogamy, the practice of marrying within a specific social group, caste, or community, reinforces tradition and preserves cultural heritage. Family expectations often emphasize endogamous unions to maintain social cohesion and honor ancestral customs. This practice sustains identity and strengthens familial bonds by aligning marriage choices with long-standing societal norms.
Exogamy in Modern Multicultural Societies
Exogamy in modern multicultural societies promotes genetic diversity and social integration by encouraging marriage outside one's immediate cultural or social group. This practice fosters cross-cultural understanding and reduces ethnic polarization, contributing to more cohesive and inclusive communities. Research indicates that exogamous marriages enhance adaptive social networks and support broader societal harmony in diverse urban settings.
The Future of Marriage: Endogamy vs Exogamy Trends
Endogamy, the practice of marrying within a specific social group, ethnicity, or cultural community, continues to influence marriage patterns through traditions and familial expectations, maintaining cultural cohesion but often limiting diversity. Exogamy, favoring marriage outside one's social or ethnic group, is increasingly prevalent due to globalization, urbanization, and shifting social norms, promoting multicultural unions and broader social networks. Future trends suggest a complex interplay where hybrid practices emerge, balancing preservation of identity with inclusive, diverse marital alliances.
endogamy vs exogamy Infographic
 relationdif.com
relationdif.com