Empathic responsiveness in pets fosters a deep emotional connection, as they intuitively sense and react to their owner's feelings, providing comfort and support during distress. In contrast, indifference in pets often results in a lack of emotional engagement, creating a barrier that may leave owners feeling isolated or misunderstood. Recognizing and nurturing empathy in pets enhances the bond, promoting mutual trust and emotional well-being.
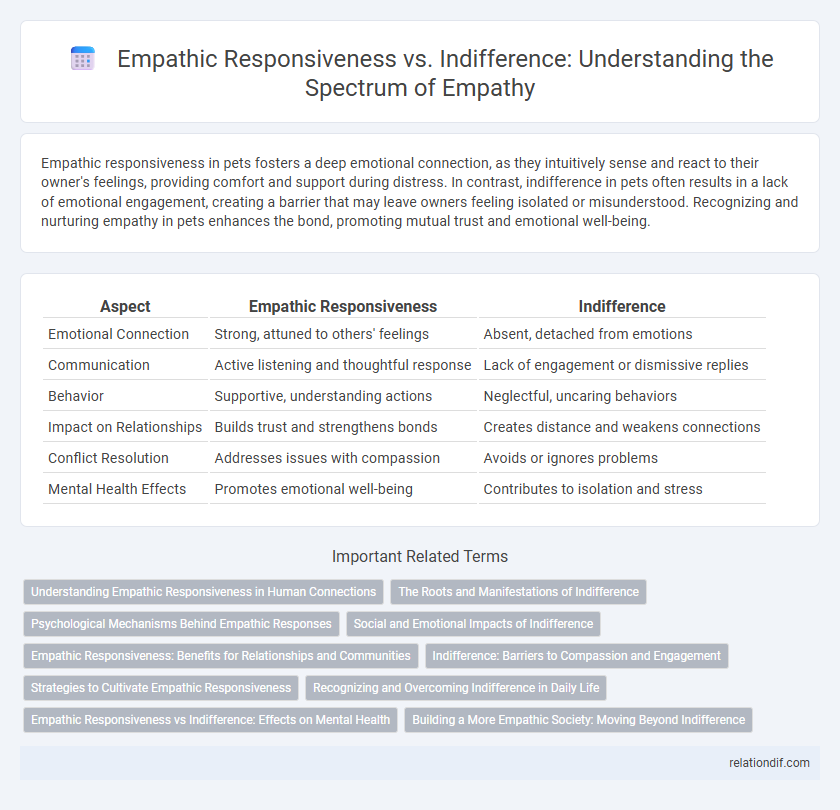
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Empathic Responsiveness | Indifference |
|---|---|---|
| Emotional Connection | Strong, attuned to others' feelings | Absent, detached from emotions |
| Communication | Active listening and thoughtful response | Lack of engagement or dismissive replies |
| Behavior | Supportive, understanding actions | Neglectful, uncaring behaviors |
| Impact on Relationships | Builds trust and strengthens bonds | Creates distance and weakens connections |
| Conflict Resolution | Addresses issues with compassion | Avoids or ignores problems |
| Mental Health Effects | Promotes emotional well-being | Contributes to isolation and stress |
Understanding Empathic Responsiveness in Human Connections
Empathic responsiveness plays a crucial role in strengthening human connections by fostering emotional attunement and validation, which enhances mutual trust and openness. In contrast, indifference often leads to emotional detachment and weakened relationships, as it signals a lack of concern for others' feelings and experiences. Understanding empathic responsiveness involves recognizing nonverbal cues, active listening, and genuine emotional engagement to support meaningful interpersonal interactions.
The Roots and Manifestations of Indifference
Indifference often originates from emotional detachment, social isolation, or cognitive overload, leading to a diminished capacity for empathic responsiveness. This manifests through behaviors such as ignoring others' feelings, lack of support during distress, and an inability to recognize emotional cues. Understanding these roots is crucial for addressing barriers to empathy and fostering deeper interpersonal connections.
Psychological Mechanisms Behind Empathic Responses
Empathic responsiveness involves neural activation in the mirror neuron system and enhanced activity in brain regions like the anterior insula and medial prefrontal cortex, which process emotional and cognitive aspects of others' feelings. In contrast, indifference often corresponds with reduced connectivity in these areas and increased activity in networks associated with self-referential thoughts, such as the default mode network. Psychological mechanisms underlying empathic responses include emotion recognition, perspective-taking, and affective sharing, which are diminished or disrupted during indifferent states.
Social and Emotional Impacts of Indifference
Indifference in social settings often leads to emotional isolation and deteriorates interpersonal relationships, causing feelings of neglect and invisibility. Empathic responsiveness fosters connection by validating emotions and promoting psychological well-being, whereas indifference triggers increased stress, anxiety, and social withdrawal. The absence of empathy disrupts social cohesion and impedes effective communication, amplifying emotional distress in vulnerable individuals.
Empathic Responsiveness: Benefits for Relationships and Communities
Empathic responsiveness fosters trust and deepens emotional connections, enhancing communication and conflict resolution in relationships. It promotes prosocial behavior, increasing cooperation and support within communities. Strong empathic engagement contributes to reduced social isolation and improved mental well-being for individuals and groups alike.
Indifference: Barriers to Compassion and Engagement
Indifference acts as a significant barrier to compassion and engagement by suppressing emotional connection and reducing awareness of others' suffering. This emotional detachment hinders interpersonal empathy, leading to social isolation and decreased support for those in need. Overcoming indifference requires conscious efforts to recognize and value others' experiences, fostering a more compassionate and responsive mindset.
Strategies to Cultivate Empathic Responsiveness
Developing empathic responsiveness involves active listening, perspective-taking, and emotional validation to foster deeper interpersonal connections. Practicing mindfulness and engaging in reflective exercises help individuals recognize and regulate their emotional reactions, promoting genuine empathy over indifference. Consistent empathy training and exposure to diverse experiences enhance the ability to respond compassionately, improving social bonds and emotional intelligence.
Recognizing and Overcoming Indifference in Daily Life
Recognizing indifference begins with noticing emotional detachment and lack of engagement in conversations or social interactions, which often leads to weakened interpersonal connections. Overcoming this barrier requires cultivating empathic responsiveness by actively listening, validating others' feelings, and practicing perspective-taking to foster genuine understanding. Consistent application of these strategies enhances emotional intelligence and promotes meaningful relationships in daily life.
Empathic Responsiveness vs Indifference: Effects on Mental Health
Empathic responsiveness significantly improves mental health by fostering emotional support and reducing feelings of isolation, while indifference often leads to increased stress, anxiety, and depression. Studies reveal that individuals receiving empathic responses exhibit lower cortisol levels and enhanced well-being compared to those encountering indifferent attitudes. Cultivating empathic responsiveness strengthens social bonds and promotes resilience against mental health disorders.
Building a More Empathic Society: Moving Beyond Indifference
Empathic responsiveness fosters deeper social connections by actively recognizing and validating others' emotions, while indifference often leads to emotional isolation and societal fragmentation. Cultivating empathy through education, open communication, and community engagement strengthens collective understanding and supports mental well-being. Building a more empathic society requires prioritizing emotional awareness and compassionate action over emotional disengagement.
Empathic responsiveness vs indifference Infographic
 relationdif.com
relationdif.com