Active listening in pet support involves fully engaging with the animal's signals and responding thoughtfully, which strengthens the bond and addresses their needs effectively. Passive acknowledgment, however, merely recognizes the pet's behavior without meaningful interaction, potentially leading to misunderstandings or unmet emotional needs. Prioritizing active listening ensures pets feel heard and supported, enhancing their overall well-being and trust in their caregivers.
Table of Comparison
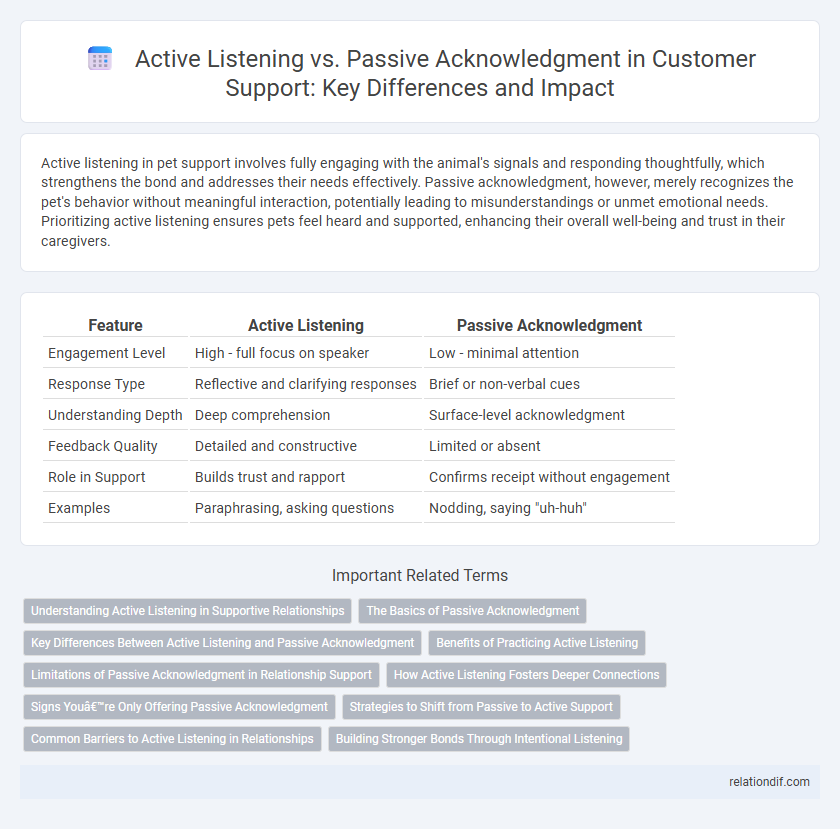
| Feature | Active Listening | Passive Acknowledgment |
|---|---|---|
| Engagement Level | High - full focus on speaker | Low - minimal attention |
| Response Type | Reflective and clarifying responses | Brief or non-verbal cues |
| Understanding Depth | Deep comprehension | Surface-level acknowledgment |
| Feedback Quality | Detailed and constructive | Limited or absent |
| Role in Support | Builds trust and rapport | Confirms receipt without engagement |
| Examples | Paraphrasing, asking questions | Nodding, saying "uh-huh" |
Understanding Active Listening in Supportive Relationships
Active listening in supportive relationships involves fully engaging with the speaker through verbal affirmations, reflective feedback, and attentive body language, which fosters trust and deeper understanding. Passive acknowledgment merely signals hearing without processing or responding to emotional cues, often leaving the speaker feeling unheard or undervalued. Emphasizing active listening enhances communication quality, emotional connection, and problem resolution effectiveness in support contexts.
The Basics of Passive Acknowledgment
Passive acknowledgment in support involves recognizing a customer's message without fully engaging or clarifying their concerns, which may lead to misunderstandings or unresolved issues. This basic technique often includes simple cues like nodding or brief verbal affirmations, but lacks the depth needed for effective problem resolution. Understanding the limits of passive acknowledgment helps support agents develop more active listening skills to enhance customer satisfaction and communication accuracy.
Key Differences Between Active Listening and Passive Acknowledgment
Active listening involves fully concentrating, understanding, and responding thoughtfully to the speaker, enhancing communication effectiveness. Passive acknowledgment merely signals that the message is received without engaging or providing feedback, often missing critical emotional or informational cues. Key differences include depth of engagement, feedback presence, and impact on relationship building, with active listening fostering trust and clarity while passive acknowledgment may lead to misunderstandings.
Benefits of Practicing Active Listening
Practicing active listening in support interactions leads to improved customer satisfaction by accurately understanding their needs and concerns. It fosters stronger rapport and trust through empathetic engagement, reducing misunderstandings and repeat inquiries. Active listening also enhances problem-solving efficiency by allowing support agents to address issues more precisely and promptly.
Limitations of Passive Acknowledgment in Relationship Support
Passive acknowledgment in relationship support often leads to misunderstandings due to a lack of verbal and nonverbal feedback, which active listening provides. It limits emotional connection and validation, preventing partners from feeling truly heard and supported. This can cause unresolved conflicts and decreased trust over time.
How Active Listening Fosters Deeper Connections
Active listening enhances support interactions by fully engaging with the speaker's emotions and content, leading to more meaningful and empathetic responses. Unlike passive acknowledgment, which merely signals receipt of information, active listening encourages trust and openness, fostering stronger relationships. This deeper connection enables more effective problem-solving and emotional validation in support settings.
Signs You’re Only Offering Passive Acknowledgment
Signs you're only offering passive acknowledgment include nodding without verbal feedback, responding with brief or generic phrases like "okay" or "uh-huh," and avoiding eye contact or showing minimal facial expressions. These behaviors indicate a lack of genuine engagement and can make the speaker feel unheard or undervalued. Active listening involves more dynamic gestures such as paraphrasing, asking clarifying questions, and maintaining consistent eye contact to demonstrate true understanding and empathy.
Strategies to Shift from Passive to Active Support
Active listening involves fully engaging with the speaker by providing feedback, asking clarifying questions, and summarizing key points, which creates a deeper emotional connection and trust. Strategies to shift from passive acknowledgment to active support include maintaining eye contact, using verbal affirmations such as "I understand" or "Tell me more," and reflecting feelings expressed by the speaker to validate their experience. Developing mindfulness and resisting the urge to interrupt or offer unsolicited advice enhances empathetic communication and strengthens the support dynamic.
Common Barriers to Active Listening in Relationships
Common barriers to active listening in relationships include distractions, emotional biases, and preconceived judgments that hinder genuine understanding. People often rely on passive acknowledgment, such as nodding without processing the speaker's message, which leads to miscommunication and unresolved conflicts. Improving active listening requires overcoming these barriers by focusing fully, empathizing sincerely, and clarifying points for mutual comprehension.
Building Stronger Bonds Through Intentional Listening
Active listening involves fully engaging with the speaker, capturing both verbal and non-verbal cues to ensure genuine understanding. Passive acknowledgment merely signals receipt without processing the deeper message, often leading to miscommunication or weakened trust. Building stronger bonds through intentional listening requires empathy, feedback, and attention, fostering meaningful connections and effective support.
active listening vs passive acknowledgment Infographic
 relationdif.com
relationdif.com