Support pets play a crucial role in both help-seeking and help-offering dynamics, providing emotional comfort to individuals in distress while actively responding to their needs. Help-seeking behaviors in support pets often involve vocalizations or physical gestures that signal the need for attention or assistance, encouraging positive interaction from their owners. These pets simultaneously offer help through their calming presence, tactile stimulation, and intuitive understanding of human emotions, creating a reciprocal relationship that enhances mental well-being.
Table of Comparison
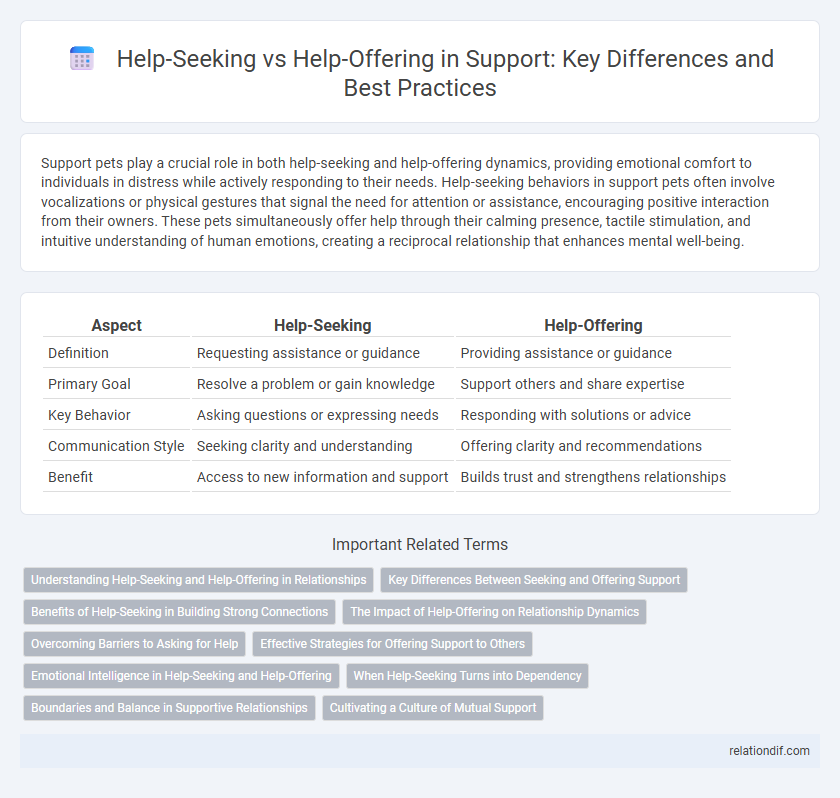
| Aspect | Help-Seeking | Help-Offering |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Requesting assistance or guidance | Providing assistance or guidance |
| Primary Goal | Resolve a problem or gain knowledge | Support others and share expertise |
| Key Behavior | Asking questions or expressing needs | Responding with solutions or advice |
| Communication Style | Seeking clarity and understanding | Offering clarity and recommendations |
| Benefit | Access to new information and support | Builds trust and strengthens relationships |
Understanding Help-Seeking and Help-Offering in Relationships
Help-seeking in relationships involves actively expressing needs and vulnerabilities to receive emotional or practical support, which fosters trust and intimacy. Help-offering requires attentiveness and empathy to recognize when a partner needs assistance, promoting mutual care and strengthening relational bonds. Balancing both dynamics enhances communication patterns and contributes to healthier, more resilient partnerships.
Key Differences Between Seeking and Offering Support
Help-seeking involves actively reaching out to others for assistance during challenging situations, signaling vulnerability and the need for external resources. Offering support, on the other hand, requires readiness to listen, provide empathy, and share solutions, emphasizing the role of the helper in fostering connection and resilience. Understanding these key differences enhances effective communication and facilitates stronger interpersonal dynamics in support networks.
Benefits of Help-Seeking in Building Strong Connections
Help-seeking fosters vulnerability and trust, laying a foundation for deeper, more resilient relationships by encouraging open communication and empathy. It creates opportunities for mutual support, allowing individuals to better understand and respond to each other's needs. By embracing help-seeking, people build stronger social bonds that enhance emotional well-being and collective problem-solving.
The Impact of Help-Offering on Relationship Dynamics
Help-offering significantly strengthens relationship dynamics by fostering trust, empathy, and mutual support among individuals. When one party actively provides assistance, it often encourages reciprocal behaviors that enhance emotional bonds and collaboration. This proactive support can create a positive feedback loop, improving communication and increasing overall relational satisfaction.
Overcoming Barriers to Asking for Help
Overcoming barriers to asking for help requires addressing common psychological factors such as fear of judgment, perceived loss of independence, and stigma associated with vulnerability. Encouraging open communication and fostering trust within support networks can create a safe environment that normalizes help-seeking behavior. Providing clear information about available resources and emphasizing reciprocal support often reduces reluctance and empowers individuals to request assistance when needed.
Effective Strategies for Offering Support to Others
Effective strategies for offering support to others emphasize active listening, empathy, and validation of their feelings to foster trust and openness. Encouraging open communication and avoiding judgment helps create a safe environment where individuals feel comfortable sharing their concerns. Providing practical assistance tailored to the person's specific needs enhances the impact of support, leading to better emotional and psychological outcomes.
Emotional Intelligence in Help-Seeking and Help-Offering
Emotional intelligence enhances both help-seeking and help-offering by enabling individuals to recognize and regulate their own emotions while accurately perceiving others' feelings, fostering effective communication and empathy. High emotional intelligence facilitates expressing vulnerability appropriately when seeking help and offering support with genuine understanding and responsiveness. Integrating emotional intelligence in support dynamics leads to stronger interpersonal connections and more successful problem resolution.
When Help-Seeking Turns into Dependency
Help-seeking becomes dependency when individuals rely excessively on others for solutions, undermining their autonomy and problem-solving skills. This dependency can hinder personal growth and strain support systems, creating imbalances in help-offering dynamics. Encouraging self-efficacy and setting clear boundaries promotes healthier interactions and sustainable support relationships.
Boundaries and Balance in Supportive Relationships
Establishing clear boundaries in supportive relationships ensures help-seeking remains respectful and prevents emotional exhaustion for help-offering individuals. Balancing the dynamic by recognizing limits promotes mutual trust and sustainable support exchanges. Effective communication about needs and capacities safeguards both parties' well-being and fosters healthy interdependence.
Cultivating a Culture of Mutual Support
Cultivating a culture of mutual support enhances organizational resilience by encouraging both help-seeking and help-offering behaviors among team members. Emphasizing psychological safety and open communication fosters an environment where individuals feel empowered to request assistance and proactively provide support, leading to improved collaboration and productivity. Tracking engagement metrics and feedback loops helps organizations identify gaps and reinforce supportive practices that sustain collective well-being.
help-seeking vs help-offering Infographic
 relationdif.com
relationdif.com