Attachment needs drive pets to seek comfort, security, and connection with their owners, fostering trust and emotional well-being. Attachment fears, on the other hand, manifest as anxiety, clinginess, or avoidance behaviors when pets feel insecure or threatened. Understanding the balance between attachment needs and fears helps create a supportive environment that promotes healthy bonds and reduces stress for pets.
Table of Comparison
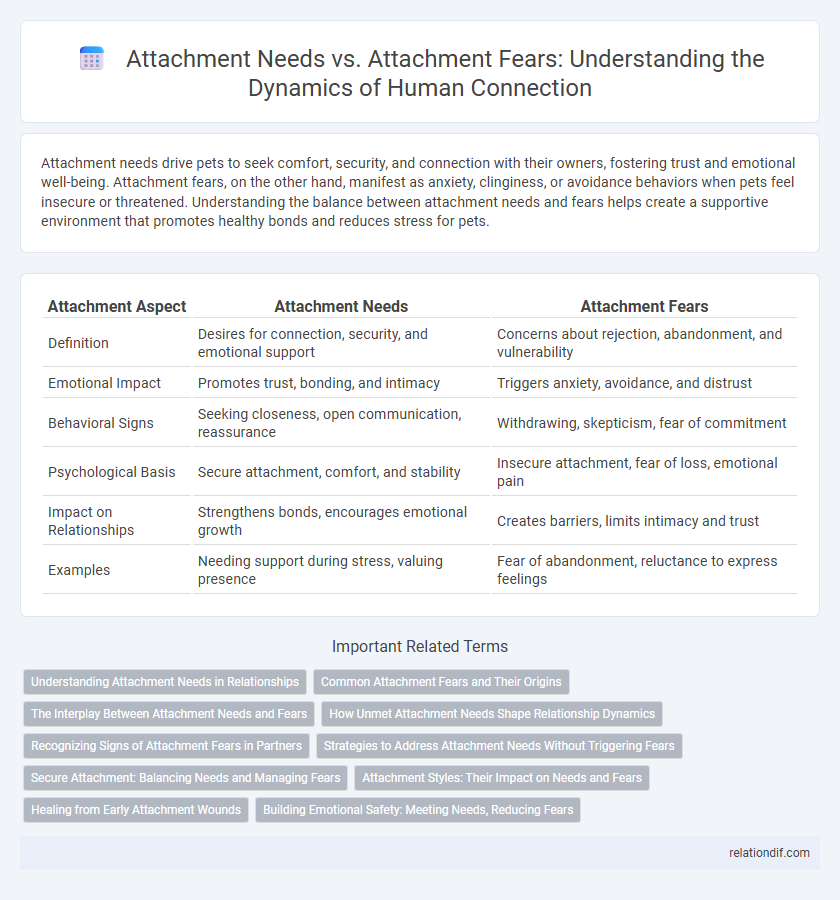
| Attachment Aspect | Attachment Needs | Attachment Fears |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Desires for connection, security, and emotional support | Concerns about rejection, abandonment, and vulnerability |
| Emotional Impact | Promotes trust, bonding, and intimacy | Triggers anxiety, avoidance, and distrust |
| Behavioral Signs | Seeking closeness, open communication, reassurance | Withdrawing, skepticism, fear of commitment |
| Psychological Basis | Secure attachment, comfort, and stability | Insecure attachment, fear of loss, emotional pain |
| Impact on Relationships | Strengthens bonds, encourages emotional growth | Creates barriers, limits intimacy and trust |
| Examples | Needing support during stress, valuing presence | Fear of abandonment, reluctance to express feelings |
Understanding Attachment Needs in Relationships
Attachment needs in relationships encompass the desire for security, emotional closeness, and reliable support, which foster trust and intimacy between partners. Attachment fears, such as fear of abandonment or rejection, can undermine these needs by triggering defensive behaviors and emotional withdrawal. Recognizing and addressing both attachment needs and fears promotes healthier communication, deeper connection, and resilience in relationships.
Common Attachment Fears and Their Origins
Common attachment fears include abandonment, rejection, and engulfment, often rooted in childhood experiences such as inconsistent caregiving or trauma. These fears develop when early attachment needs for security and trust are unmet, leading to anxious or avoidant attachment styles in adulthood. Understanding these origins helps to address and heal attachment-related anxieties through therapeutic interventions.
The Interplay Between Attachment Needs and Fears
Attachment needs drive the desire for closeness, security, and emotional connection, while attachment fears stem from concerns about rejection, abandonment, and vulnerability. The interplay between these needs and fears shapes relational dynamics, influencing attachment styles and emotional regulation. Understanding this balance is crucial for developing healthy relationships and addressing attachment-based challenges.
How Unmet Attachment Needs Shape Relationship Dynamics
Unmet attachment needs often lead to heightened fears of abandonment and rejection, deeply influencing relationship dynamics by fostering insecurity and mistrust. These fears can trigger defensive behaviors such as avoidance or clinginess, disrupting emotional intimacy and communication between partners. Understanding the impact of unresolved attachment needs is crucial for developing healthier relational patterns and emotional regulation.
Recognizing Signs of Attachment Fears in Partners
Attachment fears in partners often manifest through behaviors such as avoidance of intimacy, excessive jealousy, or resistance to emotional closeness. Recognizing these signs involves observing patterns of withdrawal during conflict, inconsistent communication, and heightened sensitivity to perceived rejection. Understanding these indicators enables healthier relationship dynamics by addressing underlying attachment insecurities.
Strategies to Address Attachment Needs Without Triggering Fears
Meeting attachment needs involves consistent emotional availability and responsive caregiving that fosters trust and security. Strategies include establishing clear boundaries while maintaining warmth, encouraging open communication to express feelings safely, and gradually increasing closeness to prevent overwhelming attachment fears. Utilizing therapeutic approaches such as Emotionally Focused Therapy (EFT) can help individuals recognize and reframe fear responses, promoting healthier attachment patterns.
Secure Attachment: Balancing Needs and Managing Fears
Secure attachment fosters a healthy balance between attachment needs and attachment fears, enabling individuals to seek support while maintaining autonomy. It involves recognizing and expressing emotional needs confidently without being overwhelmed by fears of abandonment or rejection. Developing secure attachment strengthens relationships by promoting trust, emotional regulation, and resilience in managing attachment-related anxieties.
Attachment Styles: Their Impact on Needs and Fears
Attachment styles significantly shape individual needs and fears in relationships, with secure attachment fostering healthy emotional expression and trust, while anxious attachment amplifies fears of abandonment and heightened need for reassurance. Avoidant attachment triggers discomfort with closeness, leading to fears of dependency and a tendency to suppress emotional needs. Disorganized attachment combines these fears and needs, causing confusion and unpredictability in forming stable connections.
Healing from Early Attachment Wounds
Healing from early attachment wounds involves addressing the deep-seated fears of abandonment and rejection that stem from unmet attachment needs in childhood. Therapeutic approaches like attachment-based therapy and trauma-informed care help rebuild trust and emotional security, crucial for overcoming anxieties related to attachment. Strengthening secure attachment patterns promotes resilience and healthier relationships in adulthood by resolving the impact of early attachment disruptions.
Building Emotional Safety: Meeting Needs, Reducing Fears
Building emotional safety involves consistently meeting attachment needs such as trust, empathy, and reliable support, which fosters secure bonds. Reducing attachment fears--like abandonment or rejection--requires open communication, validation of feelings, and a stable environment. Prioritizing these elements strengthens relational resilience and promotes healthy emotional connections.
attachment needs vs attachment fears Infographic
 relationdif.com
relationdif.com