Proactively offering support to a pet in distress can prevent anxiety and promote a sense of safety before behaviors escalate. Observing subtle signs of discomfort or stress allows caregivers to intervene early, fostering trust and emotional well-being. Taking initiative demonstrates attentiveness and reinforces the bond between pet and owner, enhancing overall care quality.
Table of Comparison
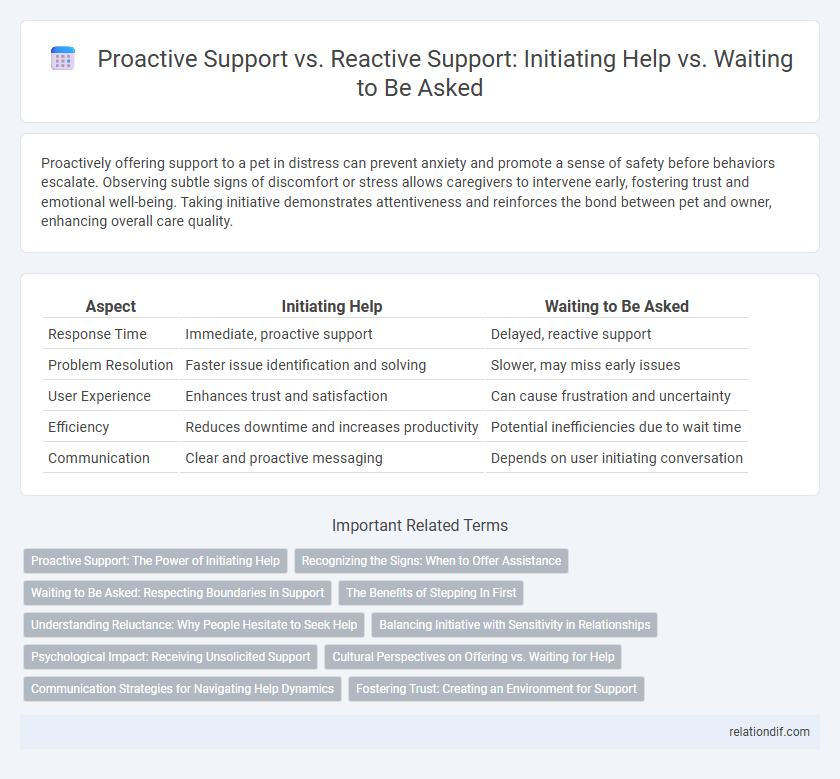
| Aspect | Initiating Help | Waiting to Be Asked |
|---|---|---|
| Response Time | Immediate, proactive support | Delayed, reactive support |
| Problem Resolution | Faster issue identification and solving | Slower, may miss early issues |
| User Experience | Enhances trust and satisfaction | Can cause frustration and uncertainty |
| Efficiency | Reduces downtime and increases productivity | Potential inefficiencies due to wait time |
| Communication | Clear and proactive messaging | Depends on user initiating conversation |
Proactive Support: The Power of Initiating Help
Proactive support significantly enhances customer satisfaction by anticipating issues and addressing them before they escalate, reducing downtime and frustration. Initiating help empowers support teams to identify potential problems through monitoring and data analysis, ensuring timely interventions that prevent disruptions. This approach fosters trust and loyalty by demonstrating a commitment to seamless user experience and continuous improvement.
Recognizing the Signs: When to Offer Assistance
Recognizing the signs of someone needing help involves observing changes in behavior, facial expressions, or body language that signal distress or confusion. Offering assistance promptly can prevent escalation and demonstrate empathy, fostering a supportive environment. Waiting to be asked may delay crucial support, underscoring the importance of proactive intervention in effective communication and care.
Waiting to Be Asked: Respecting Boundaries in Support
Waiting to be asked before offering support respects personal boundaries and fosters trust by allowing individuals to express their readiness for assistance. This approach promotes autonomy and reduces the risk of overwhelming or imposing help on someone unprepared to receive it. Respecting these boundaries creates a more empathetic environment where support is both meaningful and welcome.
The Benefits of Stepping In First
Stepping in first when offering help enhances team efficiency by addressing issues before they escalate, fostering a proactive support culture. Initiating assistance demonstrates leadership, builds trust, and encourages open communication within groups. Early intervention reduces downtime and accelerates problem resolution, benefiting overall productivity.
Understanding Reluctance: Why People Hesitate to Seek Help
Understanding reluctance is crucial in providing effective support, as many individuals hesitate to seek help due to fear of judgment, vulnerability, or perceived burden. Initiating help proactively can bridge this gap by offering reassurance and demonstrating empathy, which encourages open communication and trust. Recognizing subtle cues and respecting boundaries enhances the likelihood of timely assistance and positive outcomes.
Balancing Initiative with Sensitivity in Relationships
Taking initiative to offer support demonstrates attentiveness and care, fostering trust and connection in relationships. It is crucial to balance this proactive approach with sensitivity, recognizing when others need space or prefer to seek help themselves. Effective support respects personal boundaries while ensuring assistance is available, enhancing emotional well-being and mutual respect.
Psychological Impact: Receiving Unsolicited Support
Receiving unsolicited support often triggers mixed psychological responses, including feelings of vulnerability, gratitude, or perceived loss of autonomy. Initiating help proactively can reduce anxiety by signaling care and attentiveness, fostering trust and emotional safety. Conversely, waiting to be asked may preserve personal boundaries but risks neglecting timely assistance and deepening isolation or stress.
Cultural Perspectives on Offering vs. Waiting for Help
Cultural norms significantly influence whether individuals initiate help or wait to be asked, with collectivist societies often prioritizing proactive support to maintain group harmony. In contrast, individualistic cultures may emphasize personal autonomy, leading people to wait for explicit requests before offering assistance. Understanding these cultural perspectives enhances effective communication and fosters respectful support dynamics in diverse environments.
Communication Strategies for Navigating Help Dynamics
Effective communication strategies involve proactively initiating help to demonstrate attentiveness and build trust, rather than passively waiting for requests. Clear, empathetic messaging and open-ended questions encourage dialogue and allow support providers to understand needs before issues escalate. Timely, transparent exchanges enhance collaboration and ensure that assistance is both appropriate and impactful.
Fostering Trust: Creating an Environment for Support
Initiating help proactively fosters trust by demonstrating attentiveness and reliability, which encourages open communication and a supportive atmosphere. Creating an environment where assistance is readily offered reduces hesitation and builds strong interpersonal connections. Establishing these trustful dynamics enhances overall team cohesion and promotes a culture of mutual support.
Initiating help vs waiting to be asked Infographic
 relationdif.com
relationdif.com