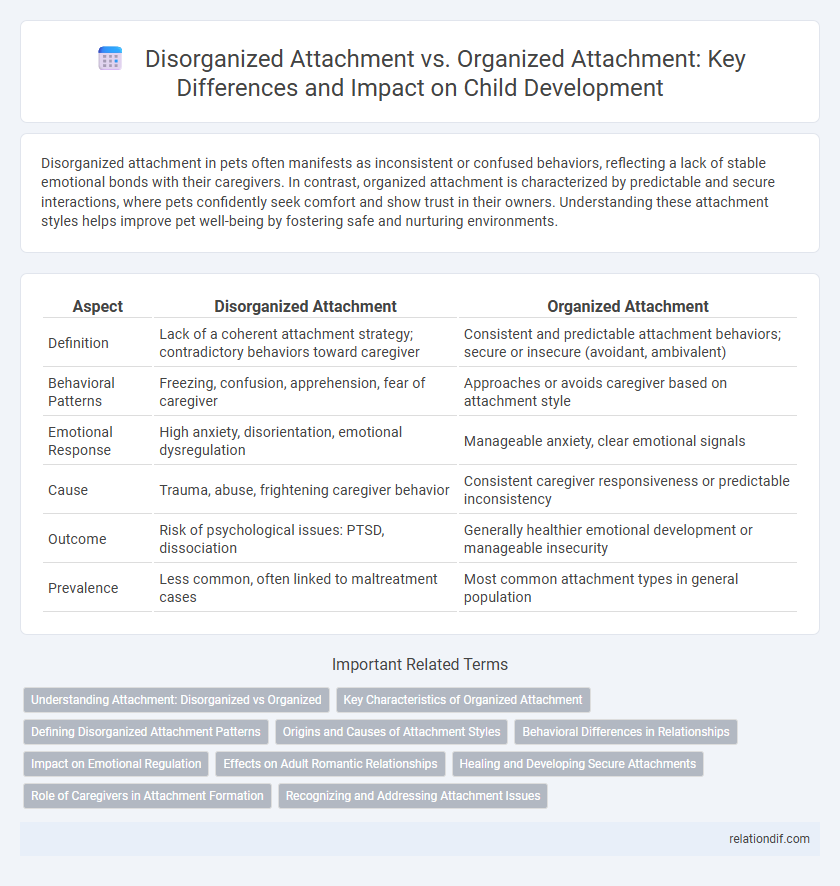
Disorganized attachment in pets often manifests as inconsistent or confused behaviors, reflecting a lack of stable emotional bonds with their caregivers. In contrast, organized attachment is characterized by predictable and secure interactions, where pets confidently seek comfort and show trust in their owners. Understanding these attachment styles helps improve pet well-being by fostering safe and nurturing environments.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Disorganized Attachment | Organized Attachment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Lack of a coherent attachment strategy; contradictory behaviors toward caregiver | Consistent and predictable attachment behaviors; secure or insecure (avoidant, ambivalent) |
| Behavioral Patterns | Freezing, confusion, apprehension, fear of caregiver | Approaches or avoids caregiver based on attachment style |
| Emotional Response | High anxiety, disorientation, emotional dysregulation | Manageable anxiety, clear emotional signals |
| Cause | Trauma, abuse, frightening caregiver behavior | Consistent caregiver responsiveness or predictable inconsistency |
| Outcome | Risk of psychological issues: PTSD, dissociation | Generally healthier emotional development or manageable insecurity |
| Prevalence | Less common, often linked to maltreatment cases | Most common attachment types in general population |
Understanding Attachment: Disorganized vs Organized
Disorganized attachment is characterized by contradictory behaviors and a lack of a coherent strategy for seeking comfort, often linked to trauma or inconsistent caregiving. In contrast, organized attachment includes secure, avoidant, or ambivalent patterns where the child develops predictable ways to seek support and manage stress. Understanding these attachment types is crucial for identifying the impact of early experiences on emotional regulation and relationship development.
Key Characteristics of Organized Attachment
Organized attachment is marked by predictable patterns of behavior where children use caregivers as a secure base to explore their environment confidently. Key characteristics include consistent emotional responsiveness, effective emotion regulation, and clear communication of needs and feelings. These children typically develop healthy coping mechanisms and show resilience in stressful situations.
Defining Disorganized Attachment Patterns
Disorganized attachment patterns are characterized by inconsistent and contradictory behaviors towards caregivers, reflecting fear and confusion instead of a secure base. Unlike organized attachment styles--secure, avoidant, or ambivalent--disorganized attachment lacks a coherent strategy to seek comfort or manage stress. This pattern often emerges in children exposed to trauma, neglect, or caregiver behavior that simultaneously frightens and frustrates their need for safety.
Origins and Causes of Attachment Styles
Disorganized attachment arises primarily from inconsistent or frightening caregiver behavior, often linked to trauma, neglect, or abuse during early development. In contrast, organized attachment styles--secure, avoidant, or anxious--develop from more predictable and responsive caregiving environments that foster emotional safety. Early parental sensitivity and the caregiver's ability to regulate the infant's distress critically influence the formation of these attachment patterns.
Behavioral Differences in Relationships
Disorganized attachment manifests in unpredictable behaviors such as anxiety, fear, and confusion during relationships, often resulting in difficulty trusting others. Organized attachment styles, including secure, avoidant, and anxious, exhibit more consistent patterns like seeking closeness or maintaining emotional distance to manage intimacy. These behavioral differences significantly impact communication, conflict resolution, and emotional regulation within interpersonal relationships.
Impact on Emotional Regulation
Disorganized attachment is strongly correlated with difficulties in emotional regulation, often leading to heightened anxiety, confusion, and unpredictable emotional responses. In contrast, organized attachment styles, such as secure attachment, consistently promote healthier emotional regulation, fostering resilience and effective coping mechanisms. Research indicates that early caregiving quality significantly impacts these attachment patterns, shaping an individual's capacity to manage emotions throughout life.
Effects on Adult Romantic Relationships
Disorganized attachment in childhood is linked to difficulties in adult romantic relationships, including heightened fear of abandonment, emotional instability, and challenges in trust and intimacy. Individuals with organized attachment styles, such as secure attachment, tend to exhibit healthier communication patterns, greater emotional regulation, and stronger relationship satisfaction. Research highlights that attachment security significantly predicts relationship quality and the ability to manage conflict effectively in adult partnerships.
Healing and Developing Secure Attachments
Disorganized attachment often stems from inconsistent caregiving and can lead to difficulties in emotional regulation and relationship trust. Healing involves therapeutic approaches such as trauma-focused cognitive behavioral therapy and attachment-based family therapy, which create safe environments to rebuild trust and resilience. Developing secure attachments requires consistent, responsive caregiving and interventions that promote emotional attunement and positive relational experiences.
Role of Caregivers in Attachment Formation
Caregivers play a critical role in attachment formation, with consistent, sensitive responses fostering organized attachment characterized by security and trust. In contrast, caregivers who display unpredictable, neglectful, or frightening behaviors often contribute to disorganized attachment, where children exhibit confusion and lack a coherent strategy to seek comfort. Secure attachment patterns support healthy emotional development and relationships, while disorganized attachment is linked to difficulties in emotional regulation and social functioning.
Recognizing and Addressing Attachment Issues
Disorganized attachment manifests through inconsistent behaviors and confusion in relationships, often stemming from trauma or neglect, contrasting with the predictable patterns seen in organized attachment types like secure, anxious, or avoidant. Recognizing these signs early, such as fearfulness, contradictory responses, and difficulty seeking comfort, is crucial for effective intervention. Therapeutic approaches emphasizing safety, trust-building, and emotional regulation, including trauma-informed therapy and caregiver sensitivity training, can help address and repair attachment disruptions.
disorganized attachment vs organized attachment Infographic
 relationdif.com
relationdif.com