Spousal sponsorship allows a lawful permanent resident or citizen to sponsor their spouse for immigration, resulting in permanent residency upon approval, while a fiance(e) visa permits entry into the country solely for marriage after which the applicant must adjust status. Spousal sponsorship often involves a longer processing time compared to the fiance(e) visa, but provides immediate eligibility for permanent resident benefits after approval. Both pathways require proof of a genuine relationship, yet the fiance(e) visa is designed exclusively for couples intending to marry within 90 days of entry.
Table of Comparison
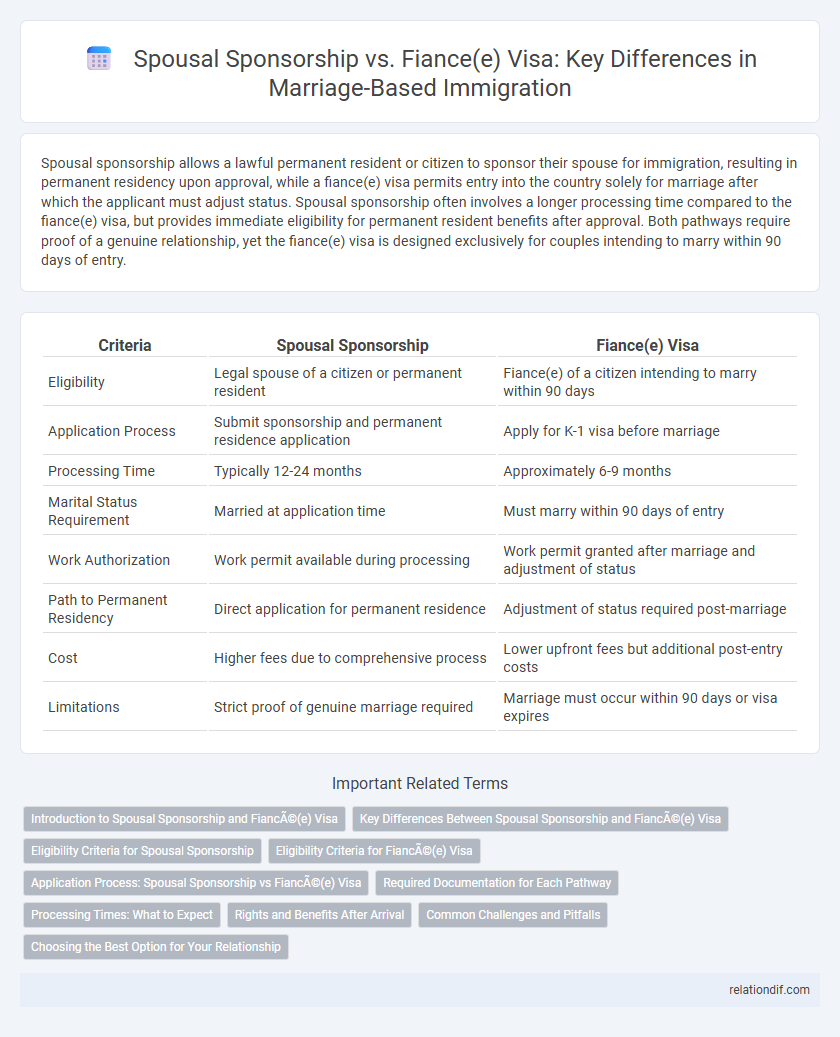
| Criteria | Spousal Sponsorship | Fiance(e) Visa |
|---|---|---|
| Eligibility | Legal spouse of a citizen or permanent resident | Fiance(e) of a citizen intending to marry within 90 days |
| Application Process | Submit sponsorship and permanent residence application | Apply for K-1 visa before marriage |
| Processing Time | Typically 12-24 months | Approximately 6-9 months |
| Marital Status Requirement | Married at application time | Must marry within 90 days of entry |
| Work Authorization | Work permit available during processing | Work permit granted after marriage and adjustment of status |
| Path to Permanent Residency | Direct application for permanent residence | Adjustment of status required post-marriage |
| Cost | Higher fees due to comprehensive process | Lower upfront fees but additional post-entry costs |
| Limitations | Strict proof of genuine marriage required | Marriage must occur within 90 days or visa expires |
Introduction to Spousal Sponsorship and Fiancé(e) Visa
Spousal sponsorship allows Canadian citizens and permanent residents to sponsor their legally married spouses for permanent residency. Fiance(e) visa, often referred to as a temporary resident visa, permits the foreign partner to enter Canada to marry within a specific timeframe. Both pathways require proof of genuine relationship, but spousal sponsorship leads directly to permanent residency while a fiance(e) visa is designed for couples planning marriage upon arrival.
Key Differences Between Spousal Sponsorship and Fiancé(e) Visa
Spousal sponsorship enables a permanent resident or citizen to sponsor their legally married spouse for immigration, while a fiance(e) visa allows a foreign national engaged to a citizen to enter the country to marry within a specified timeframe. Spousal sponsorship typically requires proof of a genuine marriage and provides immediate permanent residency, whereas fiance(e) visas are temporary, requiring the couple to marry within 90 days of entry before applying for permanent residency. Processing times and eligibility criteria differ significantly, with spousal sponsorship often having longer timelines but offering more immediate stability post-application.
Eligibility Criteria for Spousal Sponsorship
Eligibility criteria for spousal sponsorship require the applicant to be legally married to a Canadian citizen or permanent resident, demonstrating a genuine and ongoing marital relationship. The sponsor must meet financial requirements, including the ability to support the spouse without social assistance. Unlike the fiance(e) visa, spousal sponsorship mandates proof of cohabitation or shared responsibilities, confirming the authenticity of the marriage.
Eligibility Criteria for Fiancé(e) Visa
Eligibility criteria for a fiance(e) visa typically require the petitioner to be a U.S. citizen at least 18 years old and demonstrate intent to marry the foreign fiance(e) within 90 days of entry. Proof of a genuine relationship, such as evidence of having met in person within the last two years, is essential to qualify for the visa. Unlike spousal sponsorship, the fiance(e) visa does not require the couple to be legally married at the time of application.
Application Process: Spousal Sponsorship vs Fiancé(e) Visa
The spousal sponsorship application process requires submitting proof of a legally valid marriage and demonstrating the genuineness of the relationship, often involving extensive documentation and background checks. In contrast, the fiance(e) visa process focuses on proving the intent to marry within a specific timeframe, with an emphasis on relationship evidence and a binding marriage plan. Both pathways demand thorough documentation but differ in timing and the nature of required proof regarding the marital status.
Required Documentation for Each Pathway
Spousal sponsorship requires proof of a legally valid marriage, including marriage certificates, joint financial documents, and evidence of shared residence, while the fiance(e) visa demands a formal intent to marry within a specific timeframe supported by affidavits and engagement proof. Both pathways necessitate identity verification, police certificates, and medical examinations to establish eligibility and admissibility. Precise documentation of relationship authenticity is critical to satisfy immigration authorities for both sponsorship and fiance(e) visa applications.
Processing Times: What to Expect
Spousal sponsorship processing times typically range from 12 to 24 months, reflecting the thorough verification and relationship assessment involved. Fiance(e) visa processing is generally faster, averaging 6 to 12 months, as it primarily covers the initial intent to marry within a specific timeframe. Applicants should prepare for variable timelines influenced by country-specific factors, document completeness, and government backlogs.
Rights and Benefits After Arrival
Spousal sponsorship grants permanent residency immediately upon arrival, allowing the sponsored spouse full access to healthcare, employment, and social services. In contrast, a fiance(e) visa permits entry for marriage within a limited timeframe but typically requires application for permanent residency afterward, delaying access to certain benefits. Understanding these distinctions ensures informed decisions about legal rights, work authorization, and social benefits post-arrival.
Common Challenges and Pitfalls
Common challenges in spousal sponsorship include lengthy processing times and stringent documentation requirements, which often lead to delays and application denials. Fiance(e) visa applications face pitfalls such as proving genuine intent to marry within the visa's validity period and navigating complex interview processes. Both pathways require careful attention to detail to avoid errors that can result in visa refusals or prolonged separations.
Choosing the Best Option for Your Relationship
Spousal sponsorship and fiance(e) visas both facilitate reunification but differ significantly in process and timeline: spousal sponsorship requires a legal marriage and typically involves a longer approval period, while fiance(e) visas allow entrance to marry within a specified timeframe, often expediting the initial entry. Choosing the best option depends on factors such as the current relationship status, desired timeline, and long-term immigration goals, with spousal sponsorship providing a direct path to permanent residency. Understanding eligibility requirements, processing times, and the couple's future plans ensures selection of the optimal path for securing legal status and preserving relationship stability.
spousal sponsorship vs fiancé(e) visa Infographic
 relationdif.com
relationdif.com