Attachment in pets often mirrors human emotional bonds, where stable relationships foster trust, security, and consistent behavior. Volatile interactions can lead to anxiety, fearfulness, and unpredictable reactions in pets, undermining their sense of safety. Maintaining a predictable and nurturing environment strengthens attachment stability, promoting well-being and harmonious coexistence.
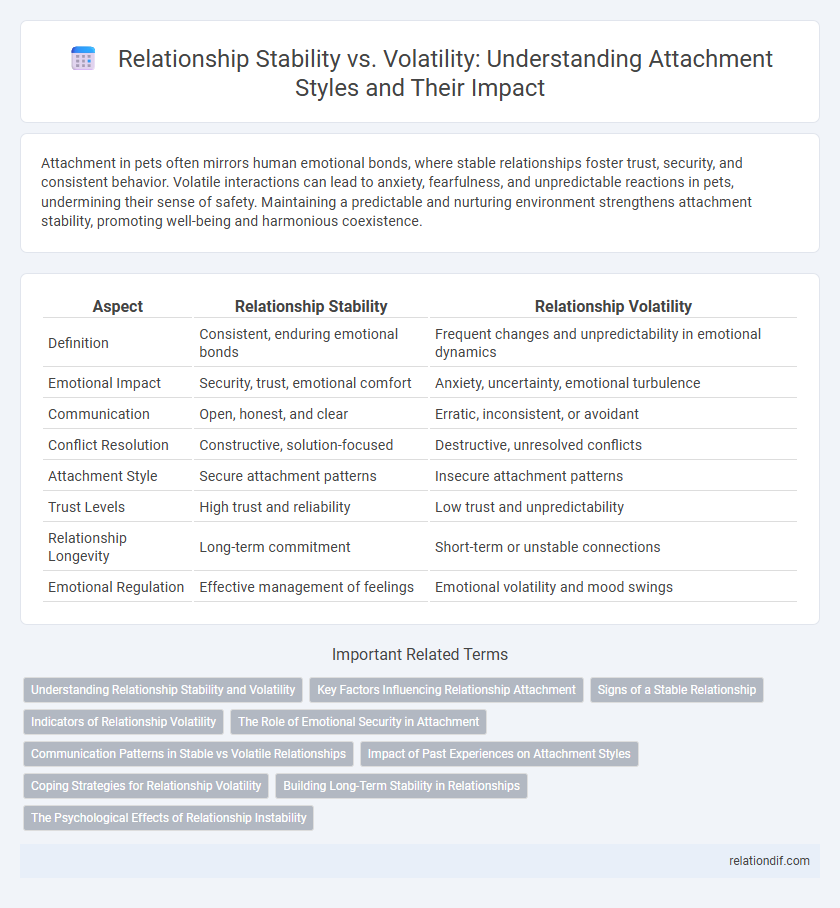
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Relationship Stability | Relationship Volatility |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Consistent, enduring emotional bonds | Frequent changes and unpredictability in emotional dynamics |
| Emotional Impact | Security, trust, emotional comfort | Anxiety, uncertainty, emotional turbulence |
| Communication | Open, honest, and clear | Erratic, inconsistent, or avoidant |
| Conflict Resolution | Constructive, solution-focused | Destructive, unresolved conflicts |
| Attachment Style | Secure attachment patterns | Insecure attachment patterns |
| Trust Levels | High trust and reliability | Low trust and unpredictability |
| Relationship Longevity | Long-term commitment | Short-term or unstable connections |
| Emotional Regulation | Effective management of feelings | Emotional volatility and mood swings |
Understanding Relationship Stability and Volatility
Relationship stability reflects consistent emotional support, trust, and secure attachment patterns that foster long-term commitment. Volatility in relationships often arises from insecure attachment styles, communication breakdowns, and emotional unpredictability, leading to frequent conflicts and instability. Understanding these dynamics enables targeted interventions to enhance emotional regulation and strengthen relational bonds.
Key Factors Influencing Relationship Attachment
Key factors influencing relationship attachment include consistent emotional support, effective communication, and mutual trust, which collectively enhance relationship stability. Attachment security is strengthened when partners exhibit responsiveness and reliability, reducing relationship volatility. Emotional regulation and conflict resolution skills further contribute to maintaining a stable attachment bond.
Signs of a Stable Relationship
Consistent communication, mutual trust, and emotional support are key signs of a stable relationship. Partners in stable relationships demonstrate effective conflict resolution skills and maintain a balanced give-and-take dynamic. Indicators such as long-term commitment, reliability, and shared goals further reinforce relationship stability.
Indicators of Relationship Volatility
Indicators of relationship volatility include frequent conflicts, inconsistent communication patterns, and rapid shifts in emotional intensity. Attachment insecurity, such as anxious or avoidant behaviors, often exacerbates these fluctuations, undermining trust and predictability. Monitoring signs like sudden withdrawal or unpredictable reactions helps identify instability in relational dynamics.
The Role of Emotional Security in Attachment
Emotional security serves as a foundational element in attachment, significantly enhancing relationship stability by fostering trust and open communication between partners. Individuals with secure attachment styles experience less relationship volatility, as their emotional confidence reduces anxiety and fear of abandonment. The presence of emotional security promotes resilience during conflicts, enabling couples to maintain consistent and supportive connections over time.
Communication Patterns in Stable vs Volatile Relationships
Stable relationships often exhibit open, consistent communication patterns where partners express emotions clearly and listen actively. In contrast, volatile relationships tend to display erratic communication marked by frequent misunderstandings, hostility, or withdrawal. Effective conflict resolution and emotional attunement strongly correlate with relationship stability and long-term satisfaction.
Impact of Past Experiences on Attachment Styles
Past experiences profoundly shape attachment styles, influencing relationship stability or volatility. Secure childhood attachments often foster stable adult relationships, while inconsistent or traumatic early interactions contribute to anxious or avoidant styles linked to higher volatility. Understanding these patterns aids in predicting relational outcomes and tailoring therapeutic interventions for healthier bonds.
Coping Strategies for Relationship Volatility
Effective coping strategies for relationship volatility include open communication, emotional regulation, and seeking external support such as therapy or counseling. Couples who practice mindfulness and validate each other's feelings tend to build resilience against instability. Developing problem-solving skills and maintaining individual self-care also contribute to reducing relational fluctuations and promoting long-term relationship stability.
Building Long-Term Stability in Relationships
Building long-term stability in relationships relies on secure attachment patterns that foster trust, effective communication, and emotional responsiveness between partners. Consistent support and conflict resolution skills mitigate relationship volatility by enhancing mutual understanding and reducing emotional distance. Couples who prioritize attachment security are more likely to sustain enduring bonds and navigate challenges effectively.
The Psychological Effects of Relationship Instability
Relationship instability triggers heightened stress responses and emotional dysregulation, impacting mental health by increasing anxiety and depressive symptoms. Attachment theory explains how inconsistent bonding fosters insecurity, leading to difficulty in trust and intimacy in future relationships. Prolonged relationship volatility can alter neural pathways related to emotional regulation, intensifying vulnerability to chronic psychological distress.
Relationship stability vs relationship volatility Infographic
 relationdif.com
relationdif.com