Attachment anxiety involves a deep fear of rejection or abandonment by a pet, leading to clingy or overly dependent behaviors. In contrast, attachment avoidance manifests as discomfort with closeness, causing individuals to maintain emotional distance from their pet. Understanding these differing attachment styles helps improve the bond and address relationship challenges between a person and their pet.
Table of Comparison
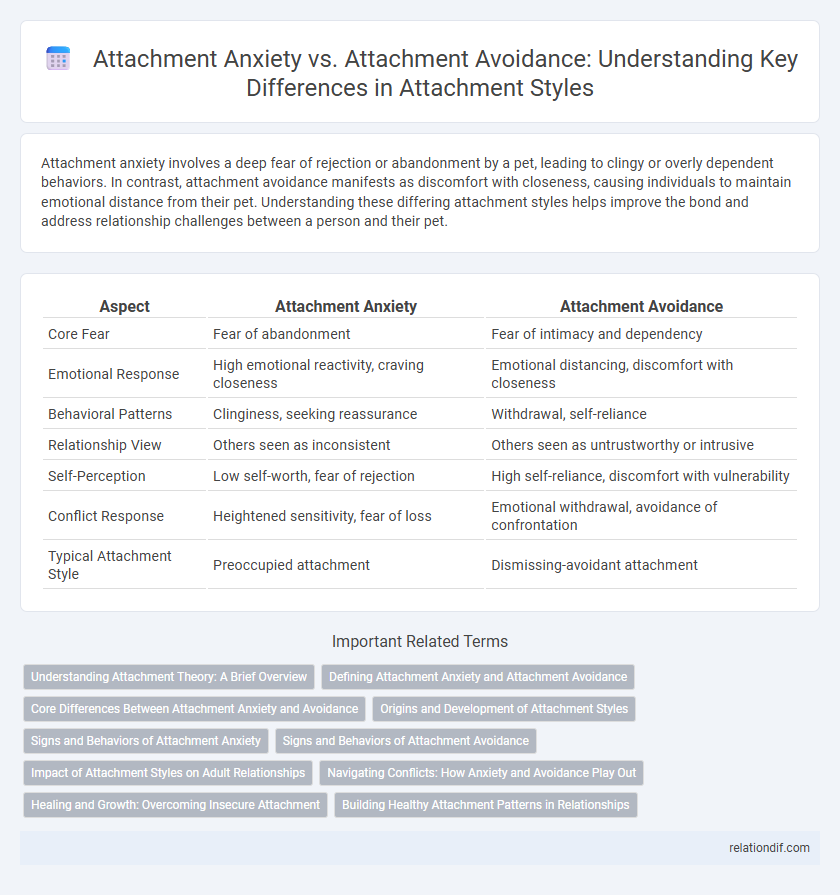
| Aspect | Attachment Anxiety | Attachment Avoidance |
|---|---|---|
| Core Fear | Fear of abandonment | Fear of intimacy and dependency |
| Emotional Response | High emotional reactivity, craving closeness | Emotional distancing, discomfort with closeness |
| Behavioral Patterns | Clinginess, seeking reassurance | Withdrawal, self-reliance |
| Relationship View | Others seen as inconsistent | Others seen as untrustworthy or intrusive |
| Self-Perception | Low self-worth, fear of rejection | High self-reliance, discomfort with vulnerability |
| Conflict Response | Heightened sensitivity, fear of loss | Emotional withdrawal, avoidance of confrontation |
| Typical Attachment Style | Preoccupied attachment | Dismissing-avoidant attachment |
Understanding Attachment Theory: A Brief Overview
Attachment anxiety involves a deep fear of rejection and excessive worry about relationships, leading to clinginess and emotional dependency. In contrast, attachment avoidance is characterized by discomfort with closeness, emotional distance, and a preference for self-reliance. Understanding these attachment styles, rooted in early caregiver interactions, is crucial for recognizing patterns that influence adult relationships.
Defining Attachment Anxiety and Attachment Avoidance
Attachment anxiety is characterized by a strong fear of abandonment and excessive need for closeness, leading individuals to seek constant reassurance in relationships. Attachment avoidance involves discomfort with intimacy and a tendency to maintain emotional distance to protect oneself from vulnerability. Both patterns stem from early relational experiences influencing emotional regulation and interpersonal dynamics.
Core Differences Between Attachment Anxiety and Avoidance
Attachment anxiety involves a heightened fear of abandonment and excessive need for reassurance, often leading to clinginess and emotional dependence. In contrast, attachment avoidance is characterized by discomfort with closeness and a strong desire for emotional self-reliance, resulting in distance and reluctance to trust. The core difference lies in anxious individuals craving intimacy despite fear of rejection, while avoidant individuals prioritize independence to evade vulnerability.
Origins and Development of Attachment Styles
Attachment anxiety originates from inconsistent caregiving, where a child's needs are unpredictably met, fostering hypervigilance and fear of abandonment. Attachment avoidance develops from caregiving that is emotionally unavailable or rejecting, leading to emotional suppression and self-reliance. Early interactions with primary caregivers critically shape these attachment styles, influencing relational patterns and emotional regulation in adulthood.
Signs and Behaviors of Attachment Anxiety
Attachment anxiety manifests through persistent fear of abandonment, excessive need for reassurance, and heightened sensitivity to perceived rejection. Individuals exhibiting these signs often display clinginess, emotional volatility, and intense worry about relationship stability. This behavior contrasts with attachment avoidance, characterized by emotional distance and reluctance to depend on others.
Signs and Behaviors of Attachment Avoidance
Attachment avoidance manifests through consistent emotional distance, reluctance to depend on others, and discomfort with intimacy. Individuals exhibiting attachment avoidance often suppress feelings, prioritize self-reliance, and may withdraw during conflicts or emotionally charged situations. These behaviors serve as defensive mechanisms to maintain autonomy and prevent vulnerability in close relationships.
Impact of Attachment Styles on Adult Relationships
Attachment anxiety often leads to heightened sensitivity to rejection and a persistent need for reassurance, significantly impacting trust and emotional intimacy in adult relationships. Attachment avoidance typically results in emotional distance and reluctance to rely on or disclose feelings to partners, hindering deep connection and vulnerability. These contrasting attachment styles shape communication patterns, conflict resolution, and overall relationship satisfaction in adults.
Navigating Conflicts: How Anxiety and Avoidance Play Out
Attachment anxiety often triggers heightened emotional responses during conflicts, leading to intense fear of rejection and persistent reassurance-seeking behaviors. In contrast, attachment avoidance manifests through emotional withdrawal and reluctance to engage, creating distance and suppressing vulnerability. Understanding these patterns enables more effective communication strategies tailored to reduce misunderstandings and foster resolution.
Healing and Growth: Overcoming Insecure Attachment
Healing from attachment anxiety involves cultivating self-awareness and practicing emotional regulation techniques to manage fears of abandonment and rejection. Overcoming attachment avoidance requires building trust through consistent, vulnerable communication and gradually embracing intimacy to foster secure connections. Therapeutic interventions like cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and mindful attachment-based practices significantly support emotional growth and relational resilience.
Building Healthy Attachment Patterns in Relationships
Attachment anxiety involves fear of abandonment and excessive need for reassurance, while attachment avoidance is marked by discomfort with intimacy and emotional distance. Building healthy attachment patterns requires developing open communication, establishing consistent boundaries, and practicing emotional regulation to foster trust and security. Recognizing these attachment styles allows couples to address underlying fears and create balanced, supportive relationships.
Attachment anxiety vs attachment avoidance Infographic
 relationdif.com
relationdif.com