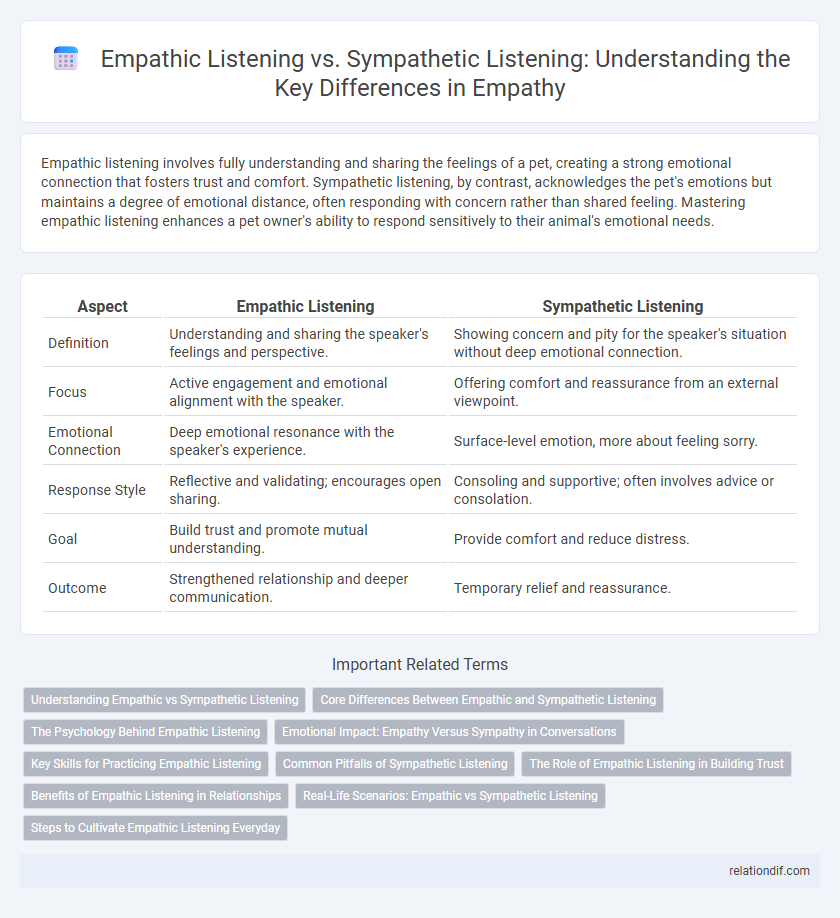
Empathic listening involves fully understanding and sharing the feelings of a pet, creating a strong emotional connection that fosters trust and comfort. Sympathetic listening, by contrast, acknowledges the pet's emotions but maintains a degree of emotional distance, often responding with concern rather than shared feeling. Mastering empathic listening enhances a pet owner's ability to respond sensitively to their animal's emotional needs.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Empathic Listening | Sympathetic Listening |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Understanding and sharing the speaker's feelings and perspective. | Showing concern and pity for the speaker's situation without deep emotional connection. |
| Focus | Active engagement and emotional alignment with the speaker. | Offering comfort and reassurance from an external viewpoint. |
| Emotional Connection | Deep emotional resonance with the speaker's experience. | Surface-level emotion, more about feeling sorry. |
| Response Style | Reflective and validating; encourages open sharing. | Consoling and supportive; often involves advice or consolation. |
| Goal | Build trust and promote mutual understanding. | Provide comfort and reduce distress. |
| Outcome | Strengthened relationship and deeper communication. | Temporary relief and reassurance. |
Understanding Empathic vs Sympathetic Listening
Empathic listening involves fully engaging with the speaker's emotions and perspectives, fostering deep connection and genuine understanding. Sympathetic listening, on the other hand, tends to respond with concern or pity without fully grasping the speaker's internal experience. Prioritizing empathic listening enhances communication by validating feelings and promoting emotional support, while sympathetic listening may create emotional distance.
Core Differences Between Empathic and Sympathetic Listening
Empathic listening involves deeply understanding and sharing the emotions of the speaker, fostering genuine connection and trust, while sympathetic listening primarily focuses on feeling compassion or pity without fully engaging with the speaker's experience. Core differences include empathic listening requiring active engagement and validation of emotions, whereas sympathetic listening often maintains an emotional distance and offers consolation. Empathic listeners prioritize perspective-taking and emotional resonance, enabling more effective communication and emotional support.
The Psychology Behind Empathic Listening
Empathic listening involves deeply understanding and sharing the feelings of another person, engaging mirror neurons and activating brain regions associated with emotional regulation and social cognition. This process contrasts with sympathetic listening, which maintains emotional distance and focuses on expressing concern without full emotional immersion. Research in psychology highlights that empathic listening fosters trust and emotional healing by validating the speaker's experience, while sympathetic listening may inadvertently create emotional distance.
Emotional Impact: Empathy Versus Sympathy in Conversations
Empathic listening involves deeply understanding and sharing another person's emotions, fostering a connection that validates their feelings and promotes healing. In contrast, sympathetic listening often maintains emotional distance, offering compassion without fully engaging in the speaker's emotional experience. This difference significantly affects emotional impact, as empathy encourages trust and emotional openness, while sympathy may inadvertently create feelings of isolation or misunderstanding.
Key Skills for Practicing Empathic Listening
Empathic listening requires active engagement, including maintaining eye contact and providing nonverbal cues that show understanding, while sympathetic listening often involves more passive responses. Key skills for practicing empathic listening encompass reflective feedback, where the listener paraphrases and validates the speaker's emotions, and withholding judgment to create a safe space for open communication. Developing patience and emotional regulation enables the listener to fully absorb the speaker's experience without imposing their own feelings or solutions.
Common Pitfalls of Sympathetic Listening
Sympathetic listening often leads to common pitfalls such as offering unsolicited advice, which can invalidate the speaker's feelings and hinder genuine emotional connection. This approach may also result in premature judgment or minimization of the speaker's experience, causing frustration and reduced trust. Unlike empathic listening, sympathetic listening tends to emphasize problem-solving over emotional understanding, limiting deeper relational support.
The Role of Empathic Listening in Building Trust
Empathic listening plays a crucial role in building trust by creating a genuine connection through understanding and validating the speaker's feelings and experiences. Unlike sympathetic listening, which often involves feeling pity or concern from a distance, empathic listening requires active engagement and emotional resonance that fosters openness and deeper communication. This mutual understanding strengthens relationships and promotes a sense of safety, making trust more likely to develop and endure.
Benefits of Empathic Listening in Relationships
Empathic listening fosters deeper emotional connections by fully understanding and validating a partner's feelings, leading to enhanced trust and mutual respect. This type of active engagement reduces misunderstandings and conflicts, promoting healthier communication patterns. Relationships benefit from increased emotional intimacy and resilience when empathic listening is consistently practiced.
Real-Life Scenarios: Empathic vs Sympathetic Listening
Empathic listening in real-life scenarios involves fully understanding and validating the speaker's emotions, fostering genuine connection and trust. Sympathetic listening, on the other hand, often offers pity or surface-level comfort without deeply engaging with the underlying feelings. In professional settings, empathic listening improves conflict resolution and teamwork, whereas sympathetic listening may lead to miscommunication and unresolved issues.
Steps to Cultivate Empathic Listening Everyday
Empathic listening involves fully concentrating on the speaker's emotions and perspectives, requiring active listening techniques such as maintaining eye contact, reflecting feelings, and withholding judgment to build genuine understanding. Sympathetic listening, however, focuses more on feeling pity or sorrow for someone's situation without deeply engaging with their experience. To cultivate empathic listening every day, practice mindfulness to remain present, ask open-ended questions to encourage sharing, and validate emotions to reinforce connection and trust.
Empathic listening vs sympathetic listening Infographic
 relationdif.com
relationdif.com