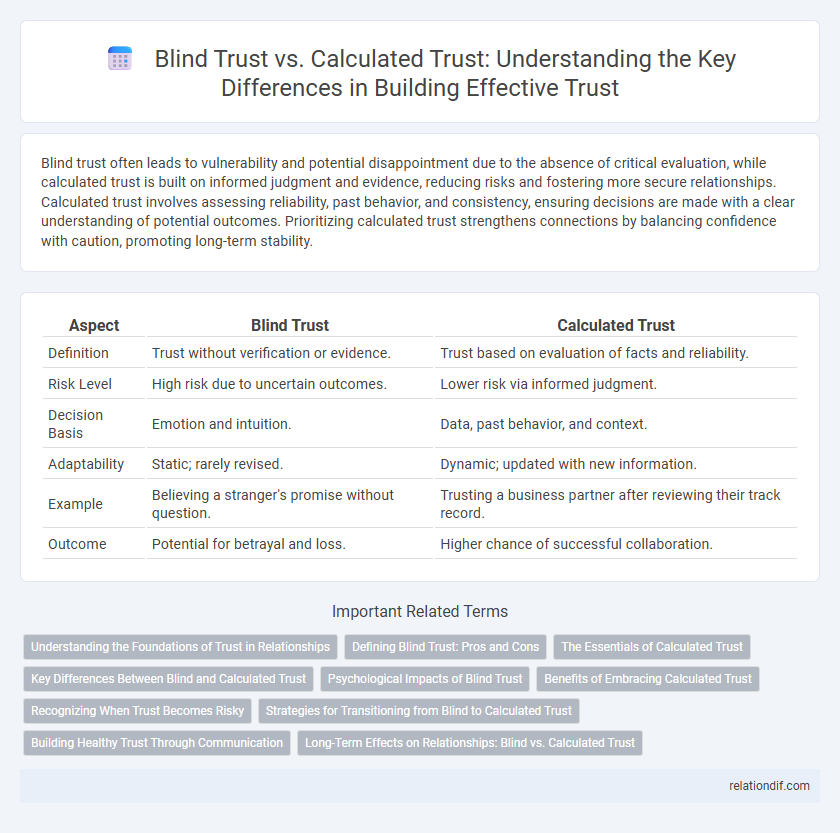
Blind trust often leads to vulnerability and potential disappointment due to the absence of critical evaluation, while calculated trust is built on informed judgment and evidence, reducing risks and fostering more secure relationships. Calculated trust involves assessing reliability, past behavior, and consistency, ensuring decisions are made with a clear understanding of potential outcomes. Prioritizing calculated trust strengthens connections by balancing confidence with caution, promoting long-term stability.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Blind Trust | Calculated Trust |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Trust without verification or evidence. | Trust based on evaluation of facts and reliability. |
| Risk Level | High risk due to uncertain outcomes. | Lower risk via informed judgment. |
| Decision Basis | Emotion and intuition. | Data, past behavior, and context. |
| Adaptability | Static; rarely revised. | Dynamic; updated with new information. |
| Example | Believing a stranger's promise without question. | Trusting a business partner after reviewing their track record. |
| Outcome | Potential for betrayal and loss. | Higher chance of successful collaboration. |
Understanding the Foundations of Trust in Relationships
Blind trust assumes reliability without evidence, often leading to vulnerability and misplaced confidence in relationships. Calculated trust is built on consistent behavior, transparency, and verified past interactions, forming a solid foundation grounded in experience and rational assessment. Understanding these trust types highlights the importance of evaluating trustworthiness through actions and communication to foster healthy, resilient relationships.
Defining Blind Trust: Pros and Cons
Blind trust involves placing complete confidence in someone without verifying their actions or intentions, which can foster quick decision-making and strengthen relationships by reducing doubt. However, it carries significant risks such as vulnerability to deception, exploitation, and potential loss of control over important outcomes. Balancing blind trust with awareness and periodic assessment is essential to mitigate negative consequences while maintaining interpersonal connections.
The Essentials of Calculated Trust
Calculated trust relies on a deliberate assessment of risks and benefits, incorporating verified information and past experiences to minimize uncertainty. It involves setting clear expectations, monitoring commitments, and maintaining transparency to ensure accountability and foster reliability. This approach strengthens relationships by balancing confidence with critical judgment, promoting sustainable and mutually beneficial interactions.
Key Differences Between Blind and Calculated Trust
Blind trust involves unquestioning confidence without verification, often leading to vulnerability due to lack of evidence or scrutiny. Calculated trust is established through careful assessment of reliability, past behavior, and risk evaluation, promoting informed decision-making and accountability. Key differences include the presence of critical analysis in calculated trust versus the acceptance of uncertainty in blind trust, impacting the level of security and control in relationships.
Psychological Impacts of Blind Trust
Blind trust often leads to increased vulnerability and stress as individuals may overlook warning signs or ignore critical information, resulting in potential emotional harm. Psychological impacts include diminished self-esteem and impaired judgment, as reliance on unquestioned trust hinders personal growth and decision-making skills. This form of trust can foster dependency, reducing an individual's ability to critically assess situations and potentially leading to betrayal or disappointment.
Benefits of Embracing Calculated Trust
Embracing calculated trust allows individuals and organizations to make informed decisions by evaluating risks and benefits, fostering stronger, more reliable relationships. Unlike blind trust, calculated trust promotes accountability and transparency through evidence-based judgment and ongoing assessment. This strategic approach reduces vulnerability to deception and enhances long-term collaboration and success.
Recognizing When Trust Becomes Risky
Blind trust disregards vulnerable signals and situational context, often leading to exploitation and unmet expectations. Calculated trust involves evaluating past behaviors, verifying intentions, and setting boundaries, minimizing potential harm. Recognizing risky trust requires attentiveness to inconsistencies, lack of transparency, and repeated breaches in trustworthiness.
Strategies for Transitioning from Blind to Calculated Trust
Shifting from blind trust to calculated trust requires implementing verification mechanisms and setting clear boundaries to minimize risks. Employing gradual information sharing and consistent performance evaluations fosters a data-driven approach, enhancing trustworthiness over time. Incorporating feedback loops and contingency plans ensures trust remains adaptive and resilient in dynamic relationships.
Building Healthy Trust Through Communication
Building healthy trust between individuals hinges on transparent communication that balances blind trust with calculated trust. Calculated trust involves assessing past behavior and reliability to make informed decisions, while blind trust relies on unconditional faith without evaluation. Encouraging open dialogue and expressing expectations clearly strengthens relationships by fostering understanding and reducing uncertainty.
Long-Term Effects on Relationships: Blind vs. Calculated Trust
Blind trust often leads to vulnerability and increased risk of betrayal, resulting in weakened relationships over time due to unmet expectations and lack of accountability. Calculated trust fosters sustainable connections by balancing openness with critical assessment, enhancing mutual respect and deeper understanding between parties. Long-term relational stability is more commonly achieved through calculated trust, which encourages transparency, consistent behavior, and gradual confidence-building.
Blind trust vs calculated trust Infographic
 relationdif.com
relationdif.com