Nonverbal empathy in pets is expressed through body language, such as gentle eye contact, soothing touches, and attentive posture, allowing them to sense and respond to human emotions without spoken words. Verbal empathy involves recognizing and responding to vocal cues, where pets may react to tone and pitch to provide comfort. Understanding both nonverbal and verbal empathy enhances the bond between pets and their owners, promoting emotional support and mutual trust.
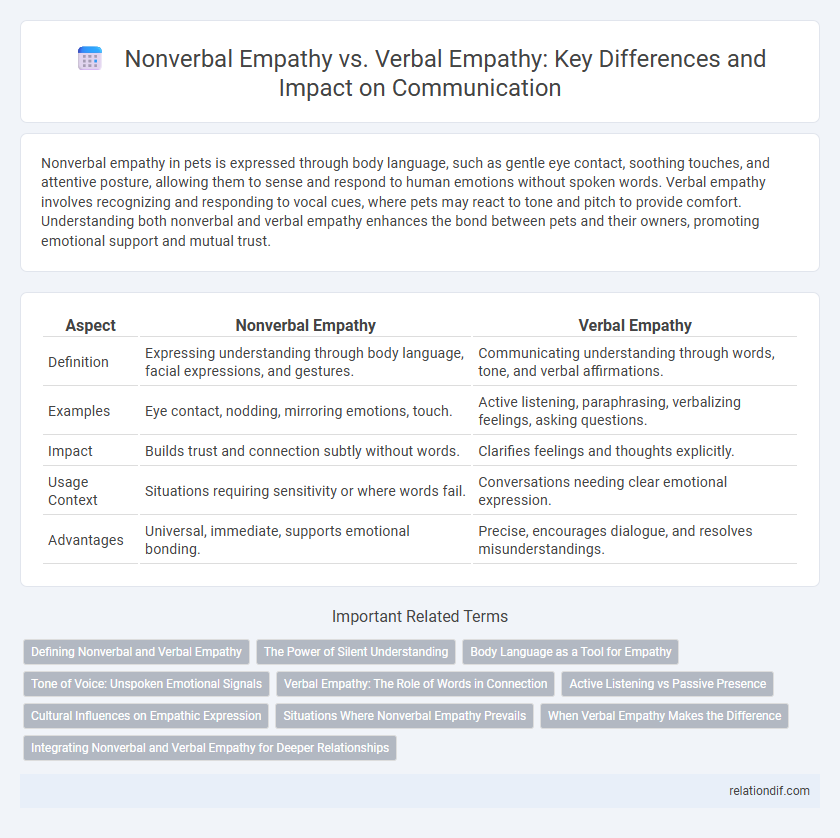
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Nonverbal Empathy | Verbal Empathy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Expressing understanding through body language, facial expressions, and gestures. | Communicating understanding through words, tone, and verbal affirmations. |
| Examples | Eye contact, nodding, mirroring emotions, touch. | Active listening, paraphrasing, verbalizing feelings, asking questions. |
| Impact | Builds trust and connection subtly without words. | Clarifies feelings and thoughts explicitly. |
| Usage Context | Situations requiring sensitivity or where words fail. | Conversations needing clear emotional expression. |
| Advantages | Universal, immediate, supports emotional bonding. | Precise, encourages dialogue, and resolves misunderstandings. |
Defining Nonverbal and Verbal Empathy
Nonverbal empathy involves understanding and sharing another person's feelings through body language, facial expressions, and gestures without using words, whereas verbal empathy relies on spoken or written language to convey comprehension and emotional support. Nonverbal cues like eye contact, nodding, and tone of voice can express empathy more subtly and often more powerfully than verbal responses. Verbal empathy, including active listening and empathetic statements, provides explicit acknowledgment of emotions, fostering clearer communication and emotional connection.
The Power of Silent Understanding
Nonverbal empathy harnesses the power of silent understanding through facial expressions, eye contact, and body language, creating a profound emotional connection without words. Research shows that nonverbal cues trigger mirror neurons in the brain, enhancing emotional resonance and fostering trust more effectively than verbal communication alone. This silent empathy often bridges cultural and language barriers, making it a universal tool for genuine human connection.
Body Language as a Tool for Empathy
Body language plays a crucial role in nonverbal empathy by conveying emotions and understanding without words, through gestures, facial expressions, and posture. It allows individuals to communicate sympathy and support effectively, often more powerfully than verbal expressions. Mastering empathetic body language enhances interpersonal connections and fosters deeper emotional resonance.
Tone of Voice: Unspoken Emotional Signals
Tone of voice serves as a powerful nonverbal cue in conveying empathy, revealing unspoken emotional signals such as warmth, concern, or understanding. Variations in pitch, tempo, and volume communicate nuanced feelings beyond the words spoken, often creating a deeper emotional connection. Studies in communication highlight that tone can significantly influence perceived empathy, sometimes outweighing the verbal content in its impact on emotional resonance.
Verbal Empathy: The Role of Words in Connection
Verbal empathy plays a crucial role in human connection by using carefully chosen words to express understanding and support, fostering deeper emotional bonds. Through active listening, reflective statements, and validating language, verbal empathy communicates recognition of others' feelings and experiences. This linguistic approach enhances relational trust and promotes effective emotional communication beyond nonverbal cues.
Active Listening vs Passive Presence
Active listening in verbal empathy involves fully engaging with the speaker by responding, asking questions, and providing feedback, which enhances understanding and emotional connection. Passive presence, a form of nonverbal empathy, emphasizes silent attentiveness through body language such as eye contact, nodding, and open posture, creating a supportive environment without interrupting the speaker. Both techniques foster empathy, but active listening requires verbal interaction, whereas passive presence relies solely on nonverbal cues to convey compassion and attentiveness.
Cultural Influences on Empathic Expression
Nonverbal empathy varies significantly across cultures, with gestures, facial expressions, and physical proximity interpreted differently worldwide. Verbal empathy also reflects cultural norms, influencing how emotions are articulated and received during communication. Understanding these cultural nuances is essential for accurate empathic expression and effective cross-cultural interactions.
Situations Where Nonverbal Empathy Prevails
Nonverbal empathy proves crucial in high-stress situations where immediate emotional support is required, such as during grief or trauma, allowing the empathizer to convey understanding through facial expressions, body language, and touch. In environments with language barriers or cultural differences, nonverbal cues facilitate connection and comfort without the need for spoken words. Situations like medical emergencies or silent mourning highlight the power of nonverbal empathy in strengthening interpersonal bonds and fostering emotional healing.
When Verbal Empathy Makes the Difference
Verbal empathy becomes crucial in complex emotional situations where clear communication and active listening help validate feelings and foster deeper understanding. Precise language and reflective statements enable individuals to express nuanced support that nonverbal cues alone cannot convey. Research shows that verbal empathy enhances relationship satisfaction and emotional resilience by explicitly addressing and acknowledging others' experiences.
Integrating Nonverbal and Verbal Empathy for Deeper Relationships
Integrating nonverbal empathy, such as facial expressions and body language, with verbal empathy enhances emotional connection and trust in relationships. Nonverbal cues often convey unspoken feelings, while verbal empathy provides clarity and validation, creating a balanced communication dynamic. This synergy deepens understanding, fosters intimacy, and supports more effective conflict resolution.
nonverbal empathy vs verbal empathy Infographic
 relationdif.com
relationdif.com