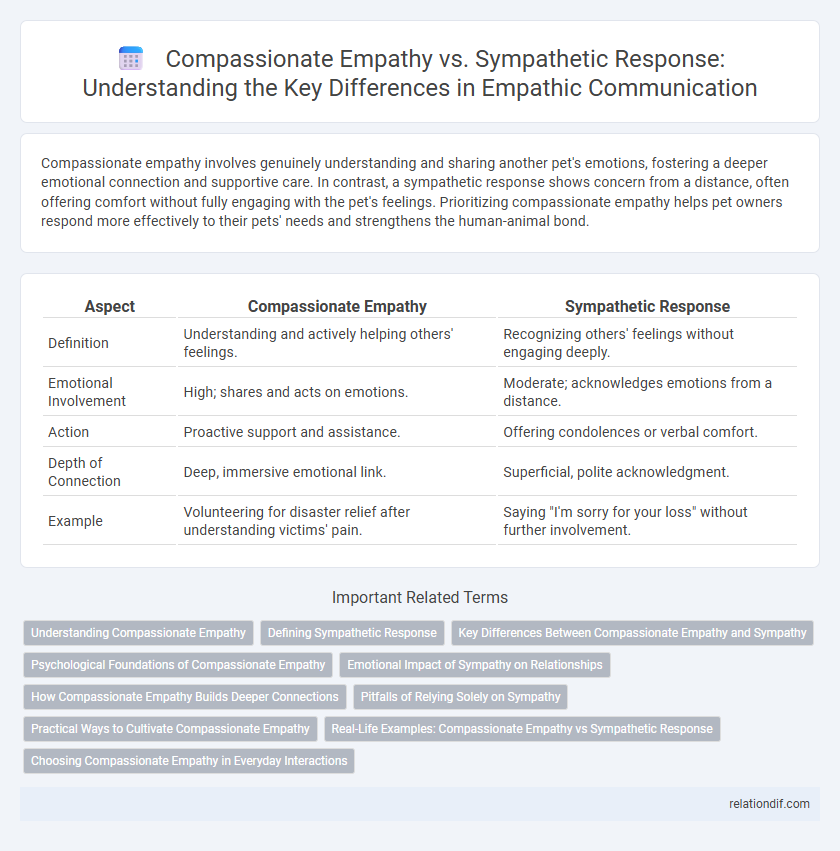
Compassionate empathy involves genuinely understanding and sharing another pet's emotions, fostering a deeper emotional connection and supportive care. In contrast, a sympathetic response shows concern from a distance, often offering comfort without fully engaging with the pet's feelings. Prioritizing compassionate empathy helps pet owners respond more effectively to their pets' needs and strengthens the human-animal bond.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Compassionate Empathy | Sympathetic Response |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Understanding and actively helping others' feelings. | Recognizing others' feelings without engaging deeply. |
| Emotional Involvement | High; shares and acts on emotions. | Moderate; acknowledges emotions from a distance. |
| Action | Proactive support and assistance. | Offering condolences or verbal comfort. |
| Depth of Connection | Deep, immersive emotional link. | Superficial, polite acknowledgment. |
| Example | Volunteering for disaster relief after understanding victims' pain. | Saying "I'm sorry for your loss" without further involvement. |
Understanding Compassionate Empathy
Compassionate empathy involves deeply understanding another person's feelings and actively wanting to help, distinguishing it from a sympathetic response that merely acknowledges someone's distress without engaging emotionally. This form of empathy requires recognizing emotions, feeling connected, and taking supportive actions to alleviate suffering. Neuroscientific studies highlight that compassionate empathy activates brain regions linked to caregiving and social bonding, fostering genuine emotional support.
Defining Sympathetic Response
A sympathetic response involves recognizing another person's emotional distress and expressing concern or sorrow without deeply engaging in their experience. It often includes offering comfort or reassurance from a distance, maintaining an emotional boundary. Unlike compassionate empathy, which motivates active support and shared feelings, sympathy remains more detached and observational.
Key Differences Between Compassionate Empathy and Sympathy
Compassionate empathy involves not only understanding and sharing another person's emotions but also taking action to help alleviate their suffering, whereas sympathy is simply feeling pity or sorrow for someone's situation without necessarily engaging in supportive behavior. The key difference lies in compassionate empathy's deeper emotional connection and proactive response, contrasting with sympathy's more detached and passive acknowledgment. Compassionate empathy fosters meaningful support and empowerment, while sympathy often remains an emotional reaction without further involvement.
Psychological Foundations of Compassionate Empathy
Compassionate empathy involves not only understanding another person's emotional state but also feeling motivated to help alleviate their suffering, supported by neural mechanisms in the anterior insula and anterior cingulate cortex that process both affective empathy and prosocial motivation. Unlike sympathetic response, which often results in emotional distancing or pity, compassionate empathy engages the mirror neuron system and oxytocin pathways, fostering genuine connection and altruistic behavior. Psychological foundations emphasize the integration of cognitive perspective-taking and affective resonance, enabling individuals to respond with kindness and proactive support rather than detached concern.
Emotional Impact of Sympathy on Relationships
Compassionate empathy involves genuinely understanding and sharing another's emotions, fostering deeper emotional connections and trust within relationships. In contrast, a sympathetic response often involves feeling pity or sorrow for someone's situation without fully engaging emotionally, which can create emotional distance or misunderstanding. The emotional impact of sympathy may unintentionally lead to feelings of isolation or resentment, whereas compassionate empathy promotes emotional support and strengthens relational bonds.
How Compassionate Empathy Builds Deeper Connections
Compassionate empathy involves not only understanding another person's feelings but also actively supporting and helping them, which fosters trust and emotional intimacy. Unlike a sympathetic response that may offer surface-level comfort, compassionate empathy encourages meaningful engagement and shared vulnerability. This deeper connection strengthens relationships by validating emotions and promoting mutual care.
Pitfalls of Relying Solely on Sympathy
Compassionate empathy involves deeply understanding and sharing another person's emotional experience, whereas a sympathetic response often entails feeling pity without truly engaging with their feelings. Relying solely on sympathy can lead to emotional distancing and may inadvertently minimize the person's experience by offering superficial comfort instead of meaningful support. This pitfall can hinder genuine connection and reduce the effectiveness of helping others in distress.
Practical Ways to Cultivate Compassionate Empathy
Cultivating compassionate empathy involves actively listening to others' emotions and validating their experiences to deepen mutual understanding. Practicing mindfulness enhances emotional awareness, allowing individuals to respond with genuine care rather than detached sympathy. Engaging in perspective-taking exercises and offering tangible support fosters meaningful connections that promote emotional healing and resilience.
Real-Life Examples: Compassionate Empathy vs Sympathetic Response
Compassionate empathy involves actively understanding and sharing another person's feelings, prompting supportive actions, such as a friend helping a colleague cope with stress by offering practical assistance. In contrast, a sympathetic response is more detached, expressing concern or pity without engaging deeply, like sending a card to someone grieving a loss without further involvement. Real-life scenarios highlight that compassionate empathy fosters connection and effective support, while sympathetic responses may provide comfort but lack the commitment to action.
Choosing Compassionate Empathy in Everyday Interactions
Compassionate empathy involves not only understanding another person's feelings but also taking proactive steps to support and alleviate their distress, creating a deeper connection. In everyday interactions, choosing compassionate empathy fosters trust and promotes emotional healing by validating experiences and offering meaningful assistance. This approach transcends the passive nature of sympathetic responses, which often involve feeling pity without engagement or support.
Compassionate empathy vs sympathetic response Infographic
 relationdif.com
relationdif.com