Assumed fidelity often relies on trust without evidence, which can lead to vulnerabilities in relationships or business partnerships. Verified loyalty, on the other hand, is established through consistent actions and transparent communication, reinforcing confidence and commitment. This distinction ensures that trust is not blindly given but earned and maintained through accountability.
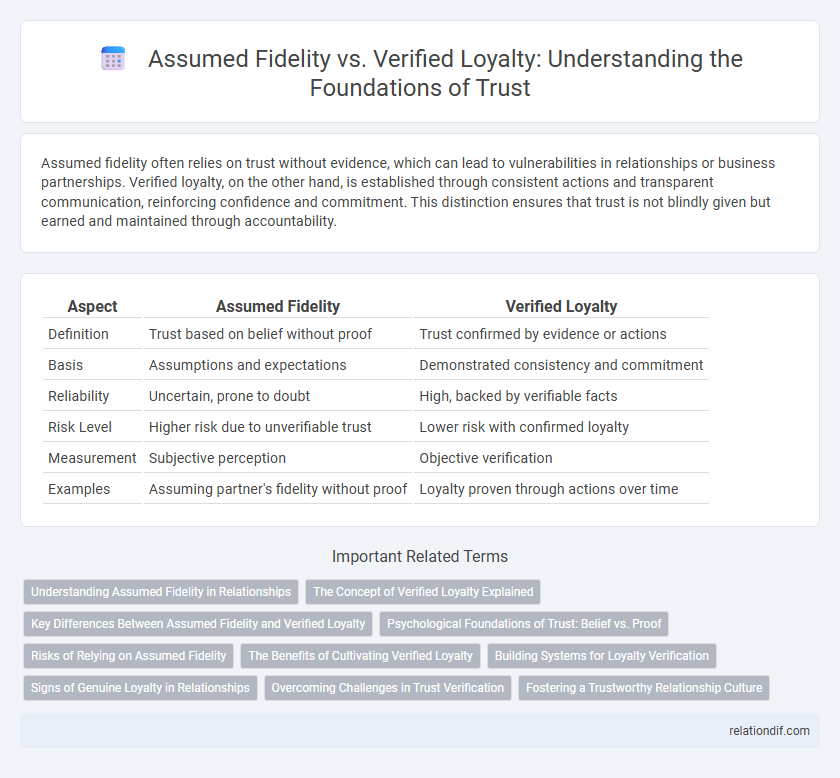
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Assumed Fidelity | Verified Loyalty |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Trust based on belief without proof | Trust confirmed by evidence or actions |
| Basis | Assumptions and expectations | Demonstrated consistency and commitment |
| Reliability | Uncertain, prone to doubt | High, backed by verifiable facts |
| Risk Level | Higher risk due to unverifiable trust | Lower risk with confirmed loyalty |
| Measurement | Subjective perception | Objective verification |
| Examples | Assuming partner's fidelity without proof | Loyalty proven through actions over time |
Understanding Assumed Fidelity in Relationships
Assumed fidelity in relationships relies on the expectation that partners remain loyal without explicit verification, often based on implicit trust and past behavior patterns. This approach can foster emotional security but risks vulnerability if expectations are unmet or communication falters. Prioritizing transparent dialogue and periodic reaffirmation helps balance assumed fidelity with the need for verified loyalty, strengthening relational trust.
The Concept of Verified Loyalty Explained
Verified loyalty involves evidence-based trust built through consistent actions and transparent communication, contrasting with assumed fidelity, which relies on unproven beliefs or expectations. This concept emphasizes accountability and measurable commitment, reducing the risk of misplaced trust in personal or professional relationships. Verified loyalty strengthens bonds by fostering reliability and demonstrating genuine, ongoing dedication.
Key Differences Between Assumed Fidelity and Verified Loyalty
Assumed fidelity relies on the expectation that trustworthiness exists without concrete proof, often leading to vulnerability in relationships or business dealings. Verified loyalty is demonstrated through consistent actions and tangible evidence, reinforcing reliability and commitment over time. Understanding the key differences between these concepts helps to build stronger, more secure interpersonal and organizational bonds based on proven integrity rather than mere assumptions.
Psychological Foundations of Trust: Belief vs. Proof
Assumed fidelity relies on belief systems where trust is granted based on perceived intentions and past behaviors, rooted in psychological predispositions toward social bonding. Verified loyalty, however, demands empirical proof or consistent actions that substantiate trustworthiness, reinforcing the neural mechanisms tied to reward and reliability in human cognition. Understanding the psychological foundations of trust reveals the tension between cognitive biases favoring belief and the necessity for tangible verification in relationships.
Risks of Relying on Assumed Fidelity
Relying on assumed fidelity exposes organizations and individuals to significant risks including betrayal, misinformation, and security breaches because trust is granted without concrete evidence. Verified loyalty, supported by consistent actions and transparent communication, mitigates these dangers by ensuring accountability and genuine commitment. Failure to distinguish between assumed fidelity and verified loyalty can lead to operational failures, financial losses, and damaged reputations in both personal and professional contexts.
The Benefits of Cultivating Verified Loyalty
Cultivating verified loyalty enhances organizational trust by ensuring commitments are consistently confirmed through transparent actions and measurable outcomes. Verified loyalty strengthens relationships, reduces risks associated with misplaced assumptions, and drives sustained collaboration by aligning incentives with demonstrated reliability. Businesses leveraging verified loyalty experience improved customer retention, higher employee engagement, and greater brand reputation in competitive markets.
Building Systems for Loyalty Verification
Building systems for loyalty verification relies on integrating biometric data, behavioral analytics, and blockchain technology to ensure accurate assessment of assumed fidelity. Verified loyalty enhances trust in digital transactions by providing immutable proof of consistent commitment, reducing fraud and insider threats. Implementing multi-layered authentication mechanisms and continuous monitoring strengthens organizational resilience and stakeholder confidence.
Signs of Genuine Loyalty in Relationships
Signs of genuine loyalty in relationships include consistent support during challenging times, honesty even when the truth is uncomfortable, and reliability in keeping promises without external verification. Assumed fidelity often relies on trust without evidence, whereas verified loyalty is demonstrated through actions that reinforce commitment and respect. Observable behaviors such as active listening, prioritizing the relationship, and transparent communication serve as indicators of true loyalty beyond mere assumption.
Overcoming Challenges in Trust Verification
Overcoming challenges in trust verification requires distinguishing between assumed fidelity and verified loyalty through consistent evidence and transparent communication. Implementing reliable methods such as behavioral analysis, third-party validation, and regular feedback loops enhances trust accuracy in personal and professional relationships. Advanced technologies like blockchain and biometric verification further strengthen the ability to authenticate loyalty and reduce reliance on assumptions.
Fostering a Trustworthy Relationship Culture
Fostering a trustworthy relationship culture requires shifting focus from assumed fidelity to verified loyalty through consistent transparency and open communication. Implementing clear expectations and regular feedback mechanisms enhances accountability and builds genuine trust among team members. Empirical data shows organizations with verified loyalty practices report a 30% increase in collaboration effectiveness and employee satisfaction.
Assumed fidelity vs verified loyalty Infographic
 relationdif.com
relationdif.com