Attachment rupture occurs when trust and emotional bonds between a pet and owner are broken, often leading to anxiety and behavioral issues in the animal. Attachment repair involves consistent, gentle interactions and positive reinforcement to rebuild security and strengthen the emotional connection. Restoring this bond is crucial for the pet's well-being and fosters a resilient, trusting relationship.
Table of Comparison
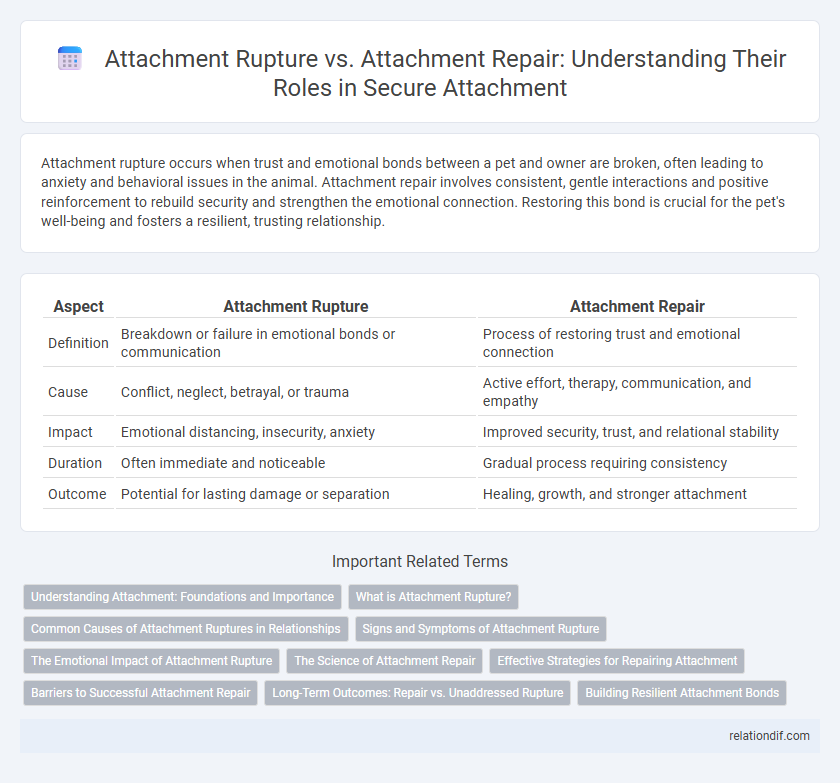
| Aspect | Attachment Rupture | Attachment Repair |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Breakdown or failure in emotional bonds or communication | Process of restoring trust and emotional connection |
| Cause | Conflict, neglect, betrayal, or trauma | Active effort, therapy, communication, and empathy |
| Impact | Emotional distancing, insecurity, anxiety | Improved security, trust, and relational stability |
| Duration | Often immediate and noticeable | Gradual process requiring consistency |
| Outcome | Potential for lasting damage or separation | Healing, growth, and stronger attachment |
Understanding Attachment: Foundations and Importance
Attachment rupture occurs when trust and emotional bonds between individuals are disrupted, leading to feelings of insecurity and disconnection. Attachment repair involves intentional efforts to restore safety and communication, reinforcing emotional security and relational resilience. Understanding these processes is crucial for fostering healthy relational dynamics and promoting psychological well-being.
What is Attachment Rupture?
Attachment rupture refers to a disruption or breakdown in the emotional connection between individuals, often occurring when trust is broken or emotional needs are unmet. This rupture can lead to feelings of insecurity, withdrawal, and increased conflict within relationships. Effective attachment repair focuses on restoring trust and emotional safety to rebuild the bond and promote secure attachment.
Common Causes of Attachment Ruptures in Relationships
Attachment ruptures in relationships commonly arise from breaches of trust, inconsistent emotional availability, and unresolved conflicts that create feelings of insecurity and abandonment. Frequent miscommunication, unmet attachment needs, and past trauma can exacerbate these ruptures, leading to withdrawal or heightened anxiety. Understanding these causes is crucial for facilitating effective attachment repair and restoring emotional connection.
Signs and Symptoms of Attachment Rupture
Signs and symptoms of attachment rupture include withdrawal, emotional detachment, and difficulty trusting caregivers, often manifesting as increased anxiety or aggression. Children may exhibit inconsistent responses to comfort, clinginess, or avoidance behaviors, signaling disrupted emotional bonds. Physiological indicators such as heightened stress responses and dysregulated cortisol levels are also common in attachment ruptures.
The Emotional Impact of Attachment Rupture
Attachment rupture triggers intense emotional distress, often manifesting as feelings of abandonment, mistrust, and heightened anxiety. This emotional turmoil disrupts the foundation of secure relationships, leading to difficulties in emotional regulation and interpersonal connection. Effective attachment repair restores emotional safety, fostering resilience and reestablishing trust critical for healthy relational dynamics.
The Science of Attachment Repair
Attachment rupture occurs when trust and emotional bonds between individuals are disrupted, leading to feelings of insecurity and disconnection. The science of attachment repair involves neurobiological processes such as oxytocin release and the activation of the prefrontal cortex to restore emotional regulation and rebuild secure bonds. Therapeutic interventions focus on enhancing emotional attunement and consistent responsiveness to promote healing and resilience in attachment relationships.
Effective Strategies for Repairing Attachment
Effective strategies for repairing attachment focus on fostering secure emotional bonds through consistent, responsive caregiving and open communication that validates feelings. Therapeutic approaches like attachment-based family therapy and emotion-focused therapy emphasize rebuilding trust and correcting misattuned interactions between caregivers and children. Incorporating mindfulness practices and reflective functioning enhances parental sensitivity, which is crucial for healing attachment ruptures and promoting long-term relational resilience.
Barriers to Successful Attachment Repair
Barriers to successful attachment repair often include unresolved past traumas, communication breakdowns, and deep-seated mistrust between partners. Emotional dysregulation and inconsistent caregiving behaviors further hinder the reestablishment of secure attachment bonds. Addressing these obstacles requires targeted therapeutic interventions focused on rebuilding trust and fostering emotional attunement.
Long-Term Outcomes: Repair vs. Unaddressed Rupture
Attachment repair fosters secure relational bonds, promoting emotional regulation and resilience, which contribute to healthier long-term interpersonal functioning. In contrast, unaddressed attachment ruptures often lead to persistent trust issues, emotional dysregulation, and increased vulnerability to mental health disorders such as anxiety and depression. Empirical studies highlight that timely and effective repair interventions significantly improve attachment security and overall psychological well-being across the lifespan.
Building Resilient Attachment Bonds
Attachment rupture occurs when trust and emotional safety between caregiver and child are disrupted, leading to feelings of insecurity and disconnection. Attachment repair focuses on consistent, sensitive responses and open communication to rebuild emotional bonds and restore trust. Building resilient attachment bonds requires recognizing rupture moments as opportunities for growth, fostering emotional regulation, and promoting secure base experiences through ongoing attuned interactions.
Attachment rupture vs attachment repair Infographic
 relationdif.com
relationdif.com