Compassionate empathy involves understanding another's emotions and responding with a desire to help, especially in caring for pets with sensitivity to their needs. Affective empathy, on the other hand, means physically feeling the emotions of the pet, such as sensing their anxiety or joy directly. Both types play vital roles in building strong emotional bonds and ensuring pets receive attentive, heartfelt care.
Table of Comparison
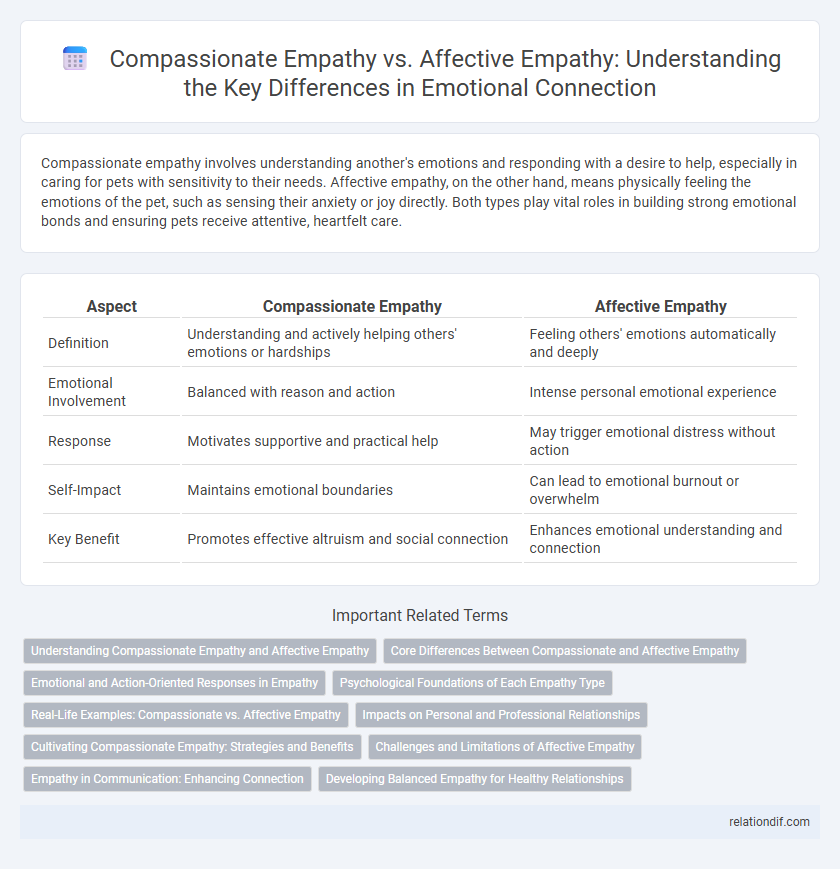
| Aspect | Compassionate Empathy | Affective Empathy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Understanding and actively helping others' emotions or hardships | Feeling others' emotions automatically and deeply |
| Emotional Involvement | Balanced with reason and action | Intense personal emotional experience |
| Response | Motivates supportive and practical help | May trigger emotional distress without action |
| Self-Impact | Maintains emotional boundaries | Can lead to emotional burnout or overwhelm |
| Key Benefit | Promotes effective altruism and social connection | Enhances emotional understanding and connection |
Understanding Compassionate Empathy and Affective Empathy
Compassionate empathy involves recognizing another's emotional state and responding with a genuine desire to help, emphasizing proactive support and understanding. Affective empathy refers to directly feeling another person's emotions, often mirroring their emotional experiences without necessarily leading to action. Distinguishing between these types clarifies how emotional connection can translate into positive social behaviors or shared emotional experiences.
Core Differences Between Compassionate and Affective Empathy
Compassionate empathy involves not only understanding and sharing another's emotions but also taking proactive steps to help alleviate their suffering, emphasizing a supportive response. Affective empathy, also known as emotional empathy, primarily focuses on directly experiencing and mirroring another person's emotional state without necessarily engaging in remedial actions. The core difference lies in compassionate empathy's blend of emotional resonance with actionable care, whereas affective empathy centers solely on emotional experience.
Emotional and Action-Oriented Responses in Empathy
Compassionate empathy involves not only recognizing and feeling another person's emotions but also being motivated to take proactive steps to alleviate their distress, highlighting an action-oriented response to emotional cues. In contrast, affective empathy refers primarily to the automatic emotional resonance or sharing of feelings without necessarily prompting intervention or supportive behavior. Understanding the distinction between these forms of empathy reveals how emotional engagement can translate into meaningful, compassionate actions that support others effectively.
Psychological Foundations of Each Empathy Type
Compassionate empathy involves recognizing another's emotional state and being motivated to help, rooted in prosocial behavior and activation of brain regions associated with empathy and caregiving, such as the anterior insula and anterior cingulate cortex. Affective empathy, by contrast, entails sharing or mirroring another's emotions directly, driven by neural mechanisms involving the mirror neuron system and limbic structures like the amygdala, which facilitate emotional contagion and resonance. Psychological theories distinguish compassionate empathy as a response promoting altruism, while affective empathy operates as an automatic emotional response essential for social bonding and emotional understanding.
Real-Life Examples: Compassionate vs. Affective Empathy
Compassionate empathy involves recognizing another's emotional state and taking actionable steps to support them, such as a friend comforting someone after a personal loss by offering help and presence. Affective empathy, by contrast, is the automatic mirroring of another's emotions, like feeling anxious when witnessing a loved one's distress without necessarily intervening. Real-life scenarios highlight that compassionate empathy drives proactive care, while affective empathy primarily fosters emotional resonance.
Impacts on Personal and Professional Relationships
Compassionate empathy, characterized by proactive support and understanding, enhances trust and cooperation in both personal and professional relationships by fostering deeper emotional connections and effective conflict resolution. Affective empathy, which involves sharing others' emotions, can strengthen emotional bonds but may sometimes lead to emotional overload or burnout in high-stress environments. Balancing compassionate and affective empathy is crucial for maintaining emotional resilience while promoting meaningful, supportive interactions.
Cultivating Compassionate Empathy: Strategies and Benefits
Cultivating compassionate empathy involves actively developing the ability to not only feel others' emotions but also respond with kindness and support, enhancing social connections and emotional resilience. Strategies include mindful listening, perspective-taking exercises, and practicing altruistic behaviors, which foster deeper understanding and reduce personal distress. The benefits of compassionate empathy extend to improved interpersonal relationships, increased prosocial behavior, and a greater capacity for emotional regulation in challenging situations.
Challenges and Limitations of Affective Empathy
Affective empathy, while crucial for emotionally resonating with others, often leads to emotional overwhelm and burnout due to its intensity. This form of empathy may impair objective decision-making as individuals struggle to separate their own feelings from those of others. Unlike compassionate empathy, affective empathy lacks the proactive element of helping, potentially limiting its effectiveness in fostering sustained support.
Empathy in Communication: Enhancing Connection
Compassionate empathy involves understanding another's emotions and taking proactive steps to support them, fostering deeper trust and connection in communication. Affective empathy, by contrast, entails directly feeling another person's emotions, which enhances emotional resonance but may not always lead to action. Integrating both forms of empathy in communication strengthens interpersonal relationships by promoting genuine understanding and responsive engagement.
Developing Balanced Empathy for Healthy Relationships
Compassionate empathy involves understanding another's emotions and taking proactive steps to support them, while affective empathy refers to directly experiencing the emotions of others. Developing balanced empathy combines these skills, enabling individuals to connect deeply without becoming overwhelmed by others' feelings. This balance fosters healthy relationships by promoting emotional support alongside personal emotional boundaries.
Compassionate Empathy vs Affective Empathy Infographic
 relationdif.com
relationdif.com