Egalitarian partnerships emphasize equal decision-making power and shared responsibilities, fostering collaboration and mutual respect among partners. Traditional partnerships often feature a hierarchical structure, with roles and authority distributed unevenly according to seniority or investment. This shift towards egalitarianism enhances transparency and accountability, creating a more balanced and inclusive business environment.
Table of Comparison
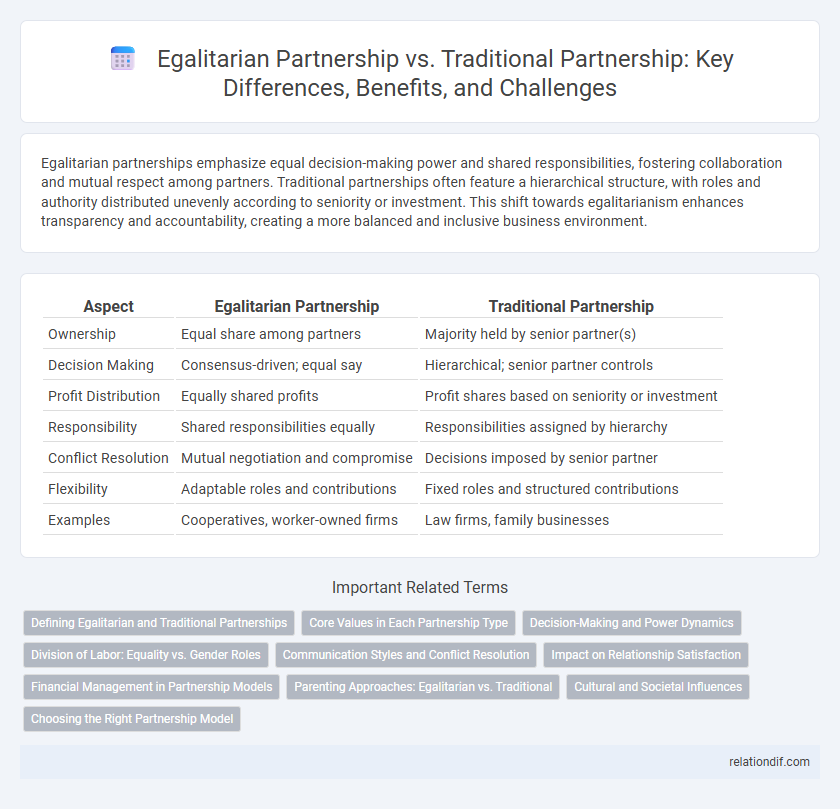
| Aspect | Egalitarian Partnership | Traditional Partnership |
|---|---|---|
| Ownership | Equal share among partners | Majority held by senior partner(s) |
| Decision Making | Consensus-driven; equal say | Hierarchical; senior partner controls |
| Profit Distribution | Equally shared profits | Profit shares based on seniority or investment |
| Responsibility | Shared responsibilities equally | Responsibilities assigned by hierarchy |
| Conflict Resolution | Mutual negotiation and compromise | Decisions imposed by senior partner |
| Flexibility | Adaptable roles and contributions | Fixed roles and structured contributions |
| Examples | Cooperatives, worker-owned firms | Law firms, family businesses |
Defining Egalitarian and Traditional Partnerships
Egalitarian partnerships emphasize equal decision-making power and shared responsibilities between partners, fostering mutual respect and balanced contributions. Traditional partnerships typically involve a hierarchical structure where roles and authority are clearly defined, often with one partner holding more control over business operations. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for selecting a partnership model aligned with the organization's values and goals.
Core Values in Each Partnership Type
Egalitarian partnerships emphasize shared decision-making, mutual respect, and equal responsibility, fostering transparency and collaboration as core values. Traditional partnerships typically prioritize hierarchy, defined roles, and accountability, with a focus on leadership authority and responsibility distribution. These foundational values shape communication dynamics and influence the overall effectiveness and sustainability of each partnership model.
Decision-Making and Power Dynamics
Egalitarian partnerships emphasize equal decision-making authority among all members, fostering collaborative power dynamics where input is valued regardless of hierarchy. Traditional partnerships often concentrate decision-making power in senior partners or founders, creating a top-down dynamic that can limit diverse perspectives. This contrast significantly impacts the agility and inclusiveness of business strategies and conflict resolution.
Division of Labor: Equality vs. Gender Roles
Egalitarian partnerships emphasize an equal division of labor, where tasks and responsibilities are shared regardless of gender, fostering mutual respect and collaboration. Traditional partnerships often assign roles based on gender norms, with women managing domestic duties and men handling external work. This division impacts relationship dynamics, job satisfaction, and overall family well-being by shaping expectations and workload distribution.
Communication Styles and Conflict Resolution
Egalitarian partnerships emphasize open, transparent communication styles where all parties actively listen and contribute equally, fostering mutual respect and understanding. Conflict resolution in such partnerships relies on collaborative problem-solving techniques that prioritize consensus and shared goals rather than hierarchical decision-making. Traditional partnerships often feature top-down communication flows and may use authoritative conflict resolution methods, potentially limiting equal participation and prolonging disputes.
Impact on Relationship Satisfaction
Egalitarian partnerships, characterized by equal power distribution and shared decision-making, tend to enhance relationship satisfaction by fostering mutual respect and collaboration. Traditional partnerships often rely on defined roles and hierarchical dynamics, which can lead to imbalance and reduced satisfaction if one partner feels undervalued. Research indicates that couples in egalitarian partnerships report higher levels of emotional support and communication, contributing to overall relational happiness.
Financial Management in Partnership Models
Egalitarian partnerships emphasize equal financial contributions, transparent profit-sharing, and joint decision-making, fostering trust and aligning incentives among partners. Traditional partnerships often feature hierarchical financial management, where capital inputs and profit allocations reflect seniority or ownership stakes, potentially causing imbalances in control and resource distribution. Effective financial management in partnership models requires clear agreements on capital roles, expense responsibilities, and equitable revenue sharing to ensure sustainable operations and partner satisfaction.
Parenting Approaches: Egalitarian vs. Traditional
Egalitarian partnerships emphasize shared parenting responsibilities, ensuring both partners actively participate in childcare, decision-making, and household duties, fostering equal involvement and mutual support. In contrast, traditional partnerships often assign primary caregiving roles to one partner, typically the mother, while the other assumes a provider role, leading to asymmetric parenting dynamics. Research shows that egalitarian parenting approaches contribute to improved child development outcomes and stronger couple satisfaction compared to traditional models.
Cultural and Societal Influences
Egalitarian partnerships promote equal decision-making and shared responsibilities, reflecting evolving cultural values of fairness and gender equality. Traditional partnerships often align with long-standing societal norms where roles are rigidly defined by gender or hierarchy. Cultural shifts towards inclusivity and empowerment increasingly challenge these conventional models, reshaping how partnerships are structured and perceived.
Choosing the Right Partnership Model
Selecting the ideal partnership model depends on aligning business goals with operational dynamics; an egalitarian partnership emphasizes equal decision-making power and profit sharing, fostering collaboration and mutual respect. In contrast, a traditional partnership often designates roles and profit distribution based on capital contribution or expertise, potentially streamlining decision processes but risking imbalance in partner influence. Evaluating factors such as trust levels, management style preferences, and long-term vision is crucial for determining whether an egalitarian or traditional partnership best supports sustainable business growth.
egalitarian partnership vs traditional partnership Infographic
 relationdif.com
relationdif.com