Attachment disruption occurs when a pet experiences separation or loss, leading to behavioral changes such as anxiety, withdrawal, or aggression. In contrast, attachment continuity ensures stable emotional bonds, promoting a pet's sense of security and well-being. Maintaining consistent interactions and routines supports attachment continuity, reducing stress and fostering trust between pets and their caregivers.
Table of Comparison
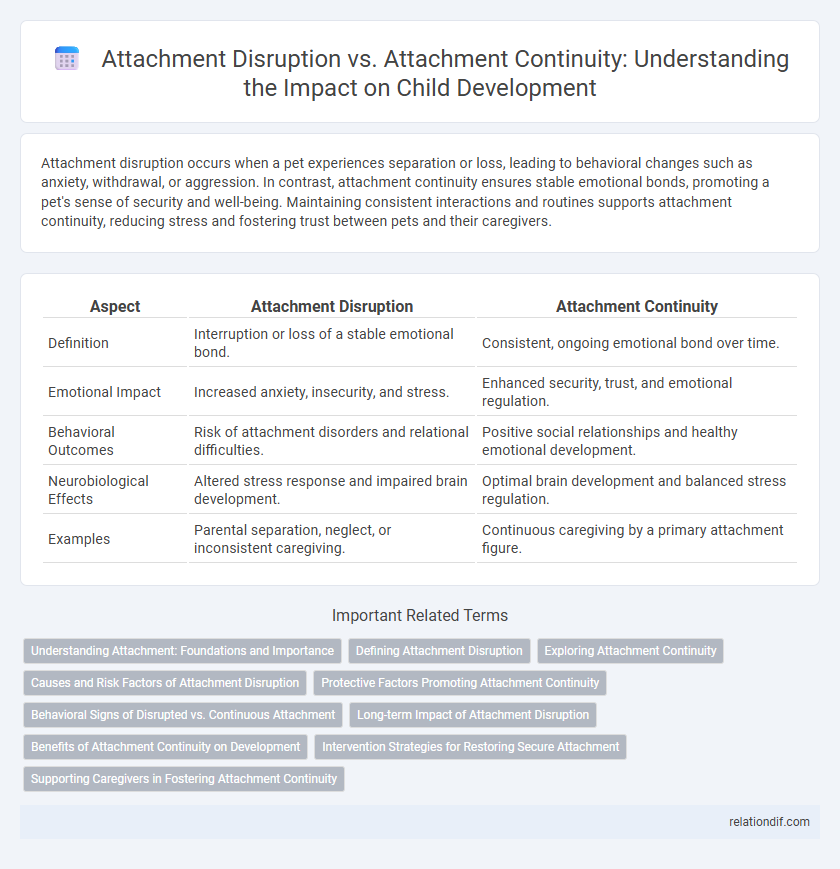
| Aspect | Attachment Disruption | Attachment Continuity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Interruption or loss of a stable emotional bond. | Consistent, ongoing emotional bond over time. |
| Emotional Impact | Increased anxiety, insecurity, and stress. | Enhanced security, trust, and emotional regulation. |
| Behavioral Outcomes | Risk of attachment disorders and relational difficulties. | Positive social relationships and healthy emotional development. |
| Neurobiological Effects | Altered stress response and impaired brain development. | Optimal brain development and balanced stress regulation. |
| Examples | Parental separation, neglect, or inconsistent caregiving. | Continuous caregiving by a primary attachment figure. |
Understanding Attachment: Foundations and Importance
Attachment disruption undermines the secure base essential for emotional regulation and healthy social development, leading to increased risks of anxiety, depression, and interpersonal difficulties. In contrast, attachment continuity fosters consistent caregiver responsiveness, reinforcing trust and adaptive coping mechanisms throughout life stages. Understanding these foundational dynamics highlights the critical role of stable early relationships in shaping resilience and psychological well-being.
Defining Attachment Disruption
Attachment disruption refers to the interruption or loss of a consistent and secure emotional bond between a child and caregiver, often resulting from separation, neglect, or changes in caregiving environments. This disruption can lead to difficulties in emotional regulation, trust, and relationship-building in later life. In contrast, attachment continuity emphasizes the preservation of stable and responsive caregiving that fosters secure attachment development and psychological well-being.
Exploring Attachment Continuity
Exploring attachment continuity reveals the importance of consistent caregiving in promoting secure emotional bonds and healthy psychological development. Attachment continuity supports resilience by maintaining stable relationships despite environmental changes or stressors. Disruptions, in contrast, often lead to increased risk of attachment insecurities and long-term relational difficulties.
Causes and Risk Factors of Attachment Disruption
Attachment disruption often results from factors such as caregiver inconsistency, abuse, neglect, or prolonged separation, which undermine the formation of secure emotional bonds in early childhood. Risk factors include parental mental illness, substance abuse, domestic violence, and frequent caregiver changes, all contributing to insecure or disorganized attachment styles. Chronic stress and trauma during critical developmental periods increase the likelihood of attachment disruptions, adversely impacting emotional regulation and social functioning.
Protective Factors Promoting Attachment Continuity
Protective factors promoting attachment continuity include consistent caregiving, sensitive responsiveness, and emotional availability, which foster secure attachment bonds despite environmental stressors. Stable family routines and supportive relationships serve as buffers against attachment disruption, enhancing child resilience and emotional regulation. Access to mental health resources and positive parent-child interactions further solidify attachment continuity by mitigating risks linked to adverse experiences.
Behavioral Signs of Disrupted vs. Continuous Attachment
Disrupted attachment often manifests through behavioral signs such as withdrawal, anxiety, difficulty trusting caregivers, and inconsistent emotional responses. In contrast, continuous attachment is characterized by secure behaviors including seeking comfort from caregivers, exploring environments confidently, and displaying regulated emotions. These behavioral distinctions highlight the critical impact of attachment stability on a child's emotional and social development.
Long-term Impact of Attachment Disruption
Attachment disruption in early childhood can lead to significant long-term impacts on emotional regulation, interpersonal relationships, and psychological well-being. Continuous secure attachment fosters resilience, social competence, and healthy stress responses, while disrupted attachment often increases risks for anxiety, depression, and behavioral problems. Research indicates persistent attachment insecurity may impair brain development related to empathy and self-control, underscoring the critical need for consistent caregiving.
Benefits of Attachment Continuity on Development
Attachment continuity fosters secure emotional bonds that enhance cognitive and social development in children. Consistent caregiving supports resilience, promotes healthy stress regulation, and improves long-term psychological well-being. Maintaining stable attachments contributes to better academic performance and stronger interpersonal relationships throughout life.
Intervention Strategies for Restoring Secure Attachment
Intervention strategies for restoring secure attachment focus on enhancing caregiver sensitivity and responsiveness through targeted therapies such as Child-Parent Psychotherapy (CPP) and Attachment-Based Family Therapy (ABFT). Consistent, nurturing interactions help rebuild trust and emotional regulation, counteracting the effects of attachment disruption. Incorporating trauma-informed practices and promoting stable caregiving environments are critical to restoring attachment continuity and fostering long-term relational stability.
Supporting Caregivers in Fostering Attachment Continuity
Supporting caregivers in fostering attachment continuity involves providing targeted interventions that enhance caregiver sensitivity and responsiveness, thereby reducing the risk of attachment disruption in children. Consistent, nurturing caregiving environments promote secure attachment patterns essential for healthy emotional and social development. Access to resources such as counseling, education, and community support strengthens caregivers' capacity to maintain stable, positive attachments across developmental stages.
Attachment disruption vs attachment continuity Infographic
 relationdif.com
relationdif.com