Secure attachment in partnerships fosters trust, open communication, and emotional stability, enabling partners to support each other confidently. In contrast, anxious attachment often leads to fear of abandonment, excessive need for reassurance, and heightened sensitivity to relationship dynamics. Understanding these attachment styles helps couples build healthier, more resilient connections.
Table of Comparison
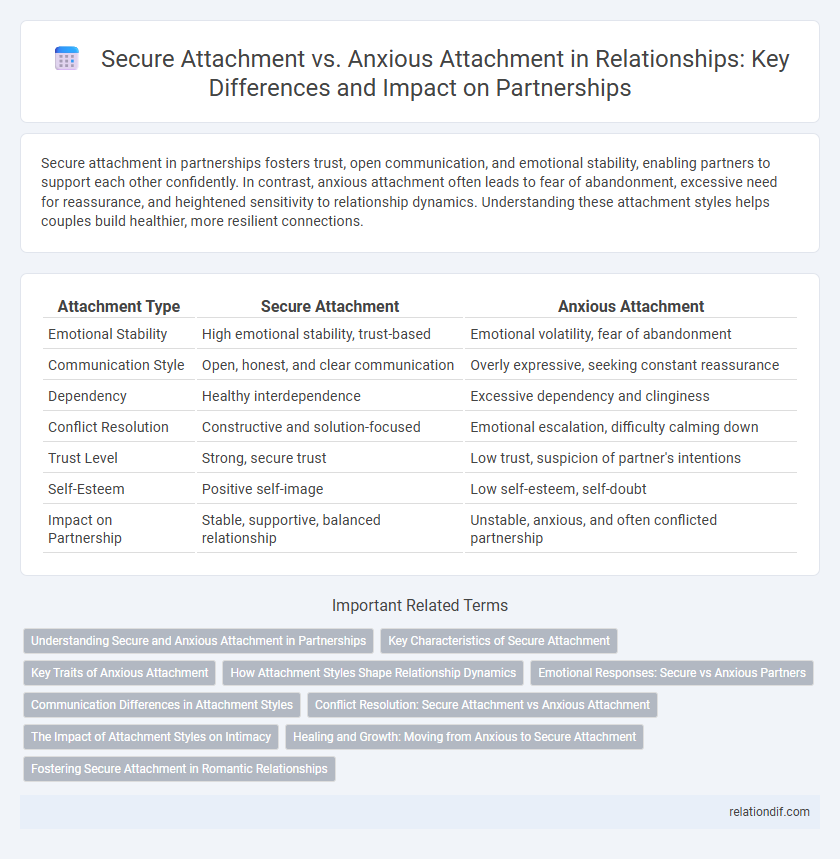
| Attachment Type | Secure Attachment | Anxious Attachment |
|---|---|---|
| Emotional Stability | High emotional stability, trust-based | Emotional volatility, fear of abandonment |
| Communication Style | Open, honest, and clear communication | Overly expressive, seeking constant reassurance |
| Dependency | Healthy interdependence | Excessive dependency and clinginess |
| Conflict Resolution | Constructive and solution-focused | Emotional escalation, difficulty calming down |
| Trust Level | Strong, secure trust | Low trust, suspicion of partner's intentions |
| Self-Esteem | Positive self-image | Low self-esteem, self-doubt |
| Impact on Partnership | Stable, supportive, balanced relationship | Unstable, anxious, and often conflicted partnership |
Understanding Secure and Anxious Attachment in Partnerships
Secure attachment in partnerships fosters trust, open communication, and emotional stability, allowing partners to feel safe and valued. In contrast, anxious attachment is characterized by fear of abandonment, heightened sensitivity to rejection, and a strong need for reassurance, which can create tension and insecurity. Recognizing these attachment styles enables couples to improve empathy, address emotional needs, and build healthier, more resilient relationships.
Key Characteristics of Secure Attachment
Secure attachment in partnerships is characterized by trust, emotional openness, and the ability to communicate effectively without fear of rejection. Individuals with secure attachment maintain a healthy balance between intimacy and independence, fostering mutual respect and support. This attachment style promotes relationship stability, resilience, and positive conflict resolution.
Key Traits of Anxious Attachment
Anxious attachment is characterized by a deep fear of abandonment, heightened sensitivity to partner's cues, and an intense need for reassurance and closeness. Individuals with this attachment style often exhibit clinginess, emotional volatility, and difficulty trusting their partner's reliability. These key traits can create challenges in forming secure and stable partnerships, as anxious attachment fosters dependency and insecurity.
How Attachment Styles Shape Relationship Dynamics
Secure attachment fosters trust and effective communication, enabling partners to navigate conflicts with empathy and support. Anxious attachment often triggers heightened need for reassurance and fear of abandonment, leading to emotional dependency and miscommunication. These attachment styles fundamentally influence intimacy, emotional regulation, and overall relationship satisfaction.
Emotional Responses: Secure vs Anxious Partners
Secure partners exhibit consistent emotional regulation, fostering trust and open communication, which strengthens relationship bonds. Anxious partners often experience heightened emotional sensitivity and fear of rejection, leading to frequent reassurance-seeking and potential misunderstandings. The interplay between secure and anxious attachment styles significantly influences emotional responses, affecting overall relationship stability and intimacy levels.
Communication Differences in Attachment Styles
Secure attachment fosters open, honest communication characterized by trust, empathy, and responsiveness to a partner's needs. In contrast, anxious attachment often leads to heightened sensitivity to perceived rejection, resulting in frequent reassurance-seeking, emotional volatility, and difficulty expressing needs without fear of abandonment. Understanding these communication patterns is essential for improving dialogue, reducing conflicts, and strengthening the partnership.
Conflict Resolution: Secure Attachment vs Anxious Attachment
Secure attachment in partnerships promotes effective conflict resolution through open communication, emotional regulation, and trust, enabling partners to address disagreements constructively. In contrast, anxious attachment often leads to heightened sensitivity, fear of rejection, and reactive behaviors that can escalate conflicts and hinder resolution. Developing secure attachment patterns fosters resilience and collaboration, reducing misunderstandings and strengthening the relational bond.
The Impact of Attachment Styles on Intimacy
Secure attachment fosters trust and open communication, enhancing emotional intimacy and relationship satisfaction. Anxious attachment often triggers fear of abandonment and hypervigilance, undermining intimacy by creating emotional distance and misunderstanding. Understanding these attachment styles helps partners navigate intimacy challenges and build stronger, more resilient connections.
Healing and Growth: Moving from Anxious to Secure Attachment
Healing from anxious attachment involves cultivating self-awareness and consistent emotional responsiveness within the partnership, fostering a secure base of trust and safety. Therapeutic interventions such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and emotionally focused therapy (EFT) support growth by addressing fear of abandonment and enhancing communication patterns. Growth toward secure attachment strengthens emotional resilience, deepens intimacy, and promotes balanced interdependence between partners.
Fostering Secure Attachment in Romantic Relationships
Fostering secure attachment in romantic relationships involves creating consistent emotional availability and open communication to build trust and intimacy. Partners who respond sensitively to each other's needs reduce anxiety and promote a sense of safety, which strengthens the bond. Developing secure attachment patterns enhances relationship satisfaction, emotional resilience, and long-term connection stability.
Secure Attachment vs Anxious Attachment Infographic
 relationdif.com
relationdif.com