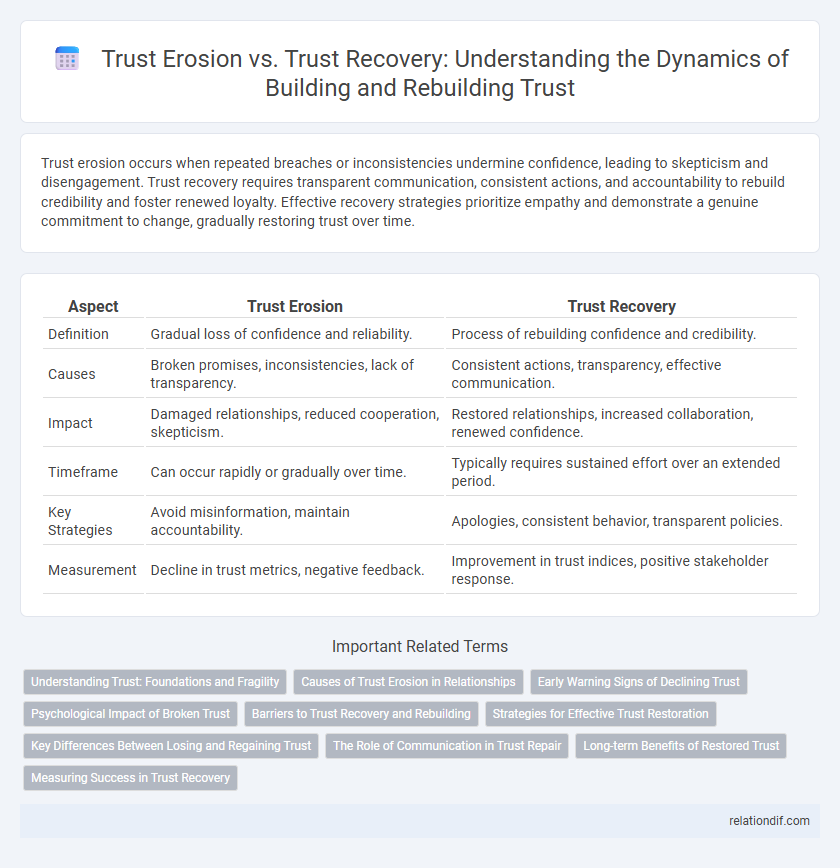
Trust erosion occurs when repeated breaches or inconsistencies undermine confidence, leading to skepticism and disengagement. Trust recovery requires transparent communication, consistent actions, and accountability to rebuild credibility and foster renewed loyalty. Effective recovery strategies prioritize empathy and demonstrate a genuine commitment to change, gradually restoring trust over time.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Trust Erosion | Trust Recovery |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Gradual loss of confidence and reliability. | Process of rebuilding confidence and credibility. |
| Causes | Broken promises, inconsistencies, lack of transparency. | Consistent actions, transparency, effective communication. |
| Impact | Damaged relationships, reduced cooperation, skepticism. | Restored relationships, increased collaboration, renewed confidence. |
| Timeframe | Can occur rapidly or gradually over time. | Typically requires sustained effort over an extended period. |
| Key Strategies | Avoid misinformation, maintain accountability. | Apologies, consistent behavior, transparent policies. |
| Measurement | Decline in trust metrics, negative feedback. | Improvement in trust indices, positive stakeholder response. |
Understanding Trust: Foundations and Fragility
Trust erosion occurs when reliability, integrity, or transparency are compromised, weakening interpersonal or organizational bonds. Understanding the psychological and social foundations of trust reveals its inherent fragility, highlighting how quickly trust can deteriorate under perceived betrayal or inconsistency. Effective trust recovery hinges on consistent actions, open communication, and demonstrated accountability to rebuild credibility and confidence over time.
Causes of Trust Erosion in Relationships
Trust erosion in relationships primarily stems from consistent dishonesty, unmet expectations, and breaches of confidentiality, which undermine emotional security and reliability. Repeated conflicts and lack of communication exacerbate doubts, fostering skepticism and emotional distance between parties. Inability to demonstrate accountability or empathy further accelerates the breakdown of trust, making recovery increasingly challenging.
Early Warning Signs of Declining Trust
Early warning signs of declining trust include increased communication breakdowns, reduced collaboration, and a rise in skepticism among team members. Persistent unmet expectations and inconsistent behavior from leadership amplify mistrust, undermining organizational cohesion. Identifying and addressing these indicators promptly is crucial for effective trust recovery strategies.
Psychological Impact of Broken Trust
Broken trust triggers feelings of betrayal, vulnerability, and anxiety, deeply impacting an individual's emotional well-being. The psychological impact often includes diminished self-esteem, heightened skepticism, and difficulty forming new relationships. Recovery requires consistent transparency, empathy, and reliable behavior to rebuild trust and restore emotional security.
Barriers to Trust Recovery and Rebuilding
Barriers to trust recovery include persistent negative perceptions, lack of transparency, and inconsistent communication. Emotional damage from broken trust often leads to skepticism, making transparency and consistent actions critical for rebuilding confidence. Organizations must address these obstacles through deliberate efforts that demonstrate accountability and foster open dialogue to overcome deep-seated mistrust.
Strategies for Effective Trust Restoration
Strategies for effective trust restoration involve transparent communication, consistent actions, and accountability to rebuild credibility after trust erosion. Implementing active listening and acknowledging past mistakes create a foundation for renewed trust between parties. Reinforcing positive behavior through ongoing engagement and demonstrating reliability strengthens long-term trust recovery.
Key Differences Between Losing and Regaining Trust
Trust erosion occurs when consistent actions or breaches cause doubt and weaken relationships, while trust recovery demands deliberate, transparent efforts to rebuild credibility. Losing trust often involves emotional harm and skepticism, whereas regaining it requires sustained accountability and demonstrated positive change. The key difference lies in trust's fragility during erosion contrasted with the proactive, ongoing commitment needed for recovery.
The Role of Communication in Trust Repair
Effective communication plays a critical role in trust recovery by fostering transparency and empathy, which helps address the root causes of trust erosion. Timely, honest, and consistent messaging facilitates understanding and reassures stakeholders, minimizing misunderstandings and rebuilding confidence. Organizations that prioritize open dialogue and active listening create a foundation for long-term trust repair and strengthened relationships.
Long-term Benefits of Restored Trust
Restored trust fosters long-term collaboration, increased loyalty, and improved organizational resilience, which are essential for sustainable growth. Trust recovery processes strengthen interpersonal relationships and enable transparent communication, fostering a culture of accountability. Maintaining trust over time reduces conflict and transaction costs, ultimately enhancing overall performance and stakeholder confidence.
Measuring Success in Trust Recovery
Measuring success in trust recovery relies on quantifiable metrics such as customer satisfaction scores, repeat engagement rates, and net promoter scores, which indicate restored confidence. Real-time feedback loops and sentiment analysis on social platforms provide insights into shifts in public perception and trust levels. Transparent communication and consistent delivery on promises serve as critical benchmarks that directly correlate with successful trust restoration.
Trust erosion vs trust recovery Infographic
 relationdif.com
relationdif.com